Feature Story
HIV community activists tackle COVID-19 in Lesotho
02 December 2020
02 December 2020 02 December 2020It is a sunny weekday morning in the small town of Morija, Lesotho. On the expansive lawn of the Morija Museum and Archives, under the shade of tall trees, a group of children and teenagers sit on evenly spaced plastic chairs.
They have all had their temperatures checked, have washed their hands at purpose-built tippy-taps and are wearing brightly coloured seshoeshoe fabric face masks.
The learners would usually be in school at this time, but schools throughout the country remain closed due to COVID-19. In response to this crisis, local community-based organizations have had to implement new and innovative programming.
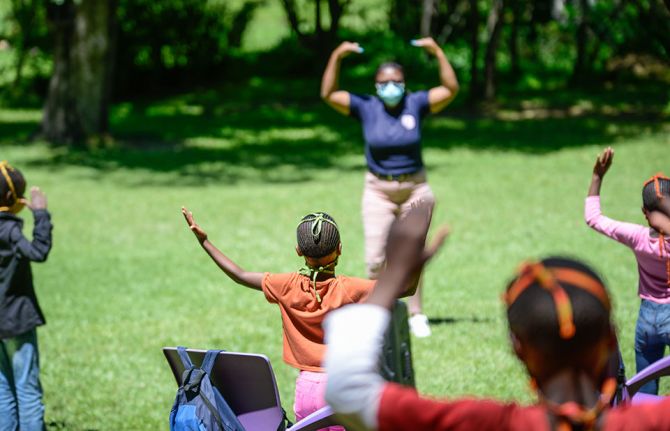
This particular programme is called Skills & Soup, implemented by the Hub, a Morija-based nongovernmental organization. On a bi-weekly basis, groups of learners visit to receive a nutritious meal and participate in a range of activities and educational programming, including dance and taekwondo, maths and science lessons and COVID-19 awareness sessions.
Today, the Hub is hosting a pair of guest facilitators from the Maseru-based nongovernmental organization Kick4Life, which specializes in delivering HIV and life skills education through sports-based curricula.
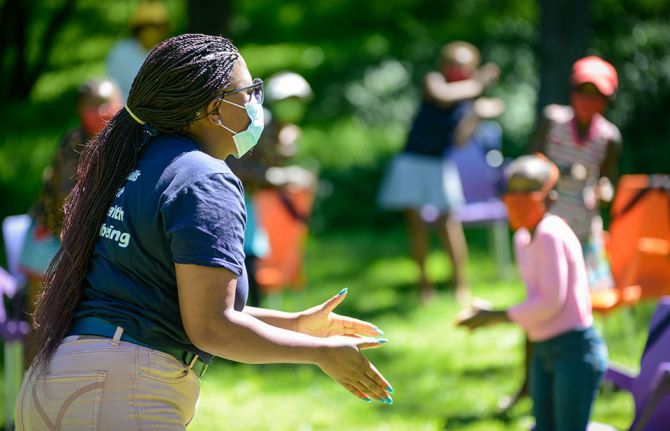
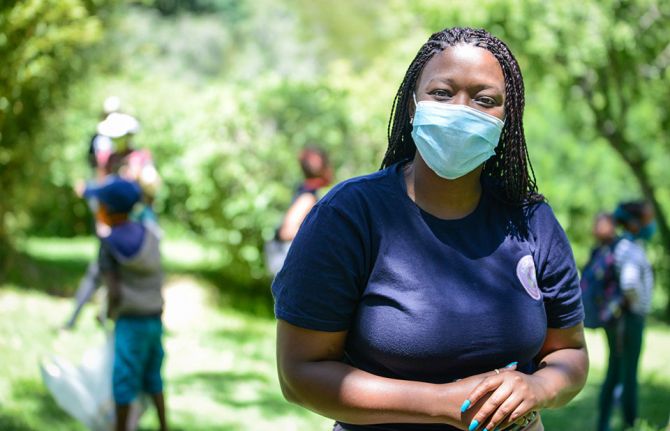
Puky Ramokoatsi, an experienced educator and gender equality activist, is leading the session with confidence and ease. She begins with an energizer, getting the learners to stand up to chant and dance along with her, all the while remaining at a two-metre distance from one another. She keeps her mask on throughout the session, the volume and authority of her voice unhindered.
During the session, Ms Ramokoatsi and her co-facilitator, Mbulelo Mochochoko, play a series of sound clips from a portable speaker. The clips, taken from new animations developed by Kick4Life, feature catchy music and short conversations between two characters who discuss a range of health-related topics, including HIV, nutrition, mental health and ways to protect oneself against COVID-19.
“Who can remind me which fluids can transmit HIV?” asks Ms Ramokoatsi after one of the clips has played. The children stand up and stretch their hands out eagerly, competing to be the first to give the correct answer.
The session is a far cry from Kick4Life’s signature programming, which typically includes close-contact games and activities, with children huddled in groups for discussions or holding hands while standing in a circle.
As with community-based organizations across the region, Kick4Life has adapted its approach to HIV and health education to mitigate the risk of COVID-19 transmission and in response to national lockdowns and government-mandated restrictions.
“We were forced to close our offices in March, when Lesotho went into lockdown, so we had to quickly adjust,” Ms Ramokoatsi explains. “We partnered with the British High Commission in Lesotho to adapt our curriculum into six short animations which could be easily distributed through our online platforms and to include new messaging about COVID-19. We also aired the sound clips from these animations on national radio stations. These are some of the ways that we continued to engage with young people even during the lockdown.”
While COVID-19 cases remain relatively low in Lesotho, at just over 2000 cumulative cases as of November 2020, testing capacity is also low. Only 25 500 tests have been conducted since March 2020. By comparison, a neighbouring country, South Africa, has conducted more tests than this in one day.
In 2019, there were 340 000 people living with HIV in Lesotho, 120 000 of whom are not on HIV treatment.
In addition, a third and silent epidemic plagues Lesotho—that of sexual and gender-based violence. It is estimated that one in three women in Lesotho have experience sexual or physical violence in their life—the same as the global average.
Ms Ramokoatsi has been involved with Kick4Life since 2010, when she began to participate in the organization’s programmes because of her love for football. At the time, she knew very little about HIV, and her interest in the issue was piqued by the fact that her aunt had recently died of AIDS-related illnesses.
“I didn’t understand enough about HIV when my aunt was sick,” recalls Ms Ramokoatsi. “I judged her negatively and didn’t support her. When I learnt more about HIV, I realized how wrong I had been. I made it my purpose after that to support people living with HIV, to give others the support that I hadn’t given my aunt.”
Having experienced sexual abuse herself, Ms Ramokoatsi is acutely aware of the healing power of sports and education and reflects on the difficult transition from face-to-face learning and close-contact activities to virtual and socially distanced programming.
“Before COVID-19 we were in the process of helping several young women who had experienced sexual violence and were slowly opening up to us after taking part in our programmes,” Ms Ramokoatsi explains. “When we were forced to close, we lost touch with some of them. We’ve had to find ways to continue with our programmes and to keep reaching out to our participants, but it hasn’t been easy.”
Ms Ramokoatsi emphasizes the importance of organizations working together in their responses to COVID-19 awareness and health education. “Today, for example, we’re delivering this session thanks to our partnerships,” she says. “I hope more organizations can work like this to share resources and information.”
“I always say that the best part of the game is the opportunity to play. That attitude applies to everything: instead of sitting on the sidelines, get involved. Learn about the situation or the issues around you, whether it’s HIV or gender-based violence or COVID-19. Learn how you can adapt, how you can take care of yourself, and then find a way to help others,” she says.
Our work
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
Francophonie calls for equitable distribution of COVID-19 vaccines
30 November 2020
30 November 2020 30 November 2020The Parliamentary Network to Combat HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Francophonie has adopted a declaration inviting heads of state and government to consult and commit to defining vaccines against COVID-19 as “universal common goods.”
“It is our role as parliamentarians to explain to our fellow citizens that it is better to vaccinate the vulnerable around the world against COVID-19 than to vaccinate the entire population of certain countries that can afford to purchase large volumes of vaccine quickly. This is both more effective and fairer. If the epidemic is to be reduced in our constituencies, we need a global rollout,” said Christian Levrat, President of the Parliamentary Network to Combat HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria.
At the annual meeting of the francophone network, UNAIDS also urged parliamentarians to stop the disproportionate use of criminal law in responses to public health crises. UNAIDS also called for the promotion of additional investments in social safety nets, for livelihood and economic empowerment programmes and for the fostering of the resilience of vulnerable groups and community-based organizations. UNAIDS urged countries to put communities at the centre of the epidemic and to recognize community health services and civil society organizations as legitimate key actors in the responses to both HIV and COVID-19
“We need more support—political, technical and financial—from governments for community-based responses, demedicalization, decentralization and the endorsement of new community-based health tools such as HIV self-testing kits and pre-exposure prophylaxis,” said Patrick Brenny, Director of the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for West and Central Africa.
A conversation on the criminalization of HIV also took place during the meeting. The HIV Justice Worldwide coalition presented the parliamentarians with an update on legislative reform efforts in various francophone countries to address HIV criminalization. Not only does HIV criminalization exacerbate the stigma faced by people living with HIV and lead to serious violations of their human rights, it also erects barriers to accessing HIV prevention, testing and treatment services. UNAIDS and HIV Justice Worldwide are calling for legislative reforms in several francophone countries, including Burkina Faso, Canada, Côte d’Ivoire and Niger.
Our work

Feature Story
Study shows how COVID-19 is impacting access to HIV care in the Russian Federation
27 November 2020
27 November 2020 27 November 2020A new study shows the negative impact that the COVID-19 pandemic is having on access to HIV care in the Russian Federation and shows that people living with HIV in the country are more susceptible to COVID-19 but less likely to seek testing or treatment.
More than a third of people living with HIV who were surveyed reported some impact on HIV services, including about 4% who reported that they had missed taking antiretroviral therapy because they could not get the medicine and nearly 9% who reported that they had missed taking medicine for tuberculosis prevention. However, the majority of respondents (about 70% of people living with HIV) did not experience problems obtaining antiretroviral therapy and about 22% reported that antiretroviral medicines were delivered to their home. More than 900 respondents from 68 regions of the Russian Federation, including people living with HIV and those who are not, were reached by the study.
“This study answers some of the most important questions about the impact of COVID-19 on people living with HIV in our country,” said Natalya Ladnaya, Principal Investigator and Senior Researcher at the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing (Rospotrebnadzor).
According to Ms Ladnaya, the study confirmed that it is crucial for people living with HIV to protect themselves against the new coronavirus. The authors of the study also note the need to provide uninterrupted HIV treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Encouraging results were obtained on how the pandemic affected access to HIV treatment—many specialized institutions have been able to adapt to the new reality,” said Alexey Mikhailov, Head of the Monitoring Department of the Treatment Preparedness Coalition, who took part in the study.
According to the study, the number of people living with HIV with COVID-19 markers was four times higher than that of HIV-negative respondents. At the same time, they were half as likely, compared with HIV-negative respondents, to be tested for coronavirus infection and were less likely to seek medical help, even if they had symptoms.
The majority of respondents with HIV and COVID-19 coinfection had a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 due to the significant number of local cases of COVID-19 and the low level of use of personal protective measures, as well as an underestimation of the real personal risk of COVID-19 disease.
Although more than two thirds of the study participants were women, among people living with HIV and having had COVID-19 the majority of respondents were men who had lived with HIV for more than 10 years.
The authors of the study point to the need for further investigation into the causes of the increased incidence of COVID-19 and the low demand for medical care to treat the symptoms of COVID-19 among people living with HIV.
“The COVID-19 pandemic continues to affect all areas of our lives. We need to closely monitor the colliding pandemics of COVID-19 and HIV and provide support so as not to lose the gains in the response to HIV that have been achieved,” said Alexander Goliusov, Director, a.i., UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
The study was conducted by the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor together with the Treatment Preparedness Coalition with the support of UNAIDS and Rospotrebnadzor.
Our work
Region/country
Related


Press Statement
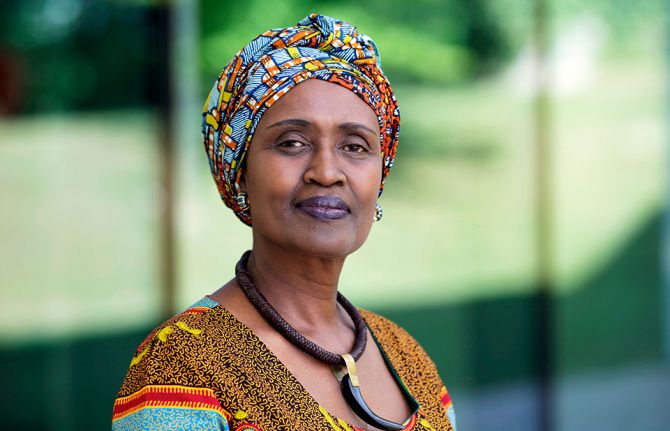
World AIDS Day 2020 message from UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima
01 December 2020 01 December 2020World AIDS Day 2020 will be like no other.
COVID-19 is threatening the progress that the world has made in health and development over the past 20 years, including the gains we have made against HIV.
Like all epidemics, it is widening the inequalities that already existed.
Gender inequality, racial inequality, social and economic inequalities. We are becoming a more unequal world.
I am proud that over the past year the HIV movement has mobilized to defend our progress, to protect people living with HIV and other vulnerable groups and to push the coronavirus back.
Whether campaigning for multimonth dispensing of HIV treatment, organizing home deliveries of medicines or providing financial assistance, food and shelter to at-risk groups, HIV activists and affected communities have again shown they are the mainstay of the HIV response. I salute you!
It is the strength within communities, inspired by a shared responsibility to each other, that has contributed in great part to our victories over HIV.
Today, we need that strength more than ever to beat the colliding epidemics of HIV and COVID-19.
Friends, in responding to COVID-19, the world cannot make the same mistakes it made in the fight against HIV, when millions in developing countries died waiting for treatment.
Even today, more than 12 million people are still waiting to get on HIV treatment and 1.7 million people became infected with HIV in 2019 because they could not access essential services.
That is why UNAIDS has been a leading advocate for a People’s Vaccine against the coronavirus.
Global problems need global solidarity.
As the first COVID-19 vaccine candidates have proven effective and safe, there is hope that more will follow, but there are serious threats to ensuring equitable access. We are calling on companies to openly share their technology and know-how and to wave their intellectual property rights so that the world can produce the successful vaccines at the huge scale and speed required to protect everyone and so that we can get the global economy back on track.
Our goal of ending the AIDS epidemic was already off track before COVID-19. We must put people first to get the AIDS response back on track. We must end the social injustices that put people at risk of contracting HIV. And we must fight for the right to health. There is no excuse for governments to not invest fully for universal access to health. Barriers such as up-front user fees that lock people out of health must come down.
Women and girls must have their human rights fully respected, and the criminalization and marginalization of gay men, transgender people, sex workers and people who use drugs must stop.
As we approach the end of 2020, the world is in a dangerous place and the months ahead will not be easy.
Only global solidarity and shared responsibility will help us beat the coronavirus, end the AIDS epidemic and guarantee the right to health for all.
Thank you.
Winnie Byanyima
Executive Director of UNAIDS
Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations
World AIDS Day 2020 playlist
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Feature Story
A tale of two Jamaican clinics during COVID-19
03 November 2020
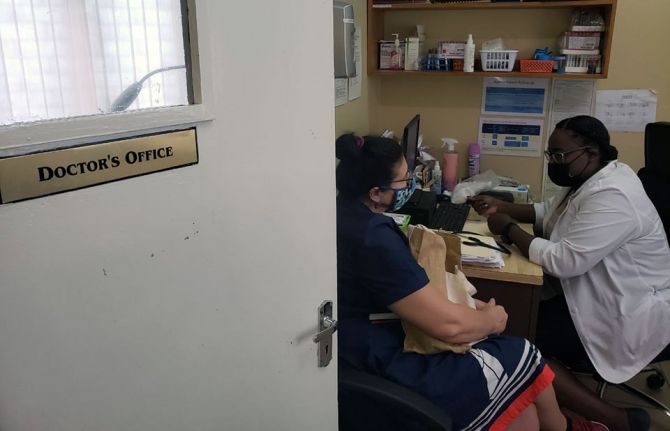
03 November 2020 03 November 2020A woman living with HIV is at the Centre for HIV Research and Education Services (CHARES) in Kingston, Jamaica. She normally gets a three-month allotment of her antiretroviral medicines. But not this time. The doctor warns her that, since April, state pharmacies have only been dispensing a one-month supply.
About a 20-minute drive away at the Comprehensive Health Clinic, a client waits for his name to be called. He doesn’t use one of the wooden benches allocated for sexual health patients. Instead, he finds a nearby seat and listens intently.
HIV service providers in Jamaica have been challenged this year with responding both to new challenges caused by COVID-19 and long-standing service delivery stumbling blocks. The UNAIDS Country Director, Manoela Manova, wanted to get a better understanding of the issues on the ground, so she visited both treatment sites to speak with everyone, from adherence counsellors to doctors.
The University Hospital of the West Indies’ CHARES has been a best practice model for HIV treatment in Jamaica. For the island as a whole, 79% of those on treatment were virally suppressed last year. At CHARES, however, an impressive nine in every 10 clients are virally suppressed and therefore keep healthy and are unable to transmit the virus.
But even for this accomplished programme, COVID-19 has presented significant challenges.
Laboratory support has been diverted toward COVID-19 and there has been a backlog in receiving viral load testing results.
CHARES had been used to writing three-month prescriptions for stable clients, but since COVID-19, state-run pharmacies have been dispensing only a one-month supply. This is part of the government’s strategy to avoid stock-outs given the supply chain challenges at this time, but it means that those on treatment need to go out to get their medicines more often. CHARES has begun home deliveries, particularly for older people, who are more reluctant to venture out given the novel coronavirus risk.
COVID-19 containment measures have increased the need for mental health support. Income loss, school closures and curfews have placed an added strain on thousands of Jamaican households, including many people living with HIV. But when clients are referred to psychiatric support in the main hospital they rarely go for fear of experiencing discrimination. Further, since the hospital in which CHARES is located is a designated COVID-19 treatment site, some clients have opted to stay away.
“We need closer monitoring and evaluation to address the challenges around patient management at this time,” said CHARES Programme Director Racquel Brown. “Optimally we would like to hire someone with responsibility for analysing patient data to make more strategic decisions around care and treatment.”
The Comprehensive Health Centre serves a number of people living with HIV alongside those infected with other sexually transmitted infections. Here, too, multimonth dispensing has not been possible during COVID-19. Patients’ need for nutrition support has been high during this period. Some have had their antiretroviral medicines but no food with which to take them.
But other challenges came before COVID-19. Two out of five clients are lost to follow-up. Patients have given service providers wrong addresses. And the clinic’s viral suppression rate stands at 70%, below the national average. Some come off their treatment against their doctor’s advice.
Ms Manova said many of the challenges at both clinics are linked to self-stigma and discrimination, which is the main issue facing Jamaica’s HIV response. For the country as a whole, just 43% of all people living with HIV were on treatment in 2019 despite the island’s relatively high testing coverage.
“Before and during COVID-19, our results are undermined by shame, fear and prejudice,” she noted. “For an effective public health response, we have to be deliberate and consistent about building trust with communities and combatting all forms of stigma and discrimination that block people from accessing care.”
“It was inspiring and sobering to spend time with these health-care providers,” Ms Manova said. “Jamaica has correctly treated community health-care employees as essential workers. Staff including community facilitators, social workers, adherence counsellors and case managers are just as needed as doctors and nurses. Their work is critical at this time to address the individual needs and emotions that could affect treatment outcomes.”
Our work
Region/country
Related




Feature Story
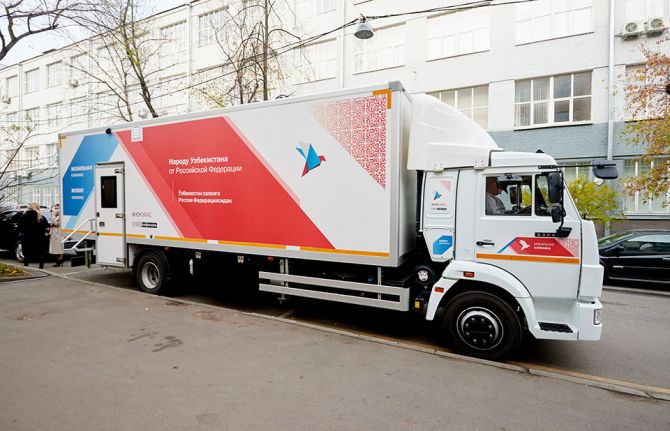
Bringing HIV and COVID-19 testing services to hard-to-reach areas in Uzbekistan
30 October 2020
30 October 2020 30 October 2020The Russian Federation has donated a mobile clinic to Uzbekistan to provide primary health care for people in remote and hard-to-reach regions of the country, including testing for HIV, COVID-19 and other diseases.
The mobile clinic is equipped with the latest medical equipment and diagnostic systems, including for HIV and COVID-19, and is ready to provide people with access to integrated HIV testing and counselling and other forms of medical diagnostics and treatment.
“Thanks to this programme, the citizens of Uzbekistan living in different regions of the country will be able to receive timely information about the symptoms and ways of transmission of infectious diseases, which has become more important than ever,” said Botirjon Asadov, Uzbekistan Ambassador to the Russian Federation.
The clinic was donated as part of a technical assistance programme supported by the Russian Government that is being implemented by UNAIDS in partnership with the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing (Rospotrebnadzor) and the nongovernmental organization AIDS Infoshare.
The programme aims to strengthen health systems, ensure better epidemiological surveillance of HIV and promote the scale-up of HIV prevention programmes among populations at higher risk in Armenia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
“Our work in today’s coronavirus pandemic is more relevant than ever. We continue our cooperation to fight COVID-19 and fully support the efforts of the Uzbek authorities to normalize the epidemic situation in the country as soon as possible, and assure that the Russian Federation is ready to provide the necessary assistance,” said Irina Bragina, Deputy Head of Rospotrebnadzor.
To date, 12 mobile clinics have been donated—four to Tajikistan, three to Armenia and five to Kyrgyzstan. Apart from the primary health-care services and a range of HIV screening services, the clinics provide tests for COVID-19, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections and obstetrics, gynaecology, cardiology and urology care. All the mobile clinics offer services free of charge. So far, more than 1.6 million people have used the services provided by the clinics.
“Mobile clinics today not only continue providing primary health-care services, including HIV testing, but also have come to the forefront to combat a new threat—COVID-19,” said Aleksandr Goliusov, Director, a.i., of the UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
Our work
Related

Feature Story
COVID-19’s impact on HIV vertical transmission services reversed
27 October 2020
27 October 2020 27 October 2020Recent data collection has shown that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on HIV testing services, but the impact on HIV treatment has been less than originally feared. The impact on services for the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV (from mother to child) is mixed—by April, countries generally saw a decline in the number of women tested for HIV at their first antenatal clinic visit, but by June that decline had been reversed.
As of August 2020, the UNAIDS, World Health Organization and United Nations Children's Fund data collection exercise to identify national, regional and global disruptions of routine HIV services caused by COVID-19 had collected data on the prevention of vertical transmission of HIV from 43 countries, of which 17 countries reported data that enable the identification of trends.
To measure the impact of COVID-19 on vertical transmission of HIV services, a ratio was calculated relative to January—for example, if the number of women reached in April was the same as in January, the ratio is 1; if there was a decline, the ratio is less than 1.
All countries except Mozambique and Jamaica experienced declines in women tested for HIV at their first antenatal clinic visit in April compared to January. By June or July, 14 of the 17 countries were back to the February level of testing (all except Indonesia, Botswana and Sierra Leone).
Among the 15 countries reporting on treatment among pregnant women living with HIV, all but five have recovered to the February numbers of women receiving treatment (except Botswana, South Africa, Sierra Leone, Togo and Guatemala).
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025


Press Release
President of Nigeria unites behind the call for a People’s Vaccine for COVID-19
16 October 2020 16 October 2020GENEVA, 16 October 2020—The President of Nigeria, Muhammadu Buhari, has announced that Nigeria will be joining the urgent global call for a People’s Vaccine for COVID-19. The President endorsed the initiative and released an official public statement in favour of the campaign.
“Learning from the painful lessons from a history of unequal access in dealing with diseases such as HIV we must heed the warning that “those who do not remember the past are doomed to repeat it”,” said Mr Buhari. “Only a People’s Vaccine with equality and solidarity at its core can protect all of humanity and get our societies safely running again. A bold international agreement cannot wait.”
Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa, home to more than 200 million people, and has the third highest number of COVID-19 cases in Africa after South Africa and Ethiopia. In March 2020, Mr Buhari set up a multisectoral Presidential Task Force to combat the COVID-19 pandemic, which produced a mid-term report in July 2020 outlining a significant body of work undertaken to stop the spread of COVID-19.
However, the report also shows that the health infrastructure and equipment levels in Nigeria are not strong enough to support a sustained national response to COVID-19 and that if the pandemic were to spread exponentially Nigeria would struggle to mount an effective response. This demonstrates the urgent need for access to a vaccine for COVID-19 in Nigeria as soon as it becomes available.
“UNAIDS and other members of the People’s Vaccine Alliance are calling for a new approach that puts public health first by sharing knowledge and maximizing supply to make sure that no one is left behind,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Anything short of that will lead to more deaths and economic chaos, forcing millions into destitution.”
The People’s Vaccine Alliance is a coalition of organizations and activists united under a common aim of campaigning for a People’s Vaccine for COVID-19. In support of actions taken by the World Health Organization (WHO), including the COVID-19 Technology Access Pool, the People’s Vaccine Alliance demands that all vaccines, treatments and tests be monopoly-free, mass produced, distributed fairly and made available to all people, in all countries, free of charge.
“The People’s Vaccine will go far in levelling the power dynamics that perpetuate inequality and fuel injustice and it will ensure that no one is left behind,” said Edward Kallon, United Nations Resident Coordinator and Humanitarian Coordinator in Nigeria. “Nobody should be denied a COVID-19 vaccine because of where they live or how much money they have—it has to be a global public good, available to all who need it, regardless of their situation.”
The People’s Vaccine Alliance is calling on pharmaceutical corporations and governments to:
- Prevent monopoly on vaccine production by making public funding for research and development conditional on research institutions and pharmaceutical companies sharing all information, data, biological material, know-how and intellectual property. The WHO COVID-19 Technology Access Pool provides the mechanism for such sharing.
- Prevent monopoly on vaccine supply by enabling as many manufacturers as possible, including in developing countries, to produce the vaccines.
- Implement fair allocation of the vaccine that prioritizes health workers and other at-risk groups in all countries. Vaccination programmes should include marginalized groups, including refugees, prisoners and people living in slums and other crowded housing conditions. Allocation between and within countries should be based on need and not ability to pay.
- Provide the vaccine free of charge at the point of use.
- Ensure the full participation of the governments of developing countries as well as global civil society in decision-making forums about the vaccines (and other COVID-19 technologies) and ensure transparency and accountability of all decisions.
To date, the People’s Vaccine has been endorsed by more than 140 leaders and advocates globally, including the President of South Africa and the Chairperson of the African Union Commission, the Presidents of Ghana and Senegal, the Prime Minister of Pakistan, the Director of the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention and the Special Rapporteur on the right of everyone to the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
The People’s Vaccine Alliance
The People’s Vaccine Alliance is a coalition of organisations and activists united under a common aim of campaigning for a People’s Vaccine’ for COVID-19 that is based on shared knowledge and is freely available for all. A global common good. It is coordinated by Oxfam and UNAIDS and its other members include: Free the Vaccine, Frontline AIDS, Global Justice Now, International Treatment Preparedness Coalition, Just Treatment, Nizami Ganjavi International Center, Open Society Foundations, STOPAIDS, SumOfUs, Wemos and Yunus Centre.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Our work
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
Region/country

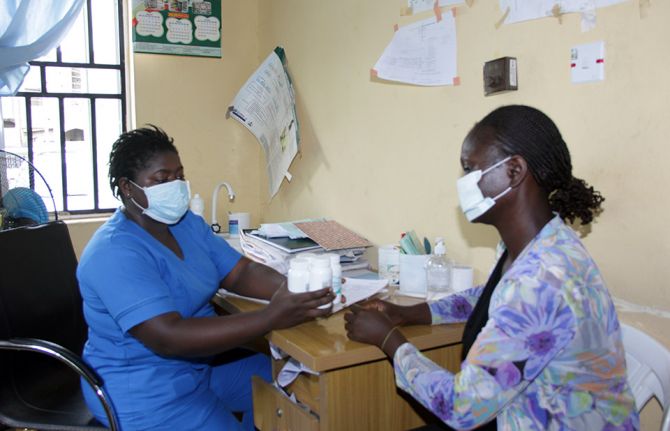
Feature Story
COVID-19’s impact on HIV treatment less severe than feared
16 October 2020
16 October 2020 16 October 2020While recent data collection has shown that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on HIV testing services, the impact on HIV treatment is less than originally feared.
As of August 2020, the UNAIDS, World Health Organization and United Nations Children's Fund data collection exercise to identify national, regional and global disruptions of routine HIV services caused by COVID-19 had collected treatment data from 85 countries, of which 22 countries reported data over a sufficient number of months to enable the identification of trends.
To measure the impact of COVID-19 on HIV treatment services, a ratio was calculated relative to January—for example, if the number of people on treatment in April was the same as in January, the ratio is 1; if there was a decline, the ratio is less than 1.
Only five countries reported monthly declines in the number of people on treatment after April—these include Zimbabwe in June, Peru and Guyana in July, the Dominican Republic in April, and Sierra Leone in May through to July. The remaining 18 countries did not show a decline and some countries showed a steady increase (e.g. Kenya, Ukraine, Togo and Tajikistan).
One challenge in interpreting trends in the number of people currently on treatment is that many countries have a three-month lost-to-follow-up definition. This means that people who disengaged from treatment in April may only be counted as not on treatment in July.
Among the 22 countries with trend data on numbers newly initiating treatment, all countries except Jamaica showed declines for at least one month or more relative to January. Only around eight of those countries showed a rebound in the number of people newly initiating treatment between January and July.
Our work
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Documents
Six concrete measures to support women and girls in all their diversity in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic
15 June 2020
COVID-19 is not only a health issue, just as HIV never was. It impacts on a wide range of human rights, and although it affects all people, it does so unequally. Women and girls in all their diversity are experiencing the greatest impact of the crisis. COVID-19 has highlighted the stark inequalities across societies, with a lack of pandemic preparedness and fragile or non-functioning institutions posing graver impacts.
Related
 UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day
UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day

06 March 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024