HIV Prevention
Documents
Latin America — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
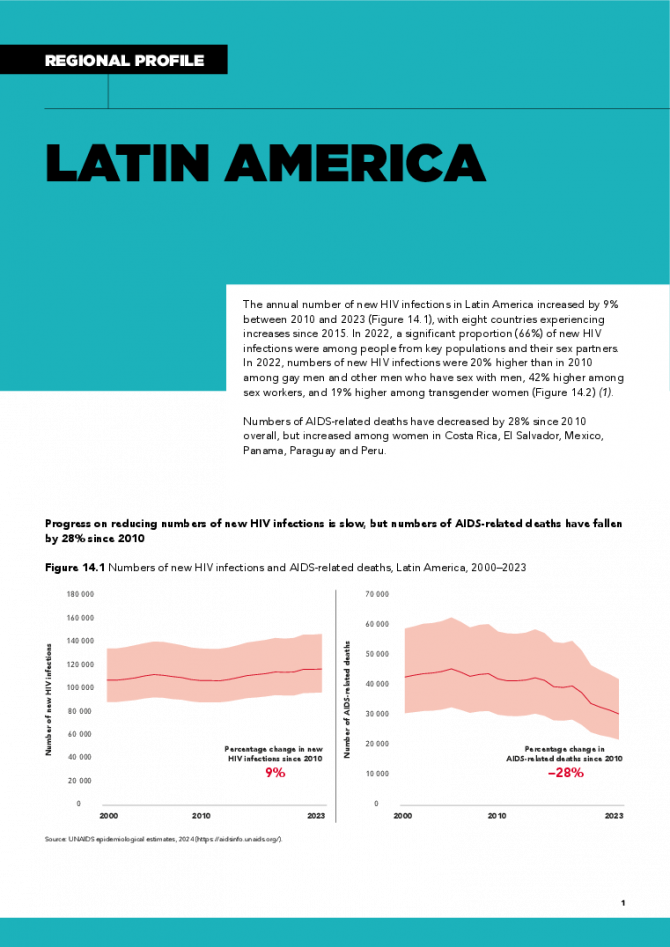
The annual number of new HIV infections in Latin America increased by 9% between 2010 and 2023, with eight countries experiencing increases since 2015. In 2022, a significant proportion (66%) of new HIV infections were among people from key populations and their sex partners. In 2022, numbers of new HIV infections were 20% higher than in 2010 among gay men and other men who have sex with men, 42% higher among sex workers, and 19% higher among transgender women. Numbers of AIDS-related deaths have decreased by 28% since 2010 overall, but increased among women in Costa Rica, El Salvador, Mexico, Panama, Paraguay and Peru. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
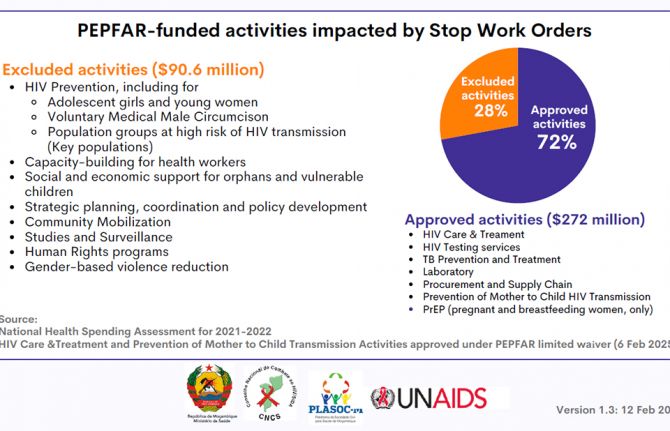
 The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
The critical impact of the PEPFAR funding freeze for HIV across Latin America and the Caribbean
19 February 2025
Documents
Eastern and Southern Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
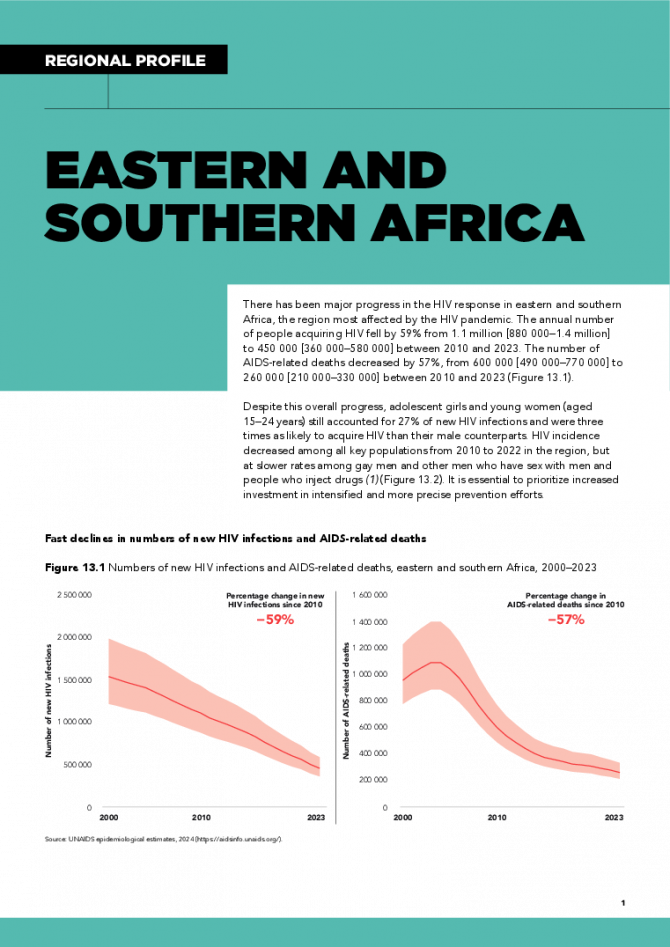
There has been major progress in the HIV response in eastern and southern Africa, the region most affected by the HIV pandemic. The annual number of people acquiring HIV fell by 59% from 1.1 million [880 000–1.4 million] to 450 000 [360 000–580 000] between 2010 and 2023. The number of AIDS-related deaths decreased by 57%, from 600 000 [490 000–770 000] to 260 000 [210 000–330 000] between 2010 and 2023. Despite this overall progress, adolescent girls and young women (aged 15–24 years) still accounted for 27% of new HIV infections and were three times as likely to acquire HIV than their male counterparts. HIV incidence decreased among all key populations from 2010 to 2022 in the region, but at slower rates among gay men and other men who have sex with men and people who inject drugs. It is essential to prioritize increased investment in intensified and more precise prevention efforts. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 The impact of the US funding freeze and cuts on Namibia’s civil society: A struggle for survival
The impact of the US funding freeze and cuts on Namibia’s civil society: A struggle for survival

10 March 2025
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads
Zambia - an HIV response at a crossroads

24 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana
Status of HIV Programmes in Botswana

20 February 2025
 Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi
Government ensures continuity of treatment in Malawi

10 February 2025
Documents
Eastern Europe and Central Asia regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
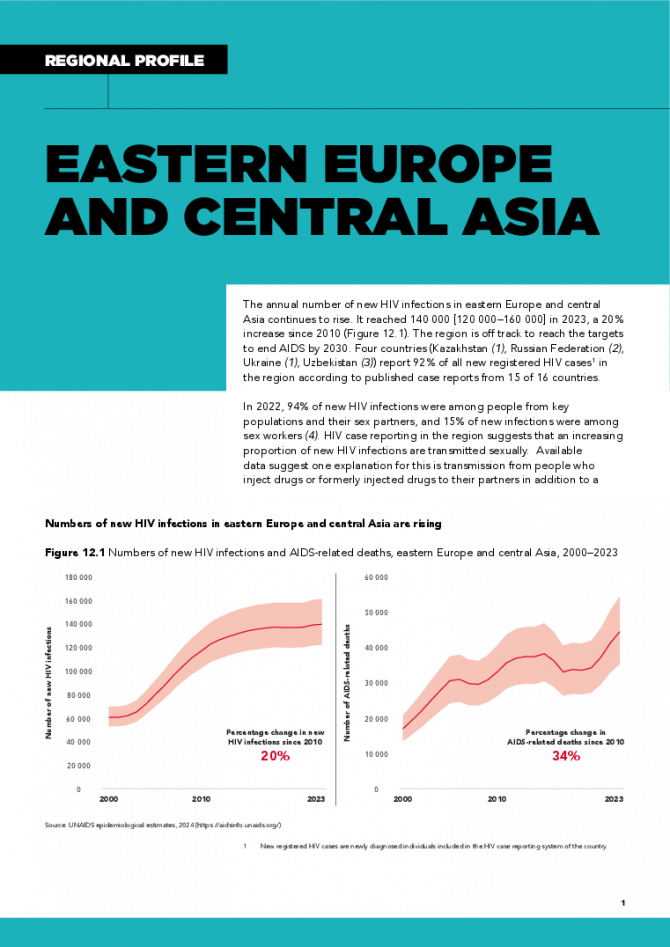
The annual number of new HIV infections in eastern Europe and central Asia continues to rise. It reached 140 000 [120 000–160 000] in 2023, a 20% increase since 2010 . The region is off track to reach the targets to end AIDS by 2030. Four countries (Kazakhstan, Russian Federation, Ukraine, Uzbekistan) report 92% of all new registered HIV cases in the region according to published case reports from 15 of 16 countries. In 2022, 94% of new HIV infections were among people from key populations and their sex partners, and 15% of new infections were among sex workers. HIV case reporting in the region suggests that an increasing proportion of new HIV infections are transmitted sexually. Available data suggest one explanation for this is transmission from people who inject drugs or formerly injected drugs to their partners in addition to a growing recognition of transmission among men who have sex with men. Unsafe drug injecting practices are a key factor in the region’s epidemic, representing 27% of new HIV infections. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
Caribbean regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
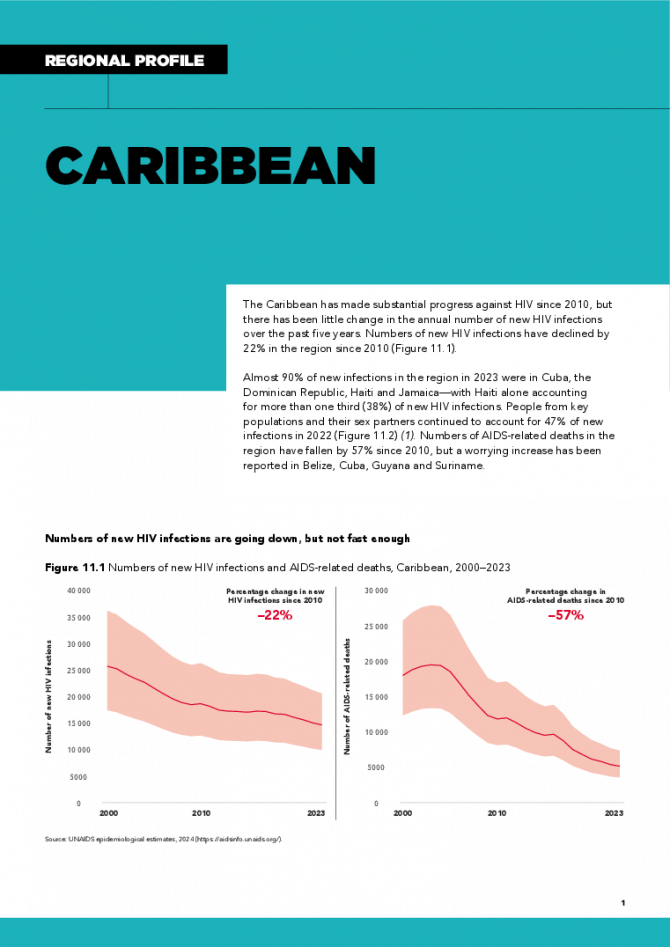
The Caribbean has made substantial progress against HIV since 2010, but there has been little change in the annual number of new HIV infections over the past five years. Numbers of new HIV infections have declined by 22% in the region since 2010. Almost 90% of new infections in the region in 2023 were in Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Haiti and Jamaica—with Haiti alone accounting for more than one third (38%) of new HIV infections. People from key populations and their sex partners continued to account for 47% of new infections in 2022. Numbers of AIDS-related deaths in the region have fallen by 57% since 2010, but a worrying increase has been reported in Belize, Cuba, Guyana and Suriname. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
Asia and the Pacific regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
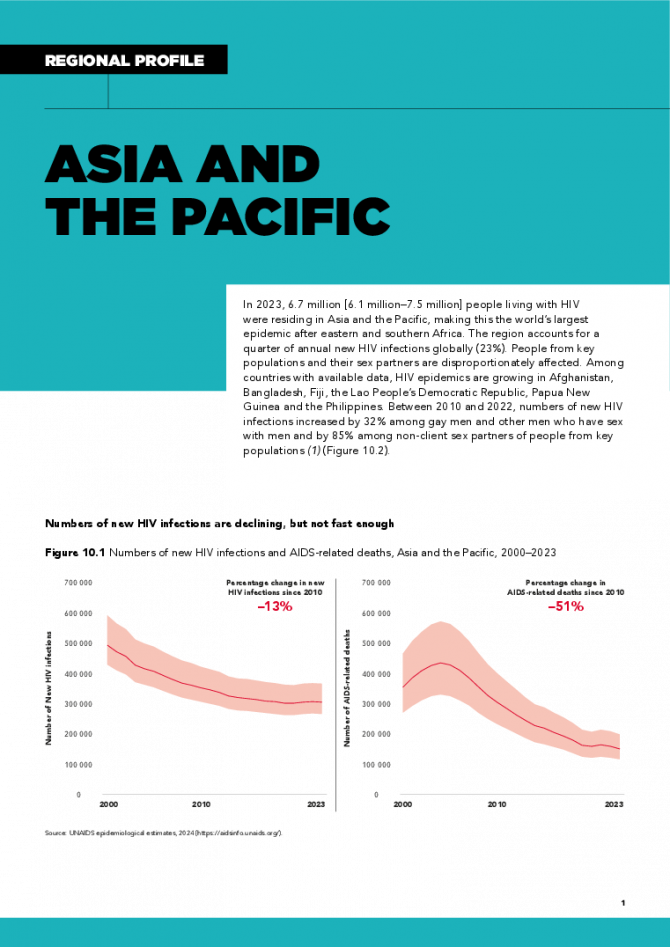
In 2023, 6.7 million [6.1 million–7.5 million] people living with HIV were residing in Asia and the Pacific, making this the world’s largest epidemic after eastern and southern Africa. The region accounts for a quarter of annual new HIV infections globally (23%). People from key populations and their sex partners are disproportionately affected. Among countries with available data, HIV epidemics are growing in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Fiji, the Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines. Between 2010 and 2022, numbers of new HIV infections increased by 32% among gay men and other men who have sex with men and by 85% among non-client sex partners of people from key populations. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025


Press Release
Stigma, criminalization and under-investment are driving worrying rises in new HIV infections in Eastern Europe and Central Asia
22 July 2024 22 July 2024MUNICH, 22 JULY 2024 – A new United Nations report released today shows that the HIV response in Eastern Europe and Central Asia is critically off track. Data in UNAIDS’ global report The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads reveals that in this region, new HIV infections have risen by 20% and AIDS-related deaths have risen by 34%, since 2010. Only half of the 2.1 million people living with HIV in the region are accessing treatment, and only 42% of all people living with HIV in the region have suppressed viral load, the lowest rate globally. The report shows that it is still possible to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030, but only if governments reform laws to protect everyone’s human rights and increase resources to ensure services are available for all.
“The promise to end AIDS is off track in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. But leaders can get on the path that ends AIDS. Programmes need to focus especially on people most affected by HIV, who are often the most marginalized and vulnerable. Community organizations need to be properly funded, supported and enabled to provide HIV services to people affected by HIV. The barriers of stigma and discrimination need to be broken down,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director.
The new data shows that in 2023, there were 140,000 new HIV infections across the region, with 93% occurring in Russia, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan. Eight out of 13 countries in the region reported increases in new infections.
Because stigma, discrimination and harmful punitive laws obstruct marginalised communities’ access to vital services, 94% of new infections were among people from key populations - including men who have sex with men, people who inject drugs, and sex workers - and the sexual partners of people from key populations. Only 58% of sex workers, 43% of gay men, 52% of people who inject drugs, and 65% of transgender people receive HIV prevention services. Only 12% of resources are dedicated to prevention programmes for key populations.
The criminalization of small amounts of drug possession for personal use, of sex work, and of HIV transmission and exposure, are driving the people most in need underground and out of reach of HIV services. All 16 countries in the region criminalize sex work, 13 criminalize the non-disclosure, exposure, or transmission of HIV, and 7 criminalize small amount of drug possession for personal use. Studies show criminalization increases HIV prevalence among key populations. Unless countries can ensure fear-free access to HIV prevention services for everyone, new infections will continue to grow.
“Restrictive legal environments and stigma are obstructing progress in the region,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Eastern Europe and Central Asia and Asia Pacific. “Restrictive laws, along with aggressive policing and stigma, push people away from medical care. If people are pushed underground, the HIV response will not succeed.”
Powerful prevention technologies like PrEP are also not widely accessible for the same reason. Criminalization fuels stigma, with many avoiding medical care due to discrimination. Nearly half of people surveyed who inject drugs in Kyrgyzstan and 32% of people living with HIV in Tajikistan reported avoiding medical care due to stigma and discrimination. UNAIDS data shows that people in key populations are experiencing high levels of violence.
"Supporting the leadership of communities is essential for reaching marginalised people providing vital outreach services. Without community leadership and the integration of community services into the health system, reaching these groups is too difficult," said Yelena Rastokina, lead of the ‘Answer-Kazakhstan’ Association.
Recent years have seen worrying restrictions of civic space and limits to communities’ involvement in public health initiatives, including those related to harm reduction, access to public health services for LGBTQ+ people, sex workers and other marginalised people. Restrictive systems at local, national, and regional levels are holding back communities’ contribution to public health.
Ganna Dovbach, Executive director of the Eurasian Harm Reduction Association, highlighted: “The shrinking of civic space and attacks on human rights threaten our response to HIV, which is based on community-led or civil society provided services. Addressing these interconnected issues is essential for a sustainable response to the AIDS epidemic in our region.”
The region’s HIV response has also been hurt by the war in Ukraine.
But despite the conflict, Ukraine remains committed to its HIV response. Through a strong coalition of the government, civil society, international organizations and donors, HIV services have been maintained, with 143,600 people receiving treatment in 2023. This collaboration has ensured vital supplies of antiretroviral and tuberculosis medicine, and opioid agonist therapy, contributing to uninterrupted HIV treatment and other services. As of January 2024, 7,900 Ukrainian refugees in other countries and 1,900 returnees were accessing antiretroviral therapy.
Many community organizations working on HIV in Ukraine refocused their efforts to addressing humanitarian issues and supporting community members while continuing national advocacy for access to HIV services and the protection of human rights.
With support from the UNAIDS and other donors ALLIANCE.GLOBAL oversees a network of five specialized shelters across the country, providing shelter, humanitarian aid, and access to specialised services, including HIV prevention and treatment, for key populations and LGBTQ+ people who are internally displaced.
Despite the war, ALLIANCE.GLOBAL together with other community-led organisations continue advocating for laws that better protect LGBTQ+ people from intolerance and from hate crimes, to enhance access to public health services, including HIV-related services.
UNAIDS new report calls on leaders to develop sustainable plans for the HIV response to2030 and beyond. These plans should include enabling legal environments, support for community-led response and a boost in domestic funding. Repealing laws and norms that prevent people from accessing services is crucial.
“Ensuring access to services and treatment for all is how we end AIDS,” said Mr Murphy.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country
Documents
2024 global AIDS report — The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
This UNAIDS 2024 report brings together new data and case studies which demonstrate that the decisions and policy choices taken by world leaders this year will decide the fate of millions of lives and whether the world’s deadliest pandemic is overcome. Related links: Press release | Special web site | Executive summary | Fact sheet | Video playlist | Epidemiology slides | Data on HIV | Annex 2: Methods Regional profiles: Asia and the Pacific | Caribbean | Eastern Europe and Central Asia | Eastern and Southern Africa| Latin America | Middle East and North Africa | Western and Central Africa | Western and Central Europe and North America Thematic briefing notes: People living with HIV | Gay men and other men who have sex with men | Transgender people | Sex workers | People who inject drugs | People in prisons and other closed settings | Adolescent girls and young women | Other translations: German
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025


Press Release
New HIV drug can only offer hope of ending AIDS if all have access, UNAIDS says
10 July 2024 10 July 2024GENEVA, 10 July 2024— UNAIDS has welcomed the release of Gilead Sciences’ trial results on the injectable long-acting HIV medicine Lenacapavir for HIV prevention. The result “provides hope of accelerating efforts to end AIDS”, UNAIDS says, “but only if Gilead ensures that all people who need it can have access to this game-changing medicine.”
The recent trial of the medicine among cis-gender women in Uganda and South Africa was so successful that it was halted early. Twice-yearly injections of Lenacapavir showed overwhelming efficacy for preventing HIV infections compared to standard oral preventative HIV medicines, known as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). Additional trials are ongoing in Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, Peru, South Africa, Thailand and the United States.
UNAIDS has welcomed the “exciting development,” and urged the company to allow generic production of Lenacapavir to all low- and middle-income countries by negotiating voluntary licensing agreements through the Medicines Patent Pool (MPP). The MPP is a UN-backed programme with extensive experience negotiating generics agreements between originators and generic pharmaceutical companies.
Gilead has not yet announced its plans for low and middle-income countries. However, UNAIDS is concerned that Gilead’s latest statement regarding its access strategy for low and middle-income countries mentions only “high incidence countries and resource limited countries” and makes no specific mention of upper-middle-income countries or the Medicines Patent Pool. Upper middle-income countries account for 41% of new HIV infections and 37% of all people living with HIV. These countries are home to millions who cannot afford the prices Gilead charges high-income countries.
“The success of Gilead’s recent Lenacapavir trial is an exciting development. While we still await regulatory approvals, normative guidance and results from the other ongoing trials, this news offers hope that we can enable everyone who would benefit, including especially the most marginalised communities, to have access to the help they need. Enabling equitable global access to new technologies can help get the world on track to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. "However, it is concerning that Gilead’s latest announcement seems to mention neither upper-middle income countries, where people cannot afford anything like Lenacapavir’s current $42,250 price tag, nor a commitment to work with the UN-backed Medicines Patent Pool. Without these safeguards, it cannot be assured that this game-changing medicine will reach all those who need it."
Notes
Data in this press release comes from UNAIDS 2023 Epidemiological estimates (aidsinfo.unaids.org)
The UNAIDS Executive Director joined more than 300 experts and activists calling for a generic version of Lenacapavir to be licensed to all low and middle-income countries through the MPP, in a letter coordinated by the People’s Medicines Alliance: https://peoplesmedicines.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Gilead-Open-Letter_May-2024.pdf
The AIDS Vaccine Advocacy Coalition provides an overview of the Lenacapavir for PrEP trials: https://avac.org/resource/infographic/an-overview-of-lenacapavir-for-prep-trials/
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Feature Story
Girls’ education for HIV prevention at 1st Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa
08 July 2024
08 July 2024 08 July 2024Girls’ education as a tool to prevent HIV infection has been centered at the 1st African Union Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa. This followed African leaders designating education as the 2024 African Union theme of the year.
At a high-level side event hosted by the Education Plus Initiative on the first day of conference held at the African Union Commission in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, leaders, girls’ and women’s networks and advocates called for greater investments in girls’ education.
“Some people claim that providing girls with secondary education is too expensive. Such claims fail to consider the exponentially higher cost of not educating them,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “We can get all our girls and boys to complete secondary education; that should be our legacy."
UNICEF calculates that 34 million girls in sub-Saharan Africa are out of secondary school. According to the Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2023, in all regions in Africa, there are more girls out of school at the secondary level than boys, with gender disparities worsening as children move up to higher levels of education in favour of boys over girls. In sub-Saharan Africa, less than half of adolescent girls complete secondary education, their percentage standing at 42% and there has been no progress at all in closing this gap in the past 20 years. Sub-Saharan Africa is the region furthest from parity at the expense of girls, with no progress since 2011 at the lower secondary level and since 2014 in upper secondary.
Gender is a key factor linked to disparities in enrolment, retention, completion, and learning outcomes through social conditioning, gender-based differences in parental expectations and education-related investments, child marriages and early childbearing, female genital mutilation, child labour, gender-based violence, period poverty and discrimination.
More than forty years into the HIV response, Africa remains an epicenter of the AIDS epidemic with adolescent girls and young women being disproportionately affected. Every week 3100 adolescent girls and young women acquired HIV in sub-Saharan Africa. Every three minutes, an adolescent girl or young woman aged 15-24 years acquired HIV in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa. Adolescent girls and young women aged 15-24 years in the region were more than three times as likely to acquire HIV than their male peers in 2022.
UN agencies, African Union representatives, government ministers, and young women leaders called for accelerated actions to translate commitments to action through leveraging girls' education for gender equality and preventing HIV, child marriage, teenage pregnancies, violence, gender-related stigma and discrimination in Africa.
Speakers emphasized the connection between health and education. Ministers spoke about key policy reforms and best practices aimed at promoting girls' education, including creating safe and inclusive school environments, strategies to get girls into secondary school, and the readmission policy that addresses high dropout rates due to pregnancy. UN co-leads emphasised the need for improved collection of data disaggregated by sex and other relevant population characteristics to better understand educational participation, progression, and learning, and using gender-sensitive data for policymaking and planning.
Other issues highlighted included the integration of digital literacy programs into the secondary education and vocational training curriculum to facilitate smooth transitions from school to employment; integrate gender equality into all aspects of the education system, including curriculum-based comprehensive sexuality education and life skills, address gender-based violence within schools and discriminatory laws and practices, and access to information, non-discriminatory HIV and sexual and reproductive health services access.
Young women leaders spoke on the role of partnerships and young women's leadership. Participants highlighted the upcoming 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration as an opportunity moment to accelerate accountability and commitments, as well as the CSW Resolution 60/2, Women, the Girl Child and HIV and AIDS as significant mechanisms to address political and resource gaps so no woman or girl is behind in the HIV response.
Education Plus is a rights-based, gender-responsive action agenda to ensure adolescent girls and young women have equal access to quality secondary education, alongside key education and health services and support for their economic autonomy and empowerment. Co-led by five UN agencies, the initiative builds on existing frameworks like the Transforming Education Summit, the Continental Education Strategy for Africa (CESA) and the Dakar Education for All (EFA) Declaration to push for access and completion of education for women and girls in Africa.
Quotes
" Some people claim that providing girls with secondary education is too expensive. Such claims fail to consider the exponentially higher cost of not educating them. We know the consequences when girls can’t finish secondary school: higher risks of sexual violence, early marriage, unwanted pregnancy, complications in pregnancy and childbirth, and HIV infection. But when a girl completes secondary school, it helps her to be safe and strong. If all girls complete secondary education, adolescent pregnancy could be cut by 75% and early marriage could be virtually eliminated. An extra year of secondary school can increase women’s eventual wages by 15-25%. We can get all our girls and boys to complete secondary education; that should be our legacy."
We must recognize the intersecting challenges girls face, including HIV. They face extraordinarily high levels of HIV infections. Women and girls represented 63% of all new HIV infections in Africa in 2022. Empowering girls with knowledge is key to ending AIDS as a public health threat. Education is the best HIV prevention tool available.”
“African nations should ensure that young people not only gain vital knowledge but also acquire life skills, values, attitudes, and make decisions in order to live healthy and fulfilled lives. Through the AU strategy, we will see increased awareness about the importance of investing in education and the health of children and adolescents.”
“Girls’ education is not only a right, but will also result in broad socio-economic development for countries. We are creating a safe and conducive environment for adolescent girls and young through the criminalization of child marriage, FGM, school-related gender-based violence, and sexual harassment, particularly sexual exploitation perpetrated by teachers. We provide life skills and comprehensive sexuality education in schools and ensure an inclusive school environment for children with disabilities, with specific attention to girls. We have enhanced social protection strategies, including cash transfers to poor households to ensure that girls go to school and are not engaged in care work and child labour.”
“Girls who dropped out due to early pregnancies or early unwanted pregnancies are readmitted. We have a national girls’ education strategy aimed at facilitating the pace at which Malawi may achieve sustainable development goals. We emphasize universal primary education, the promotion of gender equality and empowering women.”
“We are trying to remove the cultural norm barriers and negative gender stereotypes that contribute to gender-based violence and discrimination against adolescent girls and young women with a male engagement strategy. Inclusive education provides special provisions for the less privileged and disadvantaged children and youth; user-friendly infrastructure, teaching and learning materials and provision of expert teachers.”
“Education is a human right. The Education Plus Initiative is driving policy changes in Africa. Education Plus seeks to keep adolescent girls and young women in school by simply unequivocally saying no to child marriage, no to violence, no to HIV infections, no to gender-related stigma, and of course, no to harmful practices. We want to keep girls in secondary education and make sure they stay there and complete their education. We do that by supporting sexual and reproductive health and rights, comprehensive sexuality education and work for integration HIV awareness, preventing and managing learners pregnancies and addressing school-related gender-based violence.”
“We need to scale up effective interventions to increase HIV knowledge and transform gender norms, and hence girls’ access to services. We should explore the potential of innovative solutions offered by digital technologies to mobilize and provide young women and adolescent girls with comprehensive HIV information. Let's do more, particularly for those girls living with HIV to be meaningfully engaged in the HIV response. Young women must have a formal seat and a safe space to raise their needs. let's move from rhetoric to action.”
“The numbers are unfortunately very clear: highest adolescent pregnancy rates of the world are in sub-Saharan Africa, highest percentages of women first married or in union before 18, young women more than 3 times as likely of HIV infection, or unacceptably high rates of justification of wife beating among adolescents. Fortunately, we benefit from a strong set of political commitments and strategies to face these issues. There is the Education Plus Initiative, the WCA Commitment for Educated, Healthy and Thriving Adolescents and Young People, the ESA Commitment, and the AU Continental Strategy on Education for Health and Wellbeing of Young People in Africa. It is high time to convert the commitments and strategies in concrete results for adolescent girls and young women.”
“Girls need an affirming environment. Where there's ignorance, there's a lot of resistance to education and sexuality education in the curriculum. We need to engage to change the environment, talking with parents, men and boys, community members and leaders for them to have access to information because they have a great influence on the lives of these young people. We need inclusive advocacy, especially the rural grassroots and true localization of information and interventions.”
Our work


Feature Story
United Nations General Assembly debate highlights the need for urgent action to ensure that progress in the HIV response is accelerated and sustained
26 June 2024
26 June 2024 26 June 2024On 19 June 2024, the United Nations General Assembly convened to evaluate the progress made in the response to the AIDS epidemic. The yearly session provided a platform for Member States to reflect on achievements, confront persistent barriers, and chart a course forward towards ending AIDS by 2030. The UN Secretary-General’s progress report formed the basis of the debate.
Member States celebrated the significant achievements towards ending AIDS, while highlighting ongoing challenges that must be overcome to reach the promise of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
The commitment to the 95-95-95 targets and the progress made in eliminating vertical transmission of HIV, especially through the use of decentralized community-based services, were highlighted as pivotal to the success of the HIV response.
Many member states stressed the crucial role that promoting a human rights-centered approach has had in the fight against HIV. They highlighted the significance of comprehensive multi-sectoral responses, including education on sexuality and robust support for sexual and reproductive health and rights. They pointed to the harm of actions that undermine gender equality and LGBTQI+ rights. They emphasized the shared duty of every country to protect everyone’s human rights.
The need for continued global solidarity and enhanced multilateral cooperation was emphasized as key to tackling the remaining challenges. Calls for increased domestic and international funding were echoed, noting that sustained investment is crucial to maintaining progress and for expanding access to innovative prevention and treatment options.
The UN General Assembly annual review served as a poignant reminder of the collective responsibility to uphold the rights and dignity of all people affected by HIV.
Inspired by the lessons learnt from the AIDS response, the upcoming Summit of the Future scheduled for September 2024 will explore how common challenges can be overcome.
Against a backdrop of geopolitical shifts and economic uncertainties, the HIV response serves as a beacon of how multilateral solidarity saves and transforms lives.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025