HIV Prevention




Feature Story
To end AIDS, communities mobilize to engage men and boys
04 December 2024
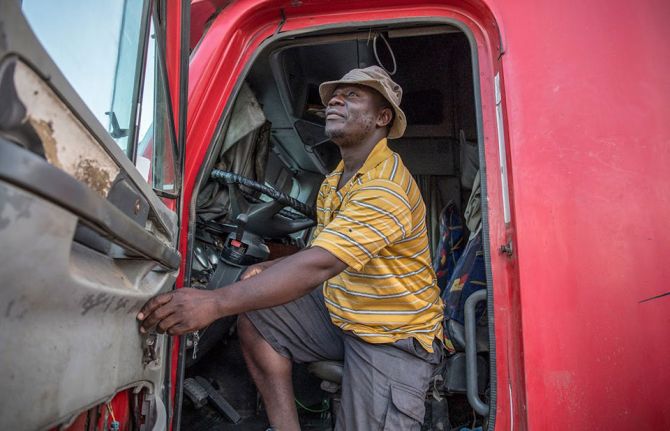
04 December 2024 04 December 2024Michael Onyango rises before dawn in his Nairobi apartment and catches a train eight hours east to Kilifi, a coastal town north of Mombasa. Resorts populate Kilifi’s sandy beaches and narrow wooden boats dot the water. Onyango heads inland to meet with the Kilifi County health management team, before dashing to an assembly of peer outreach workers from across the districts of Kaloleni, Malindi and Kilifi North.
Onyango runs the Movement of Men Against HIV in Kenya (MMAHK), spearheading a community-led monitoring initiative in the region to address the high numbers of men and boys who lack access to HIV services. In Kenya, only 65 percent of the men and boys over 15 years of age who are living with HIV are on antiretroviral therapy, compared to 80 percent of women and girls. The trend is mirrored globally: in 2024, the WHO and UNAIDS released data that men lagged on progress in achieving the 95-95-95 targets. Worldwide just 83 percent of men living with HIV know their status; 72 percent are on treatment and only 67 percent are virally suppressed.
MMAHK, in collaboration with the Masculinity Institute (MAIN), the International Network of Religious Leaders (INERELA+Kenya) and the UNAIDS Kenya country office, came together to tackle these service gaps in Kilifi County, which surrounds the town of the same name. The area, home to around 1.5 million residents, extends westward from the Indian Ocean and supports livelihoods through fisheries, factories, cashew nut mills, and farming.
In Kilifi, peer data collectors have identified that health facilities need to change their opening days and hours to accommodate the work and school day.
Community organizers are also working to challenge harmful prejudices that assert that men visiting a health facility or seeking an HIV test are “weak”.
As they rapidly roll-out peer support groups to challenge these beliefs, Onyango has had flashbacks to the pandemic’s earlier phases, when in the 1990s he worked as a counselor in a Nairobi hospital. HIV treatment was not yet available. “Many men I met who found out they were positive would resign from their jobs, go to their rural homes, sell their property, and wait to die,” Onyango said.
In 2001, Onyango and others started MMAHK to create a safe space for men to talk about their health needs. MMAHK also ran community testing, workplace outreach and targeted advocacy with religious and cultural leaders. As grassroots initiatives challenged harmful gender norms, Onyango saw social stigma and self-stigma among men decrease across Kenya. But the past few years have seen a resurgence of harmful norms around masculinity.
Onyango shares that the shift in funding away from many community initiatives, which were seen as harder to measure than biomedical interventions, has hampered community engagement efforts. Both are needed, he says. For example, although HIV treatment and voluntary male circumcision are now available in Kenya, cultural factors prevent some men from accessing these services.
A regional strategy developed in 2022 by UNAIDS, WHO, UN Women and partners –“Male Engagement in HIV Testing, Treatment and Prevention in East and Southern Africa” – outlines four key approaches: Improve access to health for men and boys and decrease vulnerability; prevent HIV among men and boys; diagnose more men and boys living with HIV; and increase the proportion of men and boys accessing and adhering to antiretroviral therapy.
“Tackling harmful masculinity also has a ripple effect,” reflects Lycias Zembe, a UNAIDS advisor in Geneva. “Harmful gender norms affect everyone, and changing these norms creates a better environment for women and girls and for men and boys.”
Community initiatives like MMAHK remain key. To challenge gender norms, MMAHK positions service access as courageous, and educates men that discussing emotions is a sign of strength. At 63, Onyango shows no signs of slowing down: “We’re going to keep addressing self-stigma and figure out how to help men access the services that they need to stay healthy,” he said. “We don’t have any other option.”
Region/country
Related




Feature Story
PrEP for her: Cambodia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines prepare to introduce the Dapivirine ring to help prevent HIV
22 November 2024
22 November 2024 22 November 2024The only HIV prevention that Elena Felix knew of was condoms. But condoms were not something that she was able to make use of, and she contracted HIV. Thirty years after her diagnosis, she’s helped conduct research to determine whether women in the Philippines would use a more confidential tool, and one that does not need a man to agree, to lower women’s risk of HIV infection.
“We hear from women that some partners insist on not using condoms. We hear cases too of rape. Women need protection that does not depend on men” the Association of Positive Women Advocates founder explained.
The Dapivirine Vaginal Ring or DVR was given the green light by the World Health Organization for women at high risk of contracting HIV in 2021. Unlike other types of pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), this one is exclusively for women. It is a silicone vaginal ring that is inserted and worn for 28 days before being replaced. It releases an antiretroviral drug locally, reducing the risk of HIV infection through vaginal sex by half.
Since its introduction, the technology was made available in several (11) African countries. And with good reason. Around two-thirds of new HIV infections in Eastern and southern Africa and Western and central Africa are among adolescent girls and women. The combination prevention strategies implemented in these two regions have super-charged progress, driving the global 39% decline in new infections since 2010.
But the Asia Pacific picture is quite different.
“This region has an HIV prevention crisis,” Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe Central Asia said. “And I am not speaking only of the countries where new infections have doubled, tripled or increased six times since 2010. The average regional decline in new infections is far too slow. At 13% it has virtually flatlined.”
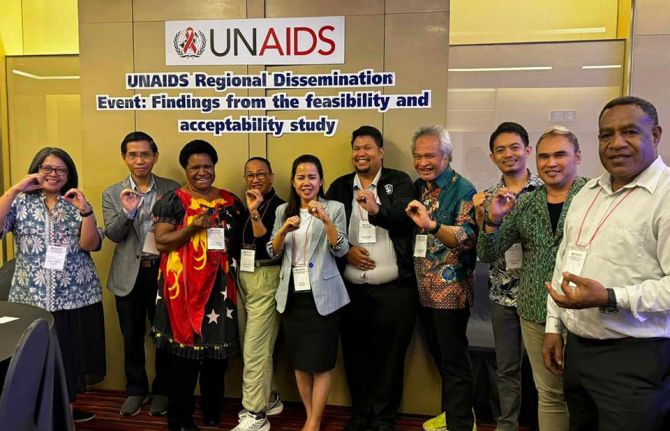
He was speaking to a group of community, government, research and development partners from Cambodia, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the Philippines who met from November 11 – 12 in Bangkok. Findings were disseminated from a DVR acceptability and feasibility study conducted by ThinkPlace, and a discussion held on next steps. UNAIDS and the World Health Organization (WHO) are providing technical support for this initiative. The Australia Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT) funded the research as part of its ongoing support for prevention work in the region.
Seven percent of new infections in Asia Pacific are among sex workers while 12 percent occur among the intimate partners of key populations. Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director, called for women in Asia and the Pacific to be provided more HIV prevention options.
“Choice is the way to go!” Ms Achrekar stressed. “Providing options in prevention tools and service delivery increases overall use and results. We must ensure that people have access and that they are supported with the appropriate policies and enabling environment. The ring has great potential to be empowering as an additional choice for women, including in Asia Pacific.”
A person newly acquires HIV in the Asia Pacific region every two minutes. Despite this, the overall momentum on rolling out pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) options has been sluggish. At the end of 2023 there were just 204,000 PrEP users in this region, 98% short of the 8,200,000 target by 2025. The vast majority of those on PrEP were men.
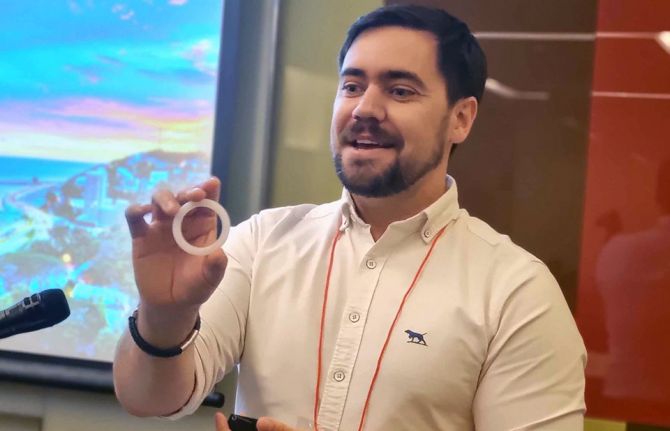
ThinkPlace Regional Director, Elliot Duffy, revealed that overall, the studies found women have high interest in this discreet, woman-controlled prevention method. Sex workers in the four countries sought the DVR given their high vulnerability to sexual violence. And in all countries the sex workers indicated that they would want to access the DVR through community-based health services or their local healthcare facilities. The research also found that healthcare providers in the four countries were enthusiastic about offering this new prevention option.
“The number one barrier is the extent to which women understand how the ring would fit. Many had questions like, “would it be lost in my body? Will I feel pain? Will I be able to have sex?’ Some women worried about a partner thinking they distrusted them,” Mr Duffy explained. “The DVR is not immune to the challenges of other HIV programs and continued effort is needed to increase awareness, generate demand and create services that are accessible.”
Already the research findings have resulted in the introduction and phased implementation of the DVR into 2024 – 2026 Global Fund grant implementation for Cambodia and Indonesia. Cambodia has begun pilot testing. At the meeting the four country teams developed plans to guide their next steps, including on further research, legal and policy reviews, regulatory approvals and community system strengthening.
DFAT Health Adviser, Joshua Metcalf-Wallach, emphasized that as stakeholders switched gears from research to rollout, they should keep communities in the driver’s seat.
“Our Indo-Pacific prevention work has shown that HIV services work best when they are key population- and community-led. As we expand prevention options for women, let us be guided by their needs and demands,” he ended.
Our work
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025




Press Release
UNAIDS calls for global solidarity to strengthen Madagascar’s HIV response to end AIDS as a public health threat
21 October 2024 21 October 2024GENEVA, 21 October 2024—The Executive Director of UNAIDS Winnie Byanyima is calling for accelerated global solidarity to strengthen Madagascar’s response to HIV, including preventing new HIV infections and expanding access to treatment, to end AIDS as a public health threat. Ms Byanyima is visiting the country between 19–24 October to support its response to the HIV epidemic. Madagascar has seen dramatic increase in new HIV infections since 2010 and a 158% increase in AIDS-related deaths over the same period. UNAIDS is concerned about what appears to be a dramatic increase in new HIV infections.
Ms Winnie Byanyima’s visit to Madagascar coincides with that of H.S.H Princess Stéphanie of Monaco, who is visiting Madagascar through the work that she does with Fight AIDS Monaco around the world, including in Madagascar, to end AIDS as a public health threat. Fight AIDS Monaco has been supporting Madagascar’s efforts to prevent new HIV infections, including ending stigma against people living with HIV and galvanising international solidarity to support efforts to end AIDS.
“Madagascar is experiencing a rapid increase in the number of new HIV infections in communities, in stark contrast to the regional trend where new HIV infections are declining,” said Ms Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Madagascar’s pandemic is driven by gaps in HIV prevention and glaring inequalities which must be urgently addressed.”
In 2023 there were an estimated 76 000 people living with HIV in Madagascar and around 3100 people died of AIDS-related illnesses. Gaps in data gathering and weak surveillance systems make estimating the scale of the pandemic difficult. Stockouts of HIV testing kits and limited access to testing facilities further hinder accurate data collection in communities.
In addition, the majority of people living with HIV do not have access to treatment. Only 22% of the estimated 76 000 people living with HIV in Madagascar had access in 2023.
In northern Manakara HIV testing campaigns by the Ministry of Health have shown urban HIV prevalence rates ranging from 3% to 18% among the population. There is a need to strengthen comprehensive data gathering to better inform the national HIV response to effectively tackle the pandemic.
UNAIDS has been actively supporting Madagascar’s HIV response, especially in strengthening the surveillance systems to ensure more accurate and comprehensive data collection. UNAIDS has also been supporting the implementation of HIV testing and counselling services and helping to expand access to antiretroviral therapy.
Madagascar is one of the most unequal countries in the world, a factor which is driving new HIV infections. In 2023, the World Bank estimated the country’s poverty rates at 62.6%. Madagascar has been hit by cyclical natural disasters including drought in the south and cyclones, making it difficult for the country to recover and mount an effective response to HIV.
“Madagascar can scale up its response to HIV but urgently needs technical and financial support from the international community to ensure that HIV prevention commodities, including condoms, testing kits and antiretroviral treatment are available to everyone in need,” said Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country

Feature Story
New long-acting HIV prevention options for women and girls in an era of choice
14 October 2024
14 October 2024 14 October 2024New long-acting technologies are changing the HIV prevention landscape. In recent years, innovation in pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has accelerated. Long acting injectable cabotegravir and the dapivirine vaginal ring as innovative formulations of PrEP have already joined oral PrEP containing tenofovir as WHO-recommended effective and acceptable options for HIV prevention, and there are additional antiretroviral-based options on the immediate horizon. These options complement other effective, non-antiretroviral-based HIV prevention products including condoms and lubricants, and harm reduction strategies.
This year clinical trial results for PURPOSE 1 and 2 showed the high prevention effectiveness of the 6-monthly long-acting injectable drug, lenacapavir for cisgender adolescent girls and women, cisgender men and transgender women. Among the cisgender adolescent girls and women participating in the trial, no HIV acquisitions were recorded during 12 months of follow-up among the women who received injectable lenacapavir. The Global HIV Prevention Coalition (GPC), UNAIDS and other partners called on Gilead Sciences to accelerate their efforts in ensuring that it is made available, accessible and cost effective especially to low- and middle-income countries. This twice-yearly injection is a promising option and offers increased choice, discretion and convenience for people who may benefit from HIV prevention.
In October 2024, at the Research for Prevention (R4P) conference in Peru, the Population Council announced phase 1 trial results from IPM 054, showing that the three-month dapivirine ring is as safe as the currently available one-month ring with similar levels of drug release. The 3-month ring like the 1-month ring is a woman-controlled option but would be more cost effective (an estimated 60% reduction in cost per user) and potentially an even more convenient HIV prevention option for women and adolescent girls.
“We need to follow the science, and the science has shown us that by making a range of effective HIV prevention options available and accessible, we can stop HIV transmission and drop new infections by addressing biomedical, behavioral and structural drivers simultaneously. Ending AIDS remains a political and financial choice”, says Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director Programmes.
This complements a partnership announcement by the Global Fund and the Children’s Investment Fund Foundation (CIFF) of an USD 2 million initiative for 2024-2025 to purchase an estimated 150 000 dapivirine vaginal rings for use as PrEP in the Global Fund grant implementing countries. This would increase accessibility to one of the most discreet HIV prevention options for women and adolescent girls.
The World Health Organization (WHO) PrEP Implementation Tool Provider Module for Oral and Long Acting PrEP, launched in July 2024, integrates clinical service delivery guidance for the three WHO recommended PrEP products (oral PrEP, the dapivirine vaginal ring and long-acting injectable cabotegravir) by a range of different providers in clinical or community settings and emphasizes the importance of access and choice.
These strategic advancements align to the HIV Prevention Choice Manifesto For Women and Girls in Africa that calls for prevention options to be made choices and urges that research and development of new HIV prevention options actual choices, thereby empowering women and girls to take control of their health and bodies. It also emphasizes the importance of ongoing research and development of innovative HIV prevention methods.
“Adolescent girls and women are gaining access to an increasing range of safe and effective options. Scale-up of HIV prevention will depend on supporting access to choice, strong country leadership and an enabling environment. An HIV free future for girls is possible, but only if the global community comes together with ambitious plans to make this range of PrEP options available with speed, scale and equity,” says Mitchell Warren, Executive Director, AVAC and GPC, Co-chair.
The GPC co-convened, by UNAIDS and UNFPA, will continue to work with its partners to accelerate HIV prevention to achieve the global target of less than 370 000 new HIV infections annually by 2025.
About the GPC
In 2017, a global coalition of United Nations Member States, donors, civil society organizations, and implementers was established to support global efforts to accelerate HIV prevention. Membership includes 38 of the highest HIV-burden countries, UNAIDS Cosponsors, donors, civil society, and private sector organizations. The overarching goal of the Global HIV Prevention Coalition is to strengthen and sustain a political commitment to primary prevention by setting a common agenda among key policymakers, funders, and program implementers.

Press Statement
UNAIDS response to ViiV’s announcement on increasing production of long-acting cabotegravir
08 October 2024 08 October 2024GENEVA, 8 October 2024—Responding to ViiV’s announcement on long-acting cabotegravir , UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima said:
“New HIV prevention medication, in the form of a long-acting injection, could transform the lives of people who struggle to take daily pills. The option of an injection that only needs to be taken once every few months is vital for people who face stigma when seen with pills, and those who are driven underground by criminalizing laws.
The people most in need of this long-acting option include adolescent girls, LGBTQ+ people, sex workers, and people who use drugs.
The arrival of long-acting injections is truly a game-changer – it can help prevent millions of new HIV infections.
But this will only happen if everyone who would benefit has access. When medicines are lifesaving, delays are fatal.
To ensure affordable pricing and worldwide availability for everyone who needs these medicines, enabling access to generic versions in all low- and middle-income countries is essential. But ViiV continues to lock out many low- and middle-income countries from this possibility. Shockingly, the company has even launched a legal challenge against Colombia for trying to access a generic version of another lifesaving HIV medicine, dolutegravir.
ViiV's announcement on increasing production of long-acting cabotegravir is a welcome first step, but their next steps must follow fast. It is not enough for ViiV to increase the number of doses up for sale.
I urge ViiV to show leadership on access to medicines now by announcing an affordable not-for-profit price, dropping its harmful legal challenge, and enabling all low and middle-income countries to access generic versions of its medicines.
That is how they can help ensure this scientific breakthrough fulfils its potential and how they can help bring an end to the AIDS pandemic."
/ENDS
Note: ViiV’s announcement can be read on their site at https://viivhealthcare.com/hiv-news-and-media/news/press-releases/2024/october/triple-annual-supply-of-long-acting-hiv-prep-for-low-and-middle-income-countries/
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.

Press Statement
UNAIDS response to Gilead’s announcement on signing voluntary licensing agreements on lenacapavir with six generic manufacturers
02 October 2024 02 October 2024GENEVA, 2 October 2024—Responding to today’s announcement by Gilead on lenacapavir, UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima said:
“We welcome Gilead’s announcement of licensing the break-through HIV medicine lenacapavir for generic production. To stem the tide of new infections, and protect people most at risk from HIV, including young women and people from marginalised communities, long-acting HIV medicines are vital. Lenacapavir, which requires only two injections per year, could be game changing – if all who would benefit can access it.
We applaud Gilead for licensing the medicine without waiting for registration, which should be the norm. We are battling a pandemic and the speed at which generic versions come to market will dictate whether this medicine can really be transformative. At UNAIDS we commit to doing all we can to speed up this process.
Including an African producer in Egypt is also very welcome.
Much more work is still urgently needed to ensure that no one who needs lenacapavir is left behind and that Gilead’s commitment to rapid, affordable access is fulfilled.
The exclusion of many middle-income countries from the licenses is deeply worrying and undermines the potential of this scientific breakthrough.
HIV prevention products need to be deployed where new HIV infections are highest – and right now, forty-one percent of new infections are in upper-middle income countries. UNAIDS urges Gilead to secure further licenses for access in all low and middle-income nations.
We welcome Gilead’s statement of commitment to non-profit pricing, but we had been waiting eagerly for a specific price. We urge Gilead to disclose it, and to provide full transparency on their costs. Respected researchers have shown it is possible to produce and sell lenacapavir for $100 per patient per year, falling to as little as $40.
Manufacturing this medicine in African countries with the highest HIV rates is crucial for sustainability and Gilead should include manufacturers in countries like South Africa where there is strong production capacity. We at UNAIDS stand ready to assist.
UNAIDS urges Gilead to secure further licenses for access in all low and middle-income nations.
We urge Gilead also to do all it can to make lenacapavir viable for treatment in low- and middle-income countries, including working together with researchers to test new combinations. Over 30 million people worldwide taking HIV treatment every day deserve long-acting options. We recognize that Gilead has included treatment use in the license, where some companies have not, but we urge that they remove the current limitation in the license to “heavily treatment-experienced patients.” To support scientists and manufacturers worldwide, licenses should not be limited to specific uses.
Leaving no one behind is how to unlock lenacapavir’s full potential, fulfil Gilead’s promise, protect a generation from HIV and bring forward the end of the AIDS pandemic."
Note: Gilead’s announcement can be read on their site at https://www.gilead.com/news/news-details/2024/gilead-signs-royalty-free-voluntary-licensing-agreements-with-six-generic-manufacturers-to-increase-access-to-lenacapavir-for-hiv-prevention-in-high-incidence-resource-limited-countries
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Release
With new HIV infections rising in a growing number of countries and regions, urgent action is needed to turn the prevention crisis around
24 July 2024 24 July 2024GENEVA/MUNICH, 24 July 2024—An estimated 1.3 million people became infected with HIV in 2023, three times more than the target of fewer than 370 000 by 2025. While there has been marked progress in sub-Saharan Africa, for the first time, in 2023 more than half of the new HIV infections occurred outside of sub-Saharan Africa.
Rising new HIV infections are evident in several countries, particularly in countries where key populations including men who have sex with men, sex workers, transgender people and people who use drugs, are most affected, and investment in prevention was lower. Key populations and their sexual partners now represent the majority (55%) of new HIV infections globally, up from 44% to 2010.
The Global HIV Prevention Coalition (GBC), established in 2017, is addressing the HIV prevention crisis. Focusing on 40 countries the GPC, a coalition of United Nations Member States and partners including UNAIDS, donors, civil society and private sector organizations, is working to strengthen and sustain political commitment for HIV prevention.
“The HIV epidemic has evolved – now more than ever, we need resilient capacity to deliver and manage integrated, differentiated and equitable HIV prevention interventions,” said Prof. Sheila Tlou, GPC Co-chair and Former Minister of Health, Botswana.
There has been great variation in progress among GPC member countries; the biggest declines occurred in countries within eastern and southern Africa including Kenya, Malawi and Zimbabwe, where new HIV infections were reduced by more than 66% and which are on track to achieve the global target of 90% reduction by 2030 – and, to a lesser extent, in western and central Africa. Expansion of access to effective HIV treatment, combined with an ongoing focus on primary prevention, are driving those achievements.
“The moment of opportunity for HIV prevention is now,” said Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director for Programmes. “Today, we have a wider range of prevention options including new long-acting antiretroviral prevention—with the new results about lenacapavir—a twice yearly injection to prevent HIV—providing a promising game-changing option—and new opportunities to communicate about HIV prevention and health.”
Long-acting technologies like pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) will play a major role in preventing new infections in the coming years. Access is increasing, but only in a few countries. Around 3.5 million people were accessing PrEP (antiretroviral medicine which prevents HIV) in 2023 up from just 200 000 in 2017, but this remains far short of the 10 million target set for 2025.
New HIV prevention products in the pipeline such as long-acting injectable cabotegravir (CAB-LA) and most recently, lenacapavir, are raising expectations due to their combination of convenience and high efficacy. However, the key is accessibility and affordability. The cost of the new long-acting injectable PrEP options, and the speed with which they are made available to potential users in the countries with the most need will be critical in expanding access to these life-saving technologies.
Persistent gaps remain in HIV prevention coverage (only 61% of areas with high incidence of HIV have programmes for young women, less than half of sex workers, and only about a third of gay men and other men who have sex with men and people who inject drugs regularly access prevention in GPC focus countries).
Condoms remain the most effective low-cost HIV prevention tool, however global condom procurement or distribution in low- and middle-income countries declined by an average of 27% between 2010 and 2022 and procurement by major donors fell by an average 32% in that period. Socially marketed distribution declined from a peak of about 3.5 billion condoms in 2011 to about 1.8 billion in 2022.
Condoms, PrEP, post exposure prophylaxis, antiretroviral therapy to ensure viral suppression thus preventing transmission of the virus, harm reduction and voluntary medical male circumcision are all HIV prevention options that should be real choices available for people at risk of HIV infection. Addressing structural and gender inequalities faced by these priority and key populations is essential in ensuring access to prevention services. The urgency to secure and sustain gains for HIV prevention cannot be overemphasized – programmes need to be community-led and country-led.
“No matter how good the science or community leadership, HIV will not end unless we have significant policy change to reverse criminalization and lessen stigmatization of affected populations. If we can’t protect human rights, then we can’t end HIV. This is never just about the virus—it’s about people, and the people must lead,” said Mitchell Warren, GPC co-chair and Executive Director, AVAC.
An enormous unmet need for resources for HIV prevention and societal enabler programmes in almost all regions persists. An estimated US$ 2.4 billion was available for primary prevention programmes in low- and middle-income countries in 2023 compared to the estimated need of USD 9.5 billion in 2025. Investing in HIV prevention now is essential to scale up programmes.
If 1.3 million people continue to acquire HIV every year, the response will become more challenging, more complex and more costly in 2030 and 2050. Increased investments in HIV prevention, strengthened political leadership, enabling legal and policy environments are urgently needed to effectively implement programmes. The time to act is now!
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Documents
Western and Central Europe and North America regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
There has been a 24% drop in the annual number of new HIV infections in western and central Europe and North America since 2010, and the number of AIDS-related deaths has declined by 34%. Numbers of new HIV infections among sex workers and their clients, however, have not declined at the same rate. Despite data showing ongoing progress in HIV prevention, persistent social and economic factors, including stigma and discrimination, continue to cause health disparities, compromising the health and well-being of people from marginalized communities. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Documents
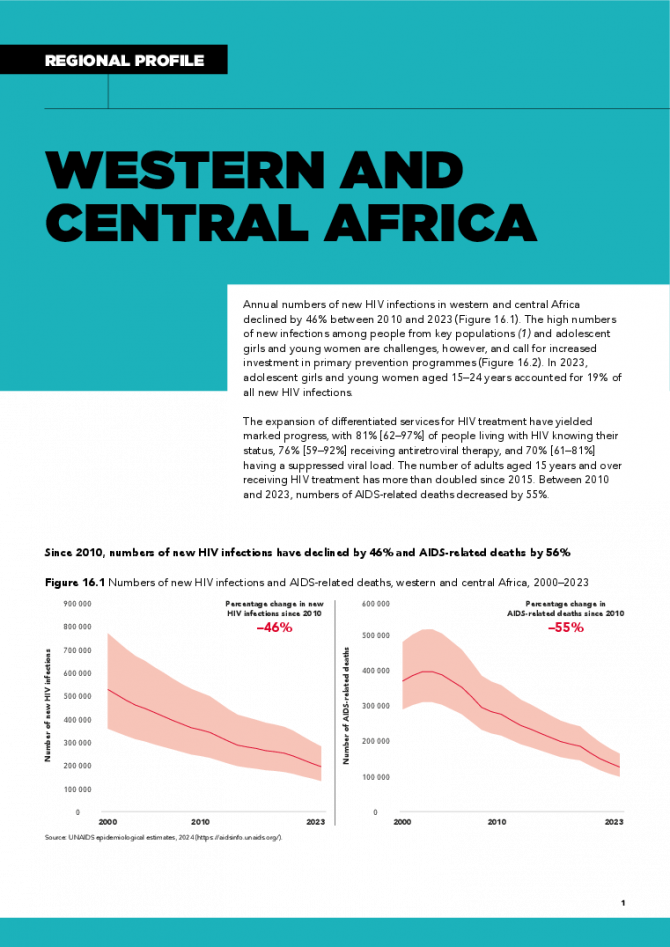
Western and Central Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
Annual numbers of new HIV infections in western and central Africa declined by 46% between 2010 and 2023. The high numbers of new infections among people from key populations and adolescent girls and young women are challenges, however, and call for increased investment in primary prevention programmes. In 2023, adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years accounted for 19% of all new HIV infections. The expansion of differentiated services for HIV treatment have yielded marked progress, with 81% [62–97%] of people living with HIV knowing their status, 76% [59–92%] receiving antiretroviral therapy, and 70% [61–81%] having a suppressed viral load. The number of adults aged 15 years and over receiving HIV treatment has more than doubled since 2015. Between 2010 and 2023, numbers of AIDS-related deaths decreased by 55%. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
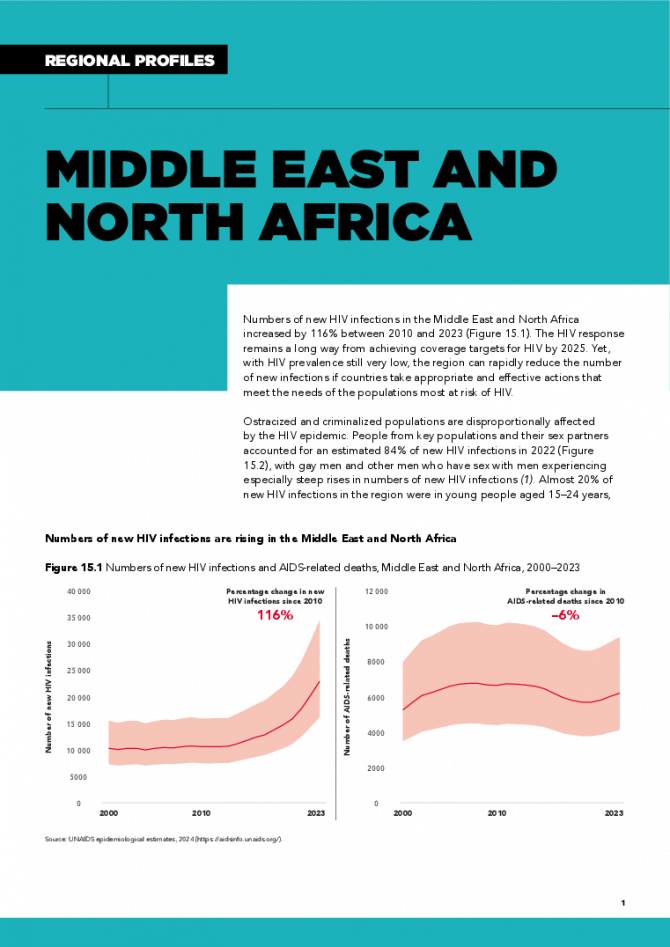
Middle East and North Africa regional profile — 2024 global AIDS update The Urgency of Now: AIDS at a Crossroads
22 July 2024
Numbers of new HIV infections in the Middle East and North Africa increased by 116% between 2010 and 2023. The HIV response remains a long way from achieving coverage targets for HIV by 2025. Yet, with HIV prevalence still very low, the region can rapidly reduce the number of new infections if countries take appropriate and effective actions that meet the needs of the populations most at risk of HIV. Ostracized and criminalized populations are disproportionally affected by the HIV epidemic. People from key populations and their sex partners accounted for an estimated 84% of new HIV infections in 2022, with gay men and other men who have sex with men experiencing especially steep rises in numbers of new HIV infections. Almost 20% of new HIV infections in the region were in young people aged 15–24 years, the majority of them male (55%). These epidemic patterns underscore the need for scaled-up HIV interventions for people from key populations and especially young people, and for reducing the societal and structural barriers that limit their access to needed services. Related links: New UNAIDS report shows AIDS pandemic can be ended by 2030, but only if leaders boost resources and protect human rights now | Full report
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025