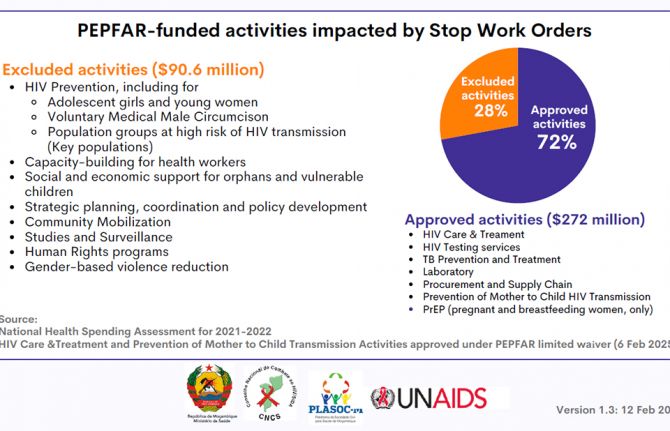
Update
TB disease and deaths declining among people living with HIV, but there have been some reversals due to the COVID-19 pandemic
23 March 2022
23 March 2022 23 March 2022Tuberculosis (TB) is a preventable and treatable disease, yet it continues to claim millions of lives each year and remains the leading cause of death among people living with HIV.
While progress has been achieved in recent years, there have been some reversals due to the COVID-19 pandemic. There has been a steady decline in the estimated number of incident TB cases among people living with HIV. However, just 48% of the estimated 787 000 TB episodes globally among people living with HIV in 2020 were diagnosed and notified. This reflects a decline for the first time since 2004 in the percentage of estimated incident TB cases among people living with HIV that were notified, from 56% in 2019.
Fully 88% of people living with HIV who were diagnosed and notified with TB were provided with antiretroviral therapy, corresponding to 42% of people living with HIV estimated to have developed TB in 2020. While until 2019 there had been a gradual increase in the number of TB patients living with HIV who were on antiretroviral therapy, 2020 data reflect a decline in the percentage of incident TB cases of people living with HIV who received antiretroviral therapy for the first time since 2004, from 49%. There was also a decline in the number of people living with HIV who received TB preventive treatment between 2019 and 2020.
While the United Nations High-Level Meeting on Tuberculosis target of 6 million people living with HIV having received TB preventive treatment between 2018 and 2022 has been reached ahead of time, with 7.5 million people living with HIV having received TB preventive treatment between 2018 and 2020, there is still a long way to go to reach the 2025 target of 90% of people living with HIV having received TB preventive treatment.
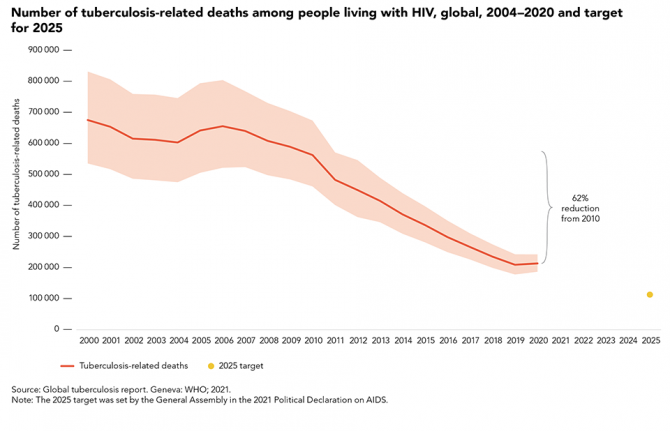
There were an estimated 214 000 TB-related deaths in 2020 among people living with HIV, a 62% reduction since 2010, when TB claimed the lives of 563 000 people living with HIV. For the first time since 2006, there was an increase in the estimated number of TB-related deaths among people living with HIV between 2019 and 2020, from an estimated 209 000. The 2021 United Nations Political Declaration on AIDS requires an 80% reduction by 2025 (compared to a 2010 baseline).