


Feature Story
Guyana’s transgender community calls for protection under anti-discrimination laws
28 February 2022
28 February 2022 28 February 2022Marcia John (not her real name), a Guyanese transgender woman, readied to leave a transgender support group meeting. She slipped off her black wig, replacing it with a bandana and hat. Her employer only allows her to perform her duties if she presents as a man.
“I have no choice,” she said. “I have to work.”
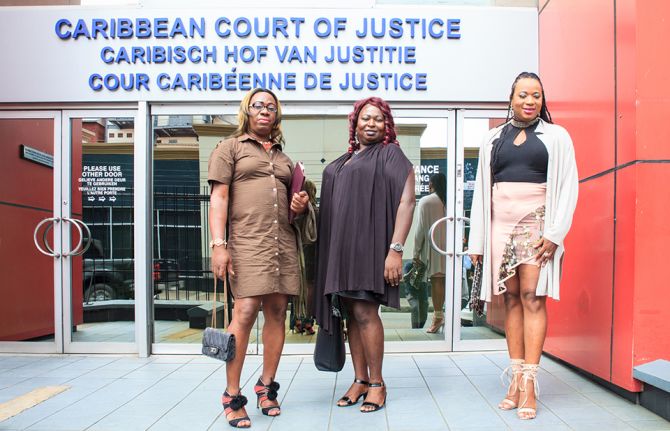
In 2018, the Caribbean Court of Justice ruled that an 1893 Guyana law that prohibited cross-dressing was unconstitutional. Last August, lawmakers formally removed that section from the law books. But for Ms John and other transgender women, this has not been enough to transform the way they navigate social spaces. Intolerant attitudes remain, with sometimes dire implications for transgender people’s welfare and livelihoods.
Led by the University of the West Indies Rights Advocacy Project, the cross-dressing law challenge started with a constitutional action filed in the Guyana High Court in 2010. Eight years and two appeals later, the litigants earned a historic win.
“At the heart of the right to equality and non-discrimination lies a recognition that a fundamental goal of any constitutional democracy is to develop a society in which all citizens are respected and regarded as equal,” the Caribbean’s final appellate court ruled in 2018.
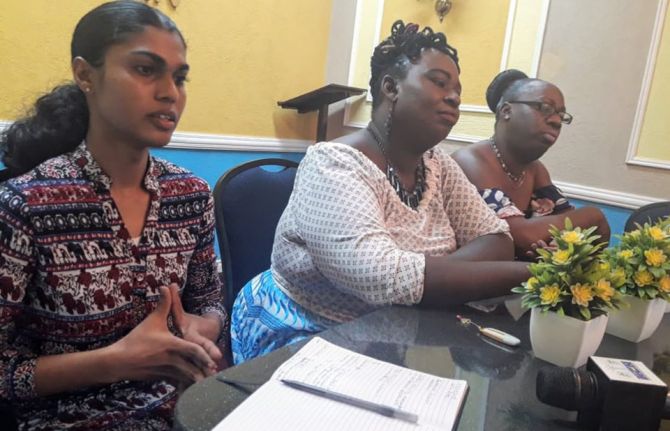
Reflecting on the impact of the landmark law reform effort, Alessandra Hereman, Guyana Trans United (GTU) Project Coordinator, said that the main benefit has been more visibility.
“The community’s increased media presence in the lead-up to the case brought transgender issues into the public space. People realized that transgender Guyanese exist and are part of our society. Some thought we should be treated equally and others held on to their religious beliefs. But transgender issues were brought to the fore and were part of public discourse,” she said from GTU’s Georgetown office.
Formed in 2012, GTU has worked over the past decade to facilitate the dialogue and sensitization that are needed alongside key law and policy reforms to create a safe and empowering social context for transgender people. They contribute to the ongoing effort to shift the attitudes and perceptions of health-care providers around sexual orientation and gender identity. This work strengthens the community’s access to health services, including HIV prevention, testing and treatment. With support from UNAIDS, GTU also trained journalists on covering transgender people and issues ethically and accurately.
“Law reform is essential, but it is not a stand-alone,” said James Guwani, the Director of the UNAIDS Caribbean Sub-Regional Office. “Alongside strategies like judicial review and political advocacy, there must be ongoing community dialogue and targeted efforts to increase social inclusion.”
At present, GTU has two high law and policy reform priorities. First, Guyana’s Prevention of Discrimination Act of 1997 makes no mention of sexual orientation or gender identity.
“Employers use the lack of this protected status to discriminate against lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) persons. Amending that legislation would mean that if you violate the rights of an LGBT person there would be some mechanism for redress. Having that in place will tell people you can’t discriminate because there will be consequences,” Ms Hereman explained.
The CARICOM Secretariat, through the Pan Caribbean Partnership against HIV and AIDS (PANCAP), has developed a model anti-discrimination bill to guide Caribbean countries in creating anti-discrimination laws. PANCAP continues to advocate with regional stakeholders, including policymakers, for countries to adopt the model as it provides for the protection of persons against discrimination, including discrimination involving harassment, victimisation and vilification on the grounds of HIV status, sexual orientation, etc. It is hoped that the model will lead to more access to health care for key populations with the overarching goal of a Caribbean free of AIDS and new HIV infections, in which all people are happier, healthier, productive, safe and respected. Next on GTU’s list is the revision of the Teachers’ Code of Conduct to be inclusive of the needs of LGBT students.
“They must know that they have a duty to create an enabling environment for all students so that LGBT pupils have an opportunity to learn without bullying,” Ms Hereman said.
Lack of gender recognition legislation and the criminalization of sex between people of the same sex remain challenges in the Guyana and wider Caribbean contexts. The United Caribbean Trans Network has mounted a campaign around gender identity recognition, while the Society against Sexual Orientation Discrimination is working to remove Sections 351 to 353 of the Criminal Law (Offences) Act, which make sex between men punishable with life imprisonment. However, GTU is first prioritizing issues that it says go to the heart of transgender’s people’s ability to get an education and access employment. Exclusion from these spaces compounds their vulnerability to poverty, violence and disease.
“We occupy the lowest socioeconomic level in society. Guyana is now an oil-producing nation. LGBT people should have opportunities as well,” Ms Hereman insisted.



