Feature Story
Science, HIV and COVID-19—where are we headed?
08 June 2021
08 June 2021 08 June 2021A side event at the United Nations High-Level Meeting on AIDS, being held in New York and online from 8 to 10 June, has highlighted the science relevant to the new UNAIDS global strategy and targets and the changing scientific environment that will take the world to 2030, the Sustainable Development Goal target date for ending AIDS.
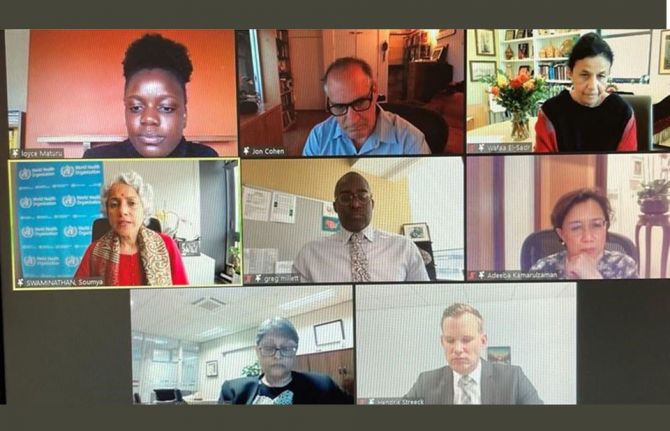
At the event, Science, HIV and COVID-19—Where are we Headed?, Jon Cohen, a leading science journalist, moderated a panel discussion that included Anthony Fauci, the Chief Medical Adviser to the President of the United States of America, Loyce Maturu, an activist working for Zvandiri in Zimbabwe, Soumya Swaminathan, the Chief Scientist at the World Health Organization, and other leading HIV scientists.
In the complexity and multidimensional nature of the global AIDS response, science has been a constant force, moulding and adapting how the world reacted. A similar role for science has been seen in the other ongoing pandemic—COVID-19. The side event was an opportunity to discuss the role of science and to review major and emerging scientific themes that will influence the trajectory of the HIV pandemic in the approach to 2030.
Mr Fauci emphasized the importance of long-term engagement and investment in surveillance and basic sciences to increase preparedness for future pandemics, noting that we must focus on building trust in science and explaining how knowledge evolves through the accumulation of reliable data that can alter clinical and public health guidance. The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us lessons in efficiency and in accelerating the translation of basic science into effective interventions, he said. However, we must address the challenges of access, intervention pricing and social biases that limit our global impact. He concluded that both the HIV pandemic and the COVID-19 pandemic have the power to strengthen the global community, and he committed the United States to being a global leader and reliable partner in those efforts.
Greg Millett celebrated the amazing fall in new HIV infections in several places, such as London, Denmark and Australia, where pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and effective testing and treatment is really working for gay men and other men who have sex with men. He highlighted the importance of recent scientific advances that have led to new technologies, such as HIV self-tests and new PrEP modalities.
A major theme was around equity. For both COVID-19 and HIV, the participants noted that we must ensure that all people in all countries reap the benefits of science. Commentators in the audience reiterated that this is even more important given the participation of so many people across so many countries as the altruistic participants in the research that has led to the exciting new tools for HIV prevention and vaccines for COVID-19. And Mr Millet pointed out that we are all interrelated and interconnected. HIV infections and other diseases are, of course, in no way limited to national boundaries.
Loyce Maturu reminded everyone that young people are central to the HIV response. Young people are often left behind and treated as end users of services that are not specifically designed to suit their lifestyles. She acknowledged that science was the reason that she was with us, healthy, beautiful and empowered after falling sick with HIV-related illnesses as a child and witnessing the death of both her mother and brother from HIV. Young people need to be central to science and brought to the tables that set the research priorities.
Quarraisha Abdool Karim, and others, exhorted political leaders not to “drop the ball” for HIV. We need to finish the job and not allow the huge challenges of dealing with it deflect us.
All the participants pushed for HIV programmes to be based firmly on scientific evidence, and Wafaa El Sadr noted that the evidence base comes not only from biomedical laboratories and large clinical trials, but also from implementation and the social sciences. The Co-Chairs of the upcoming International AIDS Society Science Conference, in July 2021, Adeeba Kamarulzaman and Hendrik Streeck, hoped that the high-level meeting would be a boost for stronger engagement with science—registrations for the conference are as high as ever, despite the COVID-19 restrictions. Mr Streeck called for a massive effort to bring thousands of HIV vaccine scientists together in one huge effort, similar to the collaboration around the Large Hadron Collider or even the Manhattan Project.
In an optimistic conclusion, Ms Swaminathan hoped that the proven success of the scientific collaboration that has produced multiple COVID-19 vaccines so quickly should be a stimulus for greater enthusiasm and investment in collaborations to end not just AIDS but also other major public health challenges, such as tuberculosis, malaria and noncommunicable diseases.
Quotes
“We must ensure that we reach all sectors of our local and global communities, in particular those that are sceptical, disadvantaged or historically exploited.”
“Please make sure that young people and adolescents are seen as decision-makers, and not just as end users. We need a bottom-up approach to ensure that research and science are driven by communities to deliver what everyone needs.”