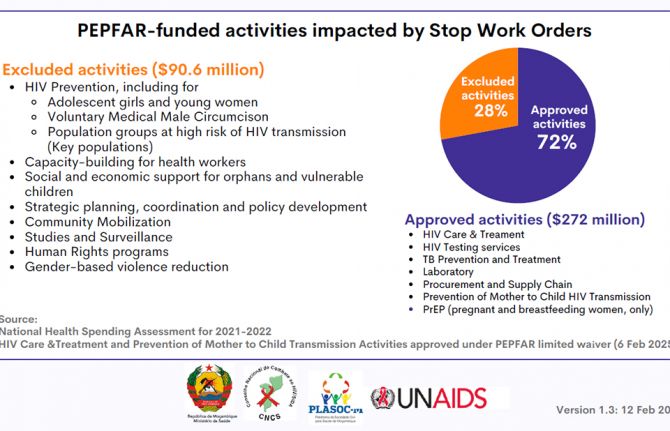
Feature Story
COVID-19 impacting HIV testing in most countries
13 October 2020
13 October 2020 13 October 2020Monthly data routinely reported to UNAIDS on disruptions to HIV testing and treatment services have found significant decreases in HIV testing services in nearly all countries with available data.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, UNAIDS, the World Health Organization and the United Nations Children's Fund have collected data from countries through an online platform (https://hivservicestracking.unaids.org) to identify national, regional and global disruptions of routine HIV services caused by COVID-19.
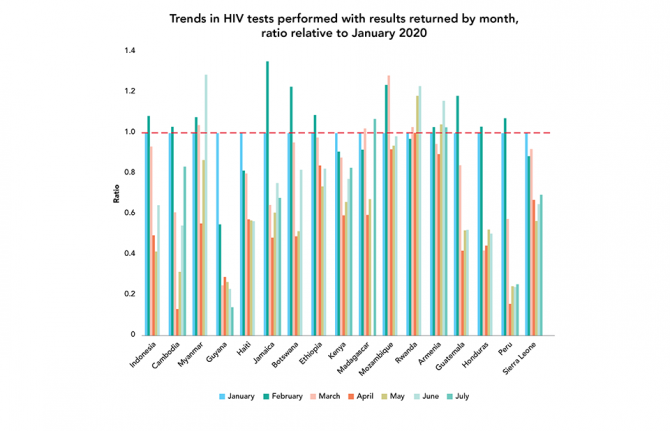
Fifty-six countries reported at least one month of HIV testing data to the platform between January and July 2020, with 17 supplying enough data to calculate trends over time. To measure the impact of COVID-19 on HIV testing services, a ratio was calculated relative to January—for example, if the number of tests in April was the same as in January, the ratio is 1; if there was a decline, the ratio is less than 1.
Large, sustained decreases in HIV testing services have been seen across all countries except Rwanda, with reduced services reported for most countries starting in April. Five countries, Myanmar, Mozambique, Madagascar, Rwanda and Armenia, have rebounded to pre-COVID-19 testing levels, while in other countries, such as Guyana and Peru, testing remains low.