40 years of the AIDS response
Universal access



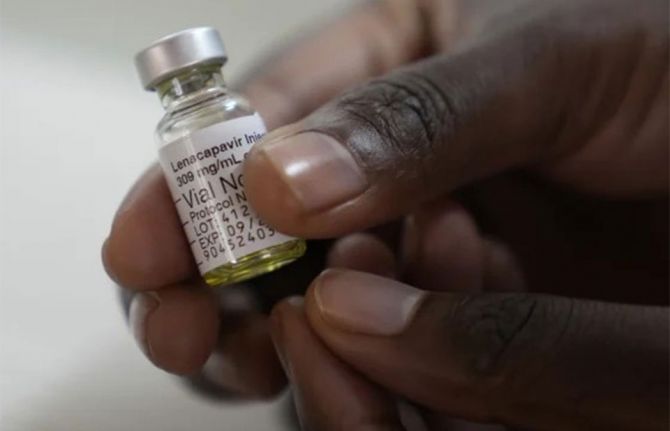

NAIROBI, 10 December 2024—Today, at the 55th Programme Coordinating Board for the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), HIV leaders from across the world called for access to long-acting medicines for everyone who would benefit from them, to build toward a new era in the AIDS response.
Over the last two years, scientific breakthroughs have brought to the fore a new class of anti-HIV medicines with long-acting effects, allowing people at risk of HIV infection and those living with the virus to take medicines every few months. One is injected just twice a year. Recent studies have shown these medicines to be among the most effective ever developed. One study showed zero new infections among young African women using long-acting prevention drugs, while a study among key populations showed them more effective than oral medicines. Another study highlighted at the session showed encouraging results using long-acting HIV treatment in low- and middle-income countries.
At the “Leadership in the AIDS Response” session at the UNAIDS board, government officials, researchers, manufacturers, and civil society called for accelerating global access to use these scientific breakthroughs to interrupt the continuing AIDS pandemic. Despite existing HIV prevention tools, in 2023 an estimated 1.3 million people newly contracted HIV – two every minute. Despite HIV treatment, there is still one AIDS-related deaths every minute.
Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS, said: “We can usher in a new era by connecting technological innovation with access for all. Let us act boldly together, bring down the curve of new infections, and dramatically accelerate the HIV response.
“Let us learn from the painful lessons of the past so that we write a new story now. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, even after antiretroviral medicines were proven to be effective and rolled out in high-income countries, 12 million people on this continent still died waiting for those drugs. We can - and must – do better with long-actings. We urge the companies producing these medicines to expand their generics licenses. And we support governments making use of all their legal flexibilities to get access to affordable medicines.
“The usual trajectory is that the Global South waits years before the science reaches them. What if we do not wait for years, what if we ensure that science is treated as the public good it is? What if we disrupt the far too slow trajectory we are on and shift to a trajectory that accelerates progress, ends the pandemic, enables sustainability, and can be a model for the world?"
Secretary Ethel Maciel, Secretary of Health of Brazil, said: “Brazil has a long history of making use of technology in the HIV response. The possibility of having new long-acting medicines in the global response is a great opportunity. But we have the huge challenge of the high cost of these medicines, and the difficulty for a range of countries, including ours, to access them.
“Brazil is committed to work together in the fight to ensure that this new technology is made available to all people all over the world who are at risk of and living with HIV.”
Dr Cissy Kityo, Executive Director of the Joint Clinical Research Centre, Uganda, a leading scientist working on trials of long-acting medicines said: “We have these fantastic new tools. The technology of long-acting ARV’s antiretrovirals is remarkable. The evidence is now clear that long acting medicines will be game-changers for both prevention and treatment. The science is in, the question is how well we will use it.”
Mr Javier Padilla Bernáldez, Secretary of State for Health, Spain, said: “This new long-acting technology puts us in an exceptional situation, not an ordinary one, an opportunity that we cannot afford to miss. Long-acting medicines can change the landscape of the HIV response. But if this game-changing innovation did not reach the people it would be a nothing-changer!
“We need to remember the 2000s’ fight for universal access. We cannot repeat the same mistakes and delays of before. We need to ensure that no countries should be pressured if they choose to use the safeguards in the TRIPS agreement. The inequality gap is a global problem. We need a universal perspective, so that all countries, including middle-income countries, are included.”
Dr Sylvia Vito, Africa Head of EVA Pharma, a company in Egypt licensed to produce a generic version of lenacapavir, said: “We are a company that will not sit comfortably, but rather be in a good hurry to support the unmet HIV medical needs for our people. We intend to move fast on product development, production, and eventual registration. It is our intention that high quality long-acting generic ARV medicine will not only be available, but made accessible and affordable as well. We intend to beat the current standard of care in HIV treatment and prevention by going further to improve on the current options for patients in low and middle-income countries.”
The importance of generic production was central to the interventions of speakers. Several speakers noted the obstacle that much of Latin America, a region of rising HIV infections, has been excluded from companies’ voluntary licenses for generic versions. This is despite Brazil, Peru, Mexico and Argentina participating in clinical trials. Speakers highlighted the importance of using TRIPS flexibilities for enabling access under World Trade Organization rules, which can enable governments to supply its citizens with generic versions of patented treatments either through domestic production or imports. In the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV/AIDS, countries committed to make use of TRIPS flexibilities, specifically geared to promoting access to medicines.
Although Gilead Sciences, the producer of lenacapavir, one of the new class of long-acting medicines, has not yet announced the price of its product for use as PrEP, it costs around $40,000 per person per year in the United States where it is used for treatment. However, experts have estimated that it could be produced and sold for $40 per person per year, in line with UNAIDS estimates for sustainable pricing in low- and middle-income countries. Speakers highlighted opportunities to bring down the price of these medicines through generics, expanded local and regional production, and the use of TRIPS flexibilities by member states.
One important opportunity for progress emphasized by speakers was to build on the progress on multilateral collaboration made by Brazil, which as chair of the G20 in 2024, successfully secured worldwide support for the Global Coalition for Local and Regional Production, Innovation and Equitable Access, laying the foundations for a greatly expanded and more equitable access to medicines.
Speakers noted also the importance of choice, and of widening access to a range of new technologies, of which lenacapavir is just one. Speakers highlighted important current innovations including 2-monthly injectable cabotegravir and a three-month dapivirine vaginal ring, as well as new technologies currently in the pipeline including a once-a-month pill may move into phase 3 trials next year.
Reinforcing the importance of accelerating access to long-acting medicines, The New England Journal of Medicine has today published an article by UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima, Linda-Gail Becker of the Desmond Tutu HIV Centre, and Matthew Kavanagh of Georgetown University’s Center for Global Health Policy and Politics, entitled “Long-Acting HIV Medicines and the Pandemic Inequality Cycle — Rethinking Access”.
The article showed that the “pandemic inequality cycle” in HIV has usually meant a decade delay between access to breakthrough HIV technologies in the global North and the global South.
In their article the authors write: “The world may look back on 2024 as a pivotal time in the fight against AIDS — the start of a revolution in the global biomedical response to HIV using long-acting antiretroviral medicines. Whether they will do so depends on whether policymakers and pharmaceutical companies avoid repeating past mistakes.”
The authors call for “a nonlinear approach to global access to ARVs that combines far more rapid sharing of technology, decentralized global production, and research and development of products that meet the needs in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean.”
They highlight the need for progress on long-acting treatment as well as prevention and “to break the long-standing pattern of failing to get HIV technologies to the people who need them most, to stop playing catch-up, stop accepting that innovations must reach people in the Global South years late, and use long-acting medicines to help end the pandemic.” The article is available at https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMms2412286
The importance of long-actings, and what is at stake in the discussions on access, was summed up by Jerop Limo, a 26 year old Kenyan activist born living with HIV who is Executive Director of the Ambassador for Youth and Adolescent Reproductive Health Program (AYARHEP):
“Taking a pill every day is not easy. It is a constant reminder of being different, and the stigmatising and shaming we experience because of it can discourage us from taking our medicines.
“This is not just about convenience. Young people living with HIV, and young people at risk of HIV, are clear: with all the pressures we face, long-acting medicines would help us stay on the medicines and help transform, and save, our lives.
“We deserve to live, and to live fully. We can’t have access on paper only. We need access for all people in all countries.
“I am inspired to see leaders coming together to centre communities and to call for access to long-acting HIV medicines. With partnership we can do this. We don’t have time to wait.”
The UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board brings together governments, civil society and the United Nations to help guide the HIV response. UNAIDS sees the development of long-actings as a vital disruptive innovation.
“The arrival of long-acting injections is a game-changer which can help prevent millions of new HIV infections, if we ensure access to all who would benefit from them,” said Ms Byanyima. “Today, in Nairobi, leaders in the global HIV response took a bold and vital step forward on the path to access for all.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




21 October 2024
21 October 2024 21 October 2024In a milestone decision, the Peruvian Congress has passed legislation that extends temporary health insurance coverage to migrants diagnosed with HIV and tuberculosis (TB). This law allows non-resident foreigners to access healthcare services through the public health insurance system (known by the Spanish acronym SIS) while they complete their immigration processes.
This law, which incorporates proposals from Law Bills 5253, 5554, and 7260, represents a significant step in reducing barriers for migrant populations, ensuring timely medical attention without the need for official residency documentation. Now, migrants affected by HIV or TB can receive vital healthcare services, including medical consultations and diagnostic exams, regardless of their immigration status.
The legislative breakthrough follows over two years of advocacy led by the Grupo Impulsor, a coalition that includes UNAIDS, alongside partners such as USAID’s flagship initiative Local Health System Sustainability Project (LHSS), IOM, UNHCR, the Peruvian Observatory of Migration and Health of the Peruvian University Cayetano Heredia (OPEMS-UPCH), Colectivo GIVAR, VENEACTIVA, the Peruvian TB Social Observatory, and Partners in Health.
Likewise, providing timely treatment for migrants with HIV or TB not only improves their quality of life but also reduces the risk of transmission, making it a crucial public health measure benefiting everyone. It also saves money: early care is far more cost-effective, preventing advanced cases that strain the health system.
A cost-benefit analysis reveals that Peru could save around 5 million soles ($1.33 million USD) annually by preventing new infections and another 54 million soles ($14.58 million USD) through avoiding productivity losses linked to AIDS and TB-related deaths.
Migrants living with HIV in Peru remain among the most discriminated groups in the country, with 70.7% reporting stigma, according to the Ministry of Justice and Human Rights. They also face heightened vulnerability due to xenophobia, violence, and exploitation—nearly half of them have experienced physical violence or sexual exploitation. Accessing healthcare is a major challenge, with only 2% of migrants with HIV covered by public health insurance, leaving the rest to pay out-of-pocket costs that many cannot afford.
“By extending health insurance to migrants, Peru is not only addressing these barriers but also aligning with global commitments, like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aimed at eradicating epidemics such as AIDS and TB by 2030”, says Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. “This legislative victory not only marks a turning point in health policy but also sets a precedent for future reforms, ensuring a more inclusive and equitable healthcare system for all.”
Protecting everyone’s rights protects public health.

Statement by Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS, on the occasion of Universal Health Coverage Day
12 December 2021
Winnie Byanyima
Executive Director of UNAIDS
Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations
As we commemorate Universal Health Coverage Day 2021, the world is entering year three of the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic has reminded us that no one is safe until everyone is safe. It shows how pandemics expose intersecting inequalities among people, countries and communities.
Universal health coverage means that all individuals and communities can access the health services they need without suffering financial hardship. But with at least half the world’s population lacking access to essential health services even before the COVID-19 pandemic, there is much work to do.
We must urgently focus on three things:
On this Universal Health Coverage Day, I call for support and urgent action to ensure health and rights for all.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


26 June 2019
26 June 2019 26 June 2019Achieving universal health coverage in a country is an ambitious, but transformative, goal. Communities are essential to the AIDS response and will be essential to the successful roll out of universal health coverage (UHC). When national governments establish a committee to coordinate UHC, it is important to ensure that all relevant communities are involved—civil society, including people living with HIV, should be included in decision-making. If civil society is not engaged early in the development of initiatives for UHC, decisions will be made about health services without the voice of the people most affected by those decisions. The graph below shows four ways in which communities contribute to the design and implementation of UHC.
30 April 2019
The target of achieving universal health coverage is ambitious, but if met could be an important step towards ensuring that all people have good health and that HIV services are available for everyone who needs them. It is essential that efforts to achieve universal health coverage include a fully funded AIDS response and strong community engagement and that they build on the gains in human rights and gender equality made by networks of people living with HIV and key populations —gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, transgender people, people who inject drugs, prisoners and other incarcerated people, migrants, as well as women and adolescent girls.
30 January 2025
21 January 2025
17 December 2024
02 December 2024
26 November 2024


NEW YORK/GENEVA, 3 June 2019—A new report from the United Nations Secretary-General, Galvanizing global ambition to end the AIDS epidemic after a decade of progress, has been presented to United Nations Member States during the 73rd session of the United Nations General Assembly. The Member States gathered at the United Nations in New York, United States of America, to review progress and share their own progress and challenges.
“A world without AIDS was almost unimaginable when the General Assembly held its first special session on the epidemic 18 years ago,” said United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres in the report. “Since then, the global determination to defeat one of history’s greatest health crises has produced remarkable progress … and … inspired a commitment within the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030.”
The Secretary-General’s report shows that results once derided as impossible in low-income settings have now been achieved following a decade of progress in the response to HIV. Between 2008 and 2017, there was a 43% reduction in AIDS-related deaths, a 45% reduction in new HIV infections among children and a 19% reduction in new HIV infections among adults globally. The number of people living with HIV on treatment also increased, by 5.5 times, reaching 21.7 million of the 36.9 million people living with HIV in 2017.
“The enormous achievements in the response to HIV in recent decades, under the strong leadership of UNAIDS, is one of the best examples of multilateralism in action,” said María Fernanda Espinosa, President of the United Nations General Assembly. “It is most definitely an indication of what we can achieve when we work together around a common cause."
The report shows that progress has been most marked in eastern and southern Africa, where AIDS-related deaths fell by 53% and new HIV infections among adults and children fell by 36%. An epidemic that once killed more than a million people in the region per year now claims fewer than 400 000 lives per year.
In other regions of the world, including Latin America, the Caribbean, Asia and the Pacific, western and central Europe and North America, increases in the coverage of HIV testing and treatment services have achieved significant reductions in AIDS-related deaths over the past decade. Most of those regions have also experienced declines in new HIV infections.
Notable exceptions are eastern Europe and central Asia, where the annual number of new HIV infections has risen by 30% since 2010, with an estimated 960 000 people newly infected over this time, and in the Middle East and North Africa, where deaths from AIDS-related illnesses increased by 11%, an estimated 140 000 people newly infected, over the same period.
The report notes that services focused on key populations within those regions are few and far between, and harsh punishments for same-sex sexual relationships, drug use and sex work in those regions and elsewhere are proving to be formidable barriers to the few services that are available.
In western and central Africa, insufficient domestic funding, weak health systems, formal and informal user fees for health care, humanitarian situations and high levels of stigma and discrimination continue to undermine efforts to scale up HIV testing and treatment.
Many challenges remain, including stigma and discrimination faced by people living with HIV and harmful gender norms. Laws and policies in many countries prevent young people, women, key populations―gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, transgender people, people who inject drugs and prisoners and other incarcerated people―indigenous people, migrants and refugees from accessing health and HIV services.
Funding for HIV responses in low- and middle-income countries globally has also remained flat for most of the past five years. In 2017, donor and domestic investments in low- and middle-income countries were US$ 20.6 billion, about 80% of the 2020 target.
“As the Secretary-General’s report makes abundantly clear, to protect the gains we have made and to tackle the challenges that stand in the way of our promise to end AIDS by 2030, we need to firm up our resolve, strengthen our partnerships and say no to complacency,” said Gunilla Carlsson, UNAIDS Executive Director, a.i. “Let’s start with a successful replenishment that results in a fully funded Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria that will enable it, along with its range of partners, including UNAIDS, to continue to deliver evidence-informed, people-centred and human-rights based support to the people and communities who need it the most.”
The report outlines that there is an important opportunity to seize the growing momentum to achieve universal health coverage, a core principle of which is leaving no one behind. Collaboration between health systems and community groups has been shown to reduce stigma and discrimination and to help to deliver services to the people in greatest need―a key recommendation of the report is the strengthening of the vital role that community groups play in the AIDS response.
In the report, the United Nations Secretary-General urges Member States to adopt the following recommendations to galvanize political will, accelerate action and build the momentum necessary to reach the 2020 targets agreed to by the United Nations General Assembly in the 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS: (a) reinvigorate primary HIV prevention; (b) diversify HIV testing and differentiate the delivery of health care to reach the 90–90–90 targets; (c) establish enabling legal and policy environments in order to reach marginalized and vulnerable populations; (d) mobilize additional resources and allocate them where they are most needed; (e) support communities to enable them to play their critical roles; and (f) incorporate a comprehensive HIV response into universal health coverage.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Download the printable version (PDF)


27 May 2019
27 May 2019 27 May 2019“If I want to see the change, I need to be the change,” said Aniz Mitha, the Executive Director of Community Health Rights Advocacy (CHeRA), an organization that works with male sex workers in Malawi. When Mr Mitha speaks of change, he does so with the quiet and unwavering authority of someone who knows what he is talking about.
From a conservative Muslim family in Malawi, Mr Mitha was thrown out of the house at a young age when his parents found out that he was gay. With nowhere to go and no means to support himself, he fled to Johannesburg, South Africa, where he spent many years as a sex worker. “For me, I was looking to survive; I wasn’t thinking about my health,” he said.
When he became ill, he took an HIV test, and he learned that he was living with HIV. Being an illegal immigrant, he couldn’t access health-care services in South Africa. He returned to Malawi, where he began HIV treatment and started CHeRA. “I thought: how can I help others not go through the same experience that I did?” he said.
CHeRA raises awareness and builds the capacity of male sex workers on HIV prevention and treatment, sexual and reproductive health and rights, economic empowerment, psychosocial support and access to justice. Through a UNAIDS funding arrangement, it recently reached more than 250 male sex workers in three priority districts in Malawi, distributed more than 30 000 condoms and lubricant and linked six male sex workers living with HIV to care and treatment. In another programme funded by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, the organization has trained 50 peer educators and distributed more than 6000 condoms and condom-compatible lubricant.
Mr Mitha is keenly aware of the many challenges that face male sex workers, having faced them himself. “In Malawi, sex work is not recognized as work, so there are no laws to protect sex workers. Also, most of our male sex workers are gay men or men who have sex with men, so they live in fear of arrest because homosexuality is illegal in Malawi,” he said.
Stigma and discrimination is institutional, he said. “Male sex workers are not recognized as a key population in the HIV response in Malawi, so we are not prioritized in government plans. And negative attitudes from health-care workers push us away from care.”
“Say I am being abused or beaten and I go to a police station,” continues Mr Mitha, “I will get questions like “Why you are dressed like this or why do you speak like this?” The abuse is institutionalized. It pushes us away, so even in terms of health care, we go to private hospitals where we pay money even if we don’t have money.”
CHeRA is now registered as a nongovernmental organization. Although started in 2016, it was only registered in 2017 after UNAIDS played a pivotal role in amending provisions in the Malawi HIV and AIDS Management Control Act of 2018 that criminalized or discriminated against certain groups, such as sex workers. This paved the way for organizations of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex people and sex workers to be registered.
Like many people who serve others, his work has spilled over into his private life. Knowing what it feels like to be disowned by one’s family, Mr Mitha gives shelter to people who have nowhere else to go, who stay as long as it takes until they can look after themselves.
He has built an unshakeable sense of self, family and community through his work and his life. “I am living openly with HIV and as a gay person; I am a role model to so many. They see that it is possible. I see a lot more people like me opening up and living openly as gay and with HIV,” he said.
Mr Mitha wants to grow CHeRA into an organization that is a strong advocate for equitable access to health care for male sex workers.
“We need more financial support to expand the work we do,” he said. “We provide access to HIV prevention information and services to a population that is being left behind. It is making a difference. When you are working as a community organization, it means what affects my community affects me too,” he said.


16 April 2019
16 April 2019 16 April 2019The Government of Côte d’Ivoire has signalled its commitment to stop people being charged for accessing HIV testing and treatment services, declaring that it will strictly apply previously announced decisions to prevent people living with or affected by HIV being asked to pay user fees.
A note circulated by the Ministry of Health has reminded all service providers that costs for HIV testing and treatment services should not be charged to people accessing those services. The directive applies for all services for pregnant and breastfeeding women, all HIV testing services, tests for viral load suppression and the prescription of antiretroviral medicines for people living with HIV.
The directive also reminds service providers that children under the age of 15 years should have free access to health services and that young women aged 15–24 years should have free access to primary health care, HIV testing and family planning services.
In several countries, the issue of user fees has been identified as a major barrier to testing people for HIV, to treating people living with HIV and to retaining people in treatment and care.
The renewed commitment of Côte d’Ivoire to confront the issue of user fees followed discussions between the President of Côte d'Ivoire, Alassane Ouattara, and the former President of Botswana, Festus Mogae, who visited the country in March in his capacity as Chairperson of the Champions for an AIDS-Free Generation in Africa.
Following their discussions, the government also announced its intention to increase domestic funding for the AIDS response by US$ 10 million in the next budget.
During his meeting with the President, Mr Mogae congratulated Mr Ouattara and the First Lady, Dominique Ouattara, for their personal commitment to ending the AIDS epidemic as a public health threat by 2030. Ms Ouattara is UNAIDS Special Ambassador for the Elimination of Mother-to-Child Transmission and the Promotion of Paediatric Treatment of HIV.
At the conclusion of his mission, Mr Mogae underlined the importance of accelerating the response to the epidemic. “We cannot be complacent and allow the huge improvements that we have made so far to be lost. If we stop now, we will lose everything we have already invested and achieved. The entire nation must be mobilized to ensure that no one is left behind,” he said.
There were 500 000 people living with HIV in Côte d’Ivoire in 2017, with around 46% accessing HIV treatment.

27 February 2025

19 February 2025





08 March 2019
08 March 2019 08 March 2019Momentum for Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Africa is building and many African countries have already integrated UHC into their national health strategies. But with 11 million Africans pushed into extreme poverty each year because of out-of-pocket health expenses, how can Africa achieve UHC which delivers a quality package of care for people living in Africa?
The UHC debate was buzzing in Rwanda’s capital Kigali this week during one of the largest health gatherings in Africa, the Africa Health Agenda International conference 2019. Co-hosted by the Ministry of Health of Rwanda and the African Medical and Research Foundation (Amref Health Africa), 1500 health leaders shared new ideas and home-grown solutions to the continent’s most pressing health challenges.
Participants discussed the need for countries to embrace the concept of UHC and do their utmost to make it work. They stressed that good health allows children to learn and adults to contribute to societies and the economy. They also underscored that it can allow people to emerge from poverty and provides the basis for long-term economic security, essential for the future of the continent.
Host country President, Paul Kagame was awarded the honour of excellence in recognition of his political leadership on UHC. In a tweet he thanked Amref saying, “We owe this progress to partners like you who have joined forces with us in our journey to deliver a dignified and healthy life for all Rwandans.” The Minister of Health of Ethiopia also received an award for Ethiopia’s work in promoting primary health care.
Ensuring that everyone has access to basic health services is a challenge and the key to the success of UHC will be ensuring that the quality of services is good enough to improve the health of the people who access them.
“We need to track the impact of UHC,” said Michel Sidibé, co-moderating a high-level ministerial panel. “Coverage is not enough, we need to be delivering quality, affordable, accessible services to all. The ultimate measure of success for UHC will be whether the poorest, the marginalized and the most vulnerable people are able to benefit.”
During the conference Mr Sidibé participated in a townhall with young people. He spoke to them about their meaningful engagement in the UHC process saying that young people need to ‘claim and own the space.’ He also talked to civil society groups about the remarkable progress towards achieving the UNAIDS 90-90-90 treatment targets across Africa and of the critical need of their continued engagement on HIV within UHC.
The first ever United Nations High-Level Meeting on Universal Health Coverage will take place on 23 September 2019 during the United Nations General Assembly under the theme ‘Universal Health Coverage: Moving Together to Build a Healthier World.’