PLHIV


Feature Story
Haiti’s crisis exacerbates vulnerability of people living with and affected by HIV. UNAIDS committed to continuing to provide support to people in need.
27 March 2024
27 March 2024 27 March 2024The humanitarian crisis in Haiti is exacerbating the vulnerability of people living with or affected by HIV, particularly women, girls, and key populations. The situation has deepened existing inequalities, and multiplied the risks faced by marginalised communities. In the face of this adversity, UNAIDS continues to work with partners to ensure that people living with or affected by HIV have access to life-saving HIV services, including treatment and prevention services.
For example, in the West Department, over 50,000 people are receiving antiretroviral treatment and are at high risk of disruption. HIV prevention and health care services also face disruption. The recent violence continues to leave thousands of families traumatized. Thousands of people now find themselves unsafe and exposed to all types of risks. Displaced people and vulnerable populations need emergency aid and safe, protected spaces.
"Communities already at risk of HIV in Haiti have been made even more vulnerable, and people living with HIV are facing greater challenges in accessing treatment and care", said UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean, Luisa Cabal. "Together with all the United Nations agencies, and with partners, UNAIDS is advocating for safe and unhindered humanitarian access, and the protection health facilities and health workers."
The situation in Haiti is dire, with over 5.5 million people in need of assistance, including more than three million children. The World Food Programme has noted that around 1.4 million Haitians are "one step away from famine." The UN Humanitarian Coordinator for Haiti has noted that the humanitarian response plan is only six percent funded. Less than half of the health facilities in Port-au-Prince are functioning at their average capacity, and there is a pressing need for safe blood products, anesthetics, and other essential medicines.
In the face of these challenges, UNAIDS and its Cosponsors, together with the United States President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, and the Observatory of Civil Society for HIV/TB/Malaria are supporting Haiti’s National AIDS Program.
UNAIDS has been working with the Ministry of Health and Population Unit for Management of Health Emergencies to support HIV treatment delivery. This support includes programmes to provide a broad package of support to affected communities. For example, together with the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and in collaboration with the Organisation de Développement et de Lutte contre la Pauvreté (ODELPA), UNAIDS supports girls and women who are survivors of gender-based violence by training community leaders and granting empowerment funds for women and men's income-generating activities.
"We are working to ensure that people living with HIV have continuity of antiretroviral treatment as well as access to essential needs, especially including the most vulnerable people across the most affected areas," explains Christian Mouala, UNAIDS Country Director for Haiti. "UNAIDS remains committed to not let the humanitarian crisis disrupt the progress that has been made in the HIV response. The United Nations stand together to support the people of Haiti."
Region/country
Related
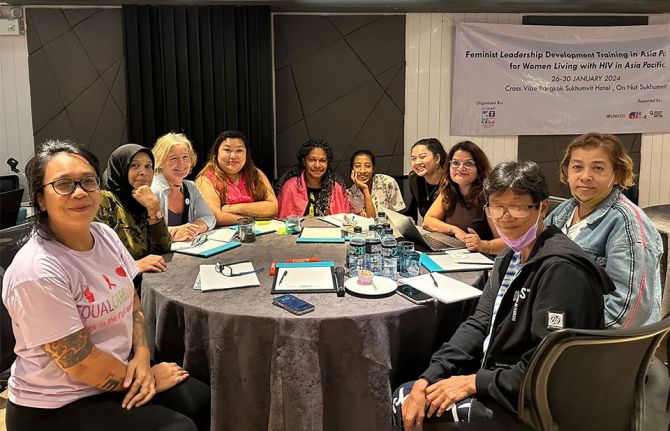




Feature Story
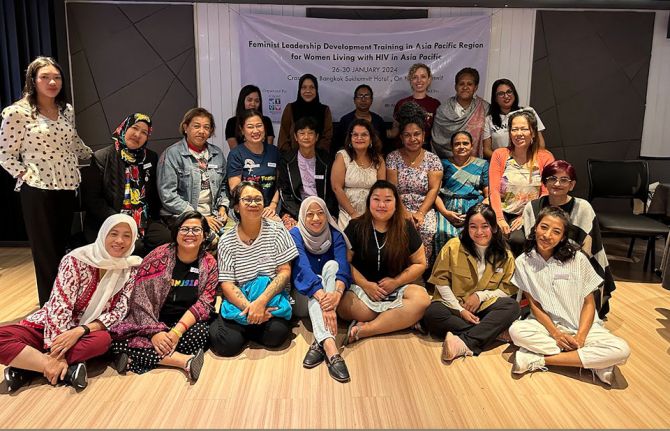
Asia Pacific women living with HIV build their power through Feminist School
08 March 2024
08 March 2024 08 March 2024One-third of people living with HIV in Asia and the Pacific are women. But their issues are often hidden.
Gender-based violence. Restricted economic opportunities. Child marriage. Underage pregnancy. Denial of property rights.
A UNAIDS-supported initiative by the International Community of Women Living with HIV Asia and Pacific (ICWAP) supports positive women’s organising. The Feminist School is a learning and consciousness raising programme that began in South Africa, and has been utilised in Asia-Pacific since 2016. The methodology, anchored in feminist principles, is specifically designed to enable women living with HIV to understand their personal experiences, locate them politically and develop strategies for community-driven advocacy.
“Marching in the month of March is not enough to realize women’s rights,” insists ICWAP Regional Director, Sita Shahi. “We need to speak up on the issue of gender inequality in the HIV response and the need for increased investments in women and girls. Women and girls living with HIV are going through serious human rights violations that, in turn, undermine their right to health.”
The Feminist School brings together women living with HIV, women from key populations, and young women from across the region. In the past two years, with support from UNAIDS, ICWAP has made adaptations to include modules on sexual and reproductive health and rights, movement building, leadership skills and the elimination of mother-to-child transmission (EMTCT).
“Feminist leadership training reveals the challenges faced by women living with HIV in the region. I have gained a lot of knowledge from the cross-country discussions and learned lessons about how women from different countries are breaking down human rights-related barriers, including stigma and discrimination,” said Salina from Malaysia.
Last year, a new module on the Global Fund processes was added.
“We recognized the importance of ensuring that interventions led by women living with HIV are included in Global Fund funding requests,” explained UNAIDS Asia Pacific Regional Adviser for Community-Led Responses, Michela Polesana.
UNAIDS supported a Global Fund Grant Cycle Seven (GC7) project focused on supporting the engagement of networks of women living with HIV in Cambodia, India, Thailand and Viet Nam in the current process. It found that organizations in these countries were at different stages of readiness and involvement. For example, India’s Positive Women Network (PWN+) was already participating in the process and benefitted from ICWAP’s technical support to strengthen their advocacy and organization.
Another UNAIDS-supported strategy ICWAP employed to bolster GC7 engagement was the facilitation of peer-to-peer growth by and for women living with HIV through the roll-out of an online Feminist School training. Through this initiative, country networks were supported in engaging in the Global Fund process and learned about its gender equality strategy, including the gender equality markers (GEM). They also received training to support them in their work to hold governments accountable.
The organization partnered with Ikatan Perempuan Positif Indonesia (IPPI), the Thai Positive Women’s Network, Viet Nam’s Women’s Network, the Association of Positive Women Advocates Inc (APWAI) from the Philippines, Women affected by HIV and AIDS (WABHA) from Papua New Guinea and an informal network of women living with HIV in Cambodia.
The groups identified priority issues for advocacy and recommendations for next steps and devised country-specific advocacy plans.
The advocates agreed on a set of three shared priorities. First, a seat for women living with HIV on each Country Coordinating Mechanism. Second, for positive women networks to reclaim antenatal care activities in prevention of mother-to-child transmission programmes. And finally, for capacity building for young positive women leaders.
Feminist school is helping women living with HIV to organize to secure their human rights. To protect women’s health it is vital to protect women’s rights. And to protect women’s rights it is vital to support women’s leadership.
“This is all about bridging the gap between outgoing leaders and an incoming, new generation,” Ms. Shahi said.
Related


Feature Story
Tajikistan takes a positive step towards decriminalization of HIV exposure and transmission
30 January 2024
30 January 2024 30 January 2024In an important decision of the Plenum of the Supreme Court on December 26, 2023, Tajikistan has marked a significant step towards decriminalization of HIV exposure and transmission in its pursuit of justice for people living with or affected by HIV.
Through a new resolution, the courts are asked to examine more objectively issues related to criminal liability for HIV exposure and transmission under Article 125 of the Criminal Code. The resolution obliges judicial practice to be based on new norms that take into account international standards and recommendations including the Undetectable = Untransmittable concept endorsed by UNAIDS and WHO which asserts that people who are living with HIV who are on antiretroviral treatment and have an undetectable viral load cannot transmit HIV.
Article 125 of the Criminal Code currently criminalizes HIV transmission and exposure with a penalty of up to two years’ imprisonment (Part 1), while transmission by someone aware of their status is penalized with two to five years’ imprisonment (Part 2), increased to five to ten years’ when committed against multiple people or a minor (Part 3).
In some cases, decisions were made solely based on a person’s HIV-positive status, criminalizing people living with HIV rather than ensuring access to HIV services, treatment and support.
More than 70% of people convicted under Article 125 have been women living with HIV. Women living with HIV may be subjected to domestic violence, stigma, and discrimination and do not seek justice in courts, due to the fear of accidental disclose of their HIV status and further criminal prosecution.
“This new resolution is encouraging because it allows for more fair interpretation of existing laws (which is very important) but it does not establish new laws or change the Criminal Code which still criminalizes HIV exposure and transmission. Therefore, it is important to continue advocacy to change the Criminal Code and decriminalize HIV transmission and exposure.” said Tahmina Haidarova, Head of the Network of Women Living with HIV in Tajikistan.
The new move towards a more just legal framework has been the result of collaborative efforts of the Supreme Court and civil society organizations, as well as long-term advocacy of UNAIDS, UNDP, and the Global Fund to fight AIDS, TB and Malaria that reflects a holistic and inclusive approach to addressing the complexities of HIV-related legal matters.
The consequences of a punitive approach, where law enforcement takes precedence over medical professionals, has contributed to the growth of the HIV epidemic in Tajikistan - the number of new HIV infections has increased by 20% over the past 10 years. The percentage of new HIV cases among women has also grown - from 31% in 2011 to 36% in 2022.
International partners, including UNAIDS, UNDP, and the Global Fund, echo the call to repeal laws criminalizing HIV. The negative impact of such legislation on HIV testing rates and adherence to treatment cannot be overstated. An evidence-based approach is crucial for fostering a healthier society.
“Tajikistan's move towards HIV decriminalization marks a positive step towards commitment to justice, inclusivity, and public health,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia-Pacific and Eastern Europe and Central Asia. “This journey is guided by the principles of compassion, cooperation, and evidence-based policymaking. UNAIDS, together with partners, welcomes the efforts of the Supreme Court to reduce prosecution and humanize the judicial system. UNAIDS will continue to support the country in its journey to fulfil the human rights of all people living with HIV.”
Resources
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV programmes in Tajikistan
Status of HIV programmes in Tajikistan

05 March 2025
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025
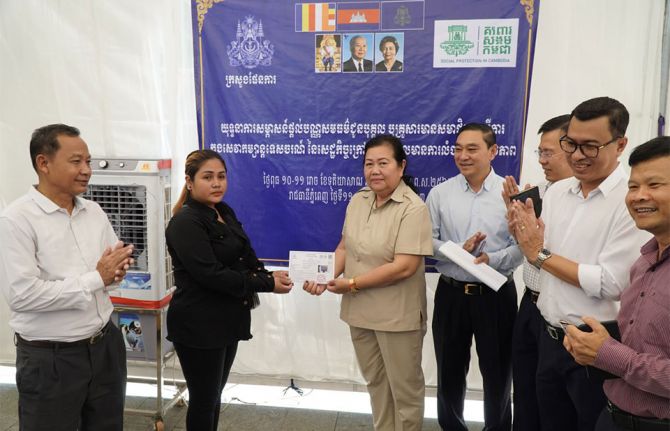
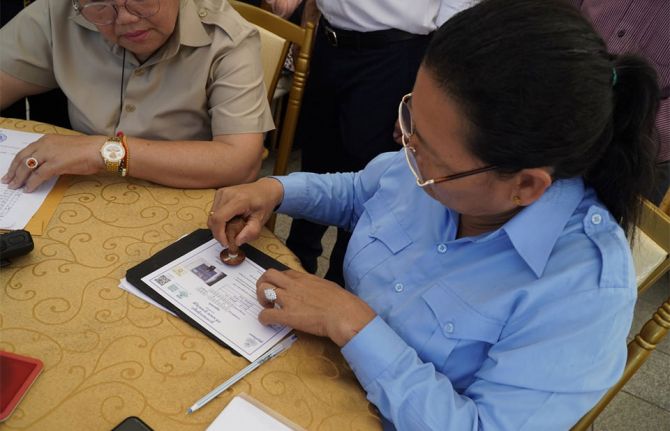
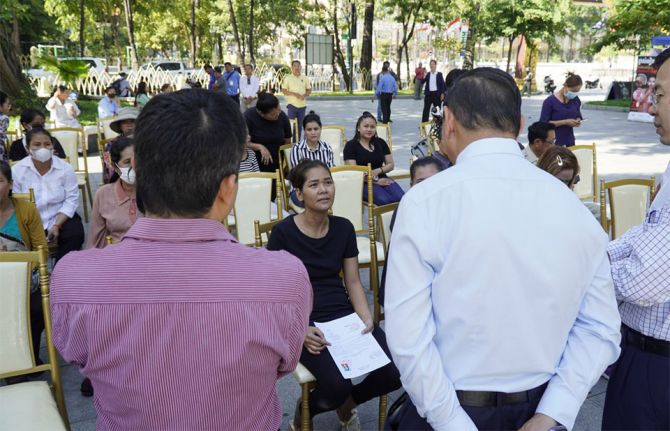




Feature Story
Cambodia social protection for people living with HIV
15 December 2023
15 December 2023 15 December 2023Imagine this: you’re a person living with HIV, and your household is facing financial hardship. You decide to run a small grocery business at home, keeping your status hidden. Despite accessing free HIV treatment, you cannot afford other essential health services. And when you need to buy medicine, you don't have enough for your children’s school supplies or nutritious meals.
Low incomes.
Unaffordable healthcare.
Employment insecurity due to HIV-related stigma and discrimination.
These realities create financial hurdles for the poor among people living with HIV and the key populations—gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender women, sex workers and people who inject drugs.
In Cambodia, stakeholders are working to ensure that the social protection safety net specifically covers people living with, and at risk of contracting, HIV.
“People living with HIV do not only need medication, but also food. If we provide only the drugs they will not survive,” said Tia Phalla, Deputy Director of Cambodia’s National AIDS Authority (NAA). He explained that nutrition support and other non-health related care are an integral part of the national policy for responding to HIV.
Cambodia is among the countries that are on-track to reach the 2025 Global AIDS Strategy testing and treatment targets. As of the end of 2022, an estimated 86% of people living with HIV in Cambodia were aware of their status. Impressively, more than 98% of diagnosed people were receiving treatment and 98% of those on treatment achieved a suppressed viral load last year.
The country hopes to further improve these results while enhancing the quality of life of people living with HIV.
“A key part of the strategy we have advocated for is to include HIV sensitivity in social protection schemes and programmes,” explained Patricia Ongpin, UNAIDS Country Director for Cambodia, Lao PDR and Malaysia. Individuals and families affected by HIV can now benefit from a range of programmes including cash transfer, food assistance, social health protection and scholarships.
Once a person living with HIV registers their household for an Equity Card, they are entitled to monthly stipends. The card also gives holders access to additional medical care. This frees individuals and families from having to choose between healthcare and expenses for other essentials such as education and food.
In 2019 Cambodia officially included people living with HIV in its IDPoor mechanism. This is a system to identify and register households living in poverty. This was followed by the HIV and Social Protection Assessment, conducted in 2020 by UNAIDS and the NAA.
“The assessment made it clear that promoting HIV-sensitive social protection could help reduce the risk of HIV, increase demand for HIV prevention services, and promote HIV testing and safe sexual behaviors, as well as adherence to treatment,” said Ms Ongpin.
To ensure a more inclusive approach for IDPoor registration there must be engagement from key stakeholders including government, local authorities, development partners, and civil society organizations.
With support from UNAIDS and UNDP, Cambodia’s Ministry of Planning launched a web-based system and mobile application for IDPoor registration in December 2022. This approach makes it easier for individuals living with HIV to register at their treatment centers. As of August this year, more than 13,600 people living with HIV have been enrolled.
By leveraging this technology-driven approach, people living with HIV feel confident revealing their HIV status and are empowered to access much-needed healthcare benefits with dignity and autonomy. The solution can also be used to register people from key population communities at risk of contracting HIV.
Community leadership is a key strategy for expanding the initiative’s reach. The Joint Forum of Networks of People Living with HIV and key populations (DFoNPAM) coordinates with the Department of Planning at district level in order to help with IDPoor registration.
One initiative specifically targeted female entertainment workers. A national registration campaign was co-organized by the Ministry of Planning, the Phnom Penh City Hall, and the NAA, with technical assistance from UNAIDS. Around five dozen workers registered during the two-day campaign, receiving Equity Cards for their households.
According to the UNAIDS Country Director, this inclusive approach is key to creating a better future for people living with HIV and key populations.
“To mobilize their participation and register them for Equity Cards, we need to understand the barriers. And to understand the barriers, we need to listen to their experiences, in their own words. By taking this step, people living with HIV and key populations can help shape the conversation and ensure that their voices are heard,” Ms Ongpin ended.
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
Seeking justice for HIV-related discrimination in the workplace in Guatemala
18 December 2023
18 December 2023 18 December 2023In the heart of the bustling Guatemala City, Juan used to face the daily grind of life with an unwavering spirit. He had been diagnosed with HIV several years ago and had learned to manage his health effectively. As a dedicated employee at a marketing firm, he poured creativity into every project he touched.
Life seemed to be on an upswing for him until an unexpected turn of events unfolded at the workplace. A colleague stumbled upon Juan's medical records and, in a breach of privacy, discovered his HIV status. Soon, whispers spread through the office, and Juan began to feel the cold stares and hushed conversations whenever he walked by. Ultimately, he was dismissed from his company for "restructuring reasons."
As the discrimination became more blatant, Juan decided it was time to take action. He sought advice from Líderes Profesionales, a network of lawyers specializing in discrimination cases for people living with HIV. With UNAIDS's support, this network is committed to fighting for justice and equality for marginalized communities.
Upon hearing Juan's story, the lawyers at Líderes Profesionales were appalled by the flagrant violation of privacy and the subsequent discrimination. They quickly assembled a legal team dedicated to ensuring justice for Juan. The lawyers explained the legal protections in place for individuals with HIV, emphasizing that workplace discrimination based on health status is a clear violation of the law.
Together with Juan, the legal team initiated a lawsuit against the firm. They filed a complaint citing violations of privacy, discrimination, and failure to provide a safe and inclusive work environment and asked for payment of benefits and compensation for unjustified dismissal.
Líderes Profesionales worked tirelessly to expose Juan's unjust treatment, seeking justice for him and advocating for broader change in workplace policies. They organized workshops to sensitize companies, urging them to implement comprehensive diversity and inclusion training and policy.
As of December 2023, the case is still ongoing. The legal team's goal is to seek compensation for Juan and foster an environment where such discrimination would not be tolerated in the future.
"Juan's experience and five other discrimination-related workplace cases this year inspire us to continue our advocacy work," says Julio Rodríguez, Director of Líderes Profesionales. "We redouble our efforts to support individuals facing discrimination, using each case as an opportunity to raise awareness and push for systemic change."
In Guatemala, 31,000 people are estimated to be living with HIV. HIV-related stigma and discrimination are still pervasive. According to the latest National Stigma Index (2017), 14% of people living with HIV reported losing their job or source of income due to their positive status for HIV, and 13% of people living with HIV reported being denied employment or opportunity to work because of HIV.
"Having access to legal support really represented a turning point for Juan. Empowered by it, he is a more vocal advocate for HIV awareness and anti-discrimination efforts," says Marie Engel, UNAIDS Country Director for Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua. "Through his journey, Juan contributes to a more just and inclusive society for all."
Let communities lead
Region/country
Related
Documents
Summary — Let Communities Lead — UNAIDS World AIDS Day report 2023
28 November 2023
This report is not only a celebration of the critical role of communities. It is a call to action to decision-makers to fully support the life-saving work of communities and to clear away the barriers that stand in their way. Press release | Full report | Fact sheet | World AIDS Day 2023
Related
 UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day
UNAIDS calls for rights, equality and empowerment for all women and girls on International Women’s Day

06 March 2025
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025


Press Release
Ahead of World AIDS Day UNAIDS is calling for urgent support to Let Communities Lead in the fight to end AIDS
30 November 2023 30 November 2023A new report by UNAIDS demonstrates the critical role communities play, and how underfunding and harmful barriers are holding back their lifesaving work and obstructing the end of AIDS.
LONDON/GENEVA, 28 November 2023—As World AIDS Day (1 December) approaches, UNAIDS is urging governments across the world to unleash the power of grassroots communities across the world to lead the fight to end AIDS. A new report launched today by UNAIDS, Let Communities Lead, shows that AIDS can be ended as a public health threat by 2030, but only if communities on the frontlines get the full support they need from governments and donors.
“Communities across the world have shown that they are ready, willing and able to lead the way. But they need the barriers obstructing their work to be pulled down, and they need to be properly resourced,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Too often, communities are treated by decision-makers as problems to be managed, instead of being recognised and supported as leaders. Communities are not in the way, they light the way to the end of AIDS.”
The report, launched in London during a World AIDS Day event organized by the civil society organization STOPAIDS, shows how communities have been the driving force for progress.
Community advocacy from the streets to the courtrooms to parliaments has secured groundbreaking changes in policy. Communities’ campaigning helped open up access to generic HIV medicines, leading to sharp, sustained reductions in the cost of treatment from US$ 25 000 per person per year in 1995 to less than US$ 70 in many countries most affected by HIV today.
Let Communities Lead shows that investing in community-led HIV programmes delivers transformational benefits. It sets out how programmes delivered by community-based organizations in Nigeria were associated with a 64% increase in access to HIV treatment, a doubling of the likelihood of HIV prevention service utilization, and a four-fold increase in consistent condom use among people at risk of HIV. It also notes how, among sex workers reached by a package of peer-based services in the United Republic of Tanzania, the HIV incidence rate was reduced to below half (5% vs 10.4%).
“We are the vehicle for change that can end systematic injustices that continue to fuel HIV transmission. We have seen groundbreaking developments with U=U, improved access to medicines, and have made great strides in decriminalisation," said Robbie Lawlor, Co-Founder of Access to Medicines Ireland. “Yet, we are expected to move mountains without being financially supported. We are supposed to fight for a more equitable world and are tasked with dismantling stigma yet are side-lined in crucial discussions. We are at a tipping point. Communities can no longer be relegated to the periphery. The time for leadership is now.”
The report highlights how communities are at the forefront of innovation. In Windhoek, Namibia, a self-funded project by the youth Empowerment Group is using e-bikes to deliver HIV medicines, food and adherence support to young people who often cannot attend clinics due to their schooling hours. In China, community organizations developed smartphone apps that link people to self-testing which contributed to a more than four-fold increase in HIV tests across the country from 2009 to 2020.
The report reveals how communities are also holding service providers to account. In South Africa five community networks of people living with HIV inspected 400 sites across 29 districts and conducted more than 33 000 interviews with people living with HIV. In the Free State province, these findings led provincial health officials to implement new appointment protocols to reduce clinic wait times and three- and six-month dispensing of antiretroviral medicines.
“I am extremely concerned about the exclusion from health services of key populations like the LGBT+ community,” said Andrew Mitchell, Minister of State for Development and Africa. “The UK champions the rights of such communities, and we will continue to protect them, working closely with our partners in civil society. I thank UNAIDS for keeping us focused on the inequities driving the pandemic and I look forward to working with our partners to champion the voice of people living with HIV and end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.”
Despite the clear evidence of community-led impact, community-led responses are unrecognized, under-resourced and in some places even under attack. Crackdowns on civil society and on the human rights of marginalized communities are obstructing communities from providing HIV prevention and treatment services. Underfunding of community-led initiatives is leaving them struggling to continue operating and holding them back from expansion. If these obstacles are removed, community-led organizations can add even greater impetus to end AIDS.
In the 2021 Political Declaration on ending AIDS, United Nations member states recognized the critical role communities play in HIV service delivery, particularly to people most at risk of HIV. However, whereas in 2012, when over 31% of HIV funding was channelled through civil society organizations, ten years later, in 2021, only 20% of funding for HIV was available—an unprecedented backsliding in commitments which has cost and is continuing to cost lives.
“At this time, community-led action is the most important countermeasure in the AIDS response,” said Solange Baptiste, Executive Director of the International Treatment Preparedness Coalition. “Yet, shockingly, it isn’t a cornerstone of global plans, agendas, strategies, or financing mechanisms for improving pandemic preparedness and health for all. It is time to change that.”
Every minute, a life is lost to AIDS. Every week, 4000 girls and young women become infected with HIV, and out of the 39 million people living with HIV, 9.2 million do not have access to lifesaving treatment. There is a Path that Ends AIDS and AIDS can be ended by 2030, but only if communities lead.
UNAIDS is calling for: Communities’ leadership roles to be made core in all HIV plans and programmes; Communities’ leadership roles to be fully and reliably funded; And for barriers to communities’ leadership roles to be removed.
The report features nine guest essays from community leaders, in which they share their experience on the achievements they have secured, the barriers they face, and what the world needs to end AIDS as a public health threat.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
communications@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Michael Hollingdale
tel. +41 79 500 2119
hollingdalem@unaids.org
World AIDS Day message
World AIDS Day 2023
Watch the launch
World AIDS Day report
World AIDS Day videos




Feature Story
Young role models combat HIV stigma in Central Asia
22 June 2023
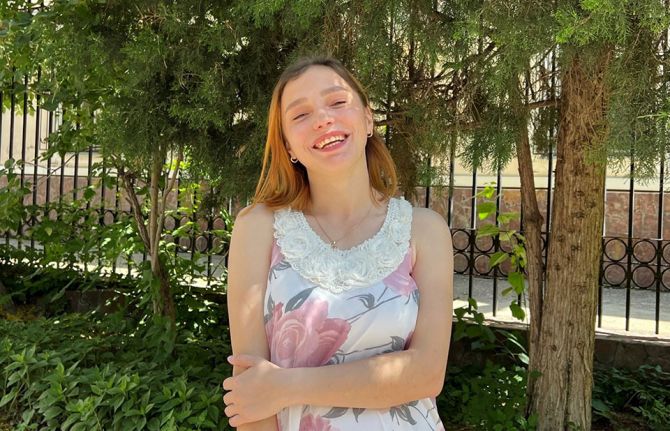
22 June 2023 22 June 2023Last year, Elina Kruglova made a bold decision. She disclosed her HIV status during the casting of a popular reality TV show in Uzbekistan.
“I disclosed my status right at the casting because the project lasted for several months, and I needed to take medicine daily,” she said. “I made the decision to be honest and mustered up the courage. I thought they wouldn't accept me, but I passed the casting," Ms Kruglova explained.
In her second-year student in the Faculty of Agricultural Economics at Tashkent State Agrarian University in Uzbekistan, she grew up in an orphanage. She was the first child living with HIV in her country to start antiretroviral (ARV) therapy seventeen years ago. Despite facing stigma, she has been taking life-saving medicine daily.
Uzbekistan struggles with HIV-related stigma and discrimination.
According to the recent Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) in Uzbekistan, 76% of women aged 15-49 in the country would refuse to purchase vegetables from a vendor living with HIV and would not accept children living with HIV attend school with other children. Prejudice is fuelled by a lack of knowledge; only 14% of women in the same age group possess comprehensive information about HIV. Uzbekistan's HIV cases have steadily risen by 44 % in the last six years (31,088 in 2016 to an estimated 45,000 in 2022.)
Throughout the TV show, Ms Kruglova shared her experiences of being an orphan and living with HIV. Over time she became an inspiration for young people and those living with HIV.
"When the TV episode aired, I started contemplating how people would perceive me, what they would say, and how they would react,” she recalled. “Psychologists were working with us during the project, which made it easier for me to handle the pressure."
To her surprise, people positively reacted when they recognized her on the streets, and she received numerous supportive messages from people living with HIV via Instagram.
"I am grateful for the trust they placed in me " she said.
For her, the Tashkent day-care center for children and families affected by HIV supported by UNICEF and UNAIDS played a crucial role in her life. It provided a safe haven, gave guidance throughout her childhood and teenage years. The center's support group, the professional consultations, and master classes helped her develop practical life skills. She is optimistic about the future and believes that people can change their attitudes towards HIV with the right information and education. In her mind, hiding only makes things worse.
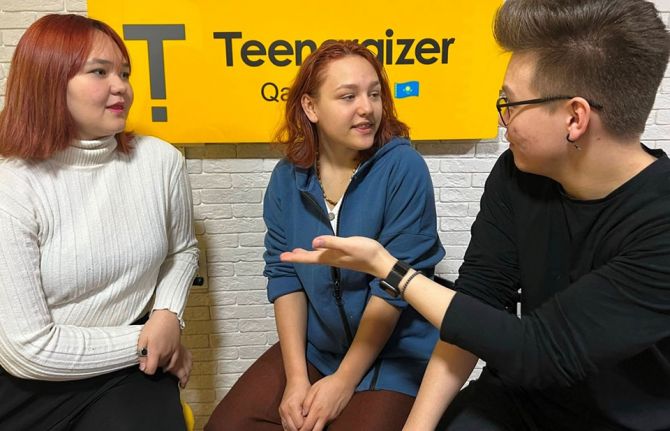
Aida Muravyova knows all about the power of disclosing her HIV status.
She is a 16-year-old school student in Kazakhstan and learned about her HIV status when she was 6 years old. Although advised against disclosing her status at school and extracurricular activities, Aida chose a different path. She shared her HIV status with her classmates in school and took on the role of breaking down the myths and misconceptions surrounding HIV in front of her peers and adults.
“When I was told about my HIV diagnosis, I thought to myself, 'Okay, I have red hair, I have HIV, I take pills... what else?!'"
Ms Muravyova found solace through the Teenergizer Movement, a youth-led initiative supported by the Kazakhstan Government, UNICEF, UNAIDS and other donors. Teenergizer aims to empower young people living with HIV. It created a safe space for young women like her to connect, have fun, and share experiences without shame or stigma. The movement has reached many young people in the country, creating a ripple effect of reliable information and support.
When Teenergizer came along, Ms Muravyova invited classmates to join. "They got valid information, learned with me, and even conducted training sessions,” she said. “The most gratifying part was when one of my classmates' mothers, initially frightened by my HIV status, learned about HIV through her child's participation in Teenergizer.”
Her friend told her that her family had an open conversation, hashed out concerns, and now everything is okay.
Gender assessments conducted in several countries of Central Asia, including Kazakhstan, confirmed that gender inequality, stereotypes, customs and practices increase women’s vulnerability to HIV as well as limit their choices and expose them to socioeconomic and health difficulties.
Ms Muravyova refuses to let her HIV status define her or limit her dreams.. "I have seen many people living with HIV, but never in my field of Electrical and Aerospace Engineering... I want to change that perception and demonstrate that living with HIV can be different, cool, and interesting."
The UNAIDS Regional Policy and Equality Officer in Central Asia, Elena Kiryushina, sees role models like Elina and Aida as well as community networks as key.
“Promoting leadership among adolescent girls and young women, fostering positive masculinities in boys and men, providing care and support to adolescents living with HIV, especially those who lost parents and access to comprehensive sexuality education in and out of schools, and supporting gender-transformative approaches are essential steps to address HIV and gender-related stigma and to build foundation for the gender equality in Central Asia and beyond,” she said.
UNAIDS and partners believe empowering women and girls and challenging cultural norms is crucial to address HIV stigma and ensure equal access to support and health services.
Ms Muravyova has one mantra. “Speak, and don't be afraid!,” she said. “We are together, and together we'll make it through.”
Region/country
Related
Documents
Executive summary — The path that ends AIDS: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2023
13 July 2023
This report makes clear that there is a path to end AIDS. Taking that path will help ensure preparedness to address other pandemic challenges, and advance progress across the Sustainable Development Goals. The data and real-world examples in the report make it very clear what that path is. It is not a mystery. It is a choice. Some leaders are already following the path—and succeeding. It is inspiring to note that Botswana, Eswatini, Rwanda, the United Republic of Tanzania and Zimbabwe have already achieved the 95–95–95 targets, and at least 16 other countries (including eight in sub-Saharan Africa) are close to doing so. Also available: Additional resources (regional and thematic factsheets) | Annex 1: Progress towards the 2025 targets | Annex 2: Methods | Slide set | Press release | Microsite
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025


Press Release
New report from UNAIDS shows that AIDS can be ended by 2030 and outlines the path to get there
13 July 2023 13 July 2023GENEVA, 13 July 2023—A new report released today by UNAIDS shows that there is a clear path that ends AIDS. This path will also help prepare for and tackle future pandemics and advance progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. The report, ‘The Path that Ends AIDS’, contains data and case studies which highlight that ending AIDS is a political and financial choice, and that the countries and leaders who are already following the path are achieving extraordinary results.
Botswana, Eswatini, Rwanda, the United Republic of Tanzania, and Zimbabwe have already achieved the “95-95-95” targets. That means 95% of the people who are living with HIV knowing their HIV status, 95% of the people who know that they are living with HIV being on lifesaving antiretroviral treatment, and 95% of people who are on treatment being virally suppressed. A further 16 other countries, eight of them in sub-Saharan Africa, the region which accounts for 65% of all people living with HIV, are also close to doing so.
“The end of AIDS is an opportunity for a uniquely powerful legacy for today’s leaders,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “They could be remembered by future generations as those who put a stop to the world’s deadliest pandemic. They could save millions of lives and protect the health of everyone. They could show what leadership can do.”
The report highlights that HIV responses succeed when they are anchored in strong political leadership. This means following the data, science, and evidence; tackling the inequalities holding back progress; enabling communities and civil society organizations in their vital role in the response; and ensuring sufficient and sustainable funding.
Progress has been strongest in the countries and regions that have the most financial investments, such as in eastern and southern Africa where new HIV infections have been reduced by 57% since 2010.
Thanks to support for and investment in ending AIDS among children, 82% of pregnant and breastfeeding women living with HIV globally were accessing antiretroviral treatment in 2022, up from 46% in 2010. This has led to a 58% reduction in new HIV infections among children from 2010 to 2022, the lowest number since the 1980’s.
Progress in the HIV response has been strengthened by ensuring that legal and policy frameworks do not undermine human rights, but enable and protect them. Several countries removed harmful laws in 2022 and 2023, including five (Antigua and Barbuda, the Cook Islands, Barbados, Saint Kitts and Nevis, and Singapore) that have decriminalized same-sex sexual relations.
The number of people on antiretroviral treatment worldwide rose almost fourfold, from 7.7 million in 2010 to 29.8 million in 2022.
However, the report also sets out that ending AIDS will not come automatically. AIDS claimed a life every minute in 2022. Around 9.2 million people still miss out on treatment, including 660 000 children living with HIV.
Women and girls are still disproportionately affected, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. Globally, 4,000 young women and girls became infected with HIV every week in 2022. Only 42% of districts with HIV incidence over 0.3% in sub-Saharan Africa are currently covered with dedicated HIV prevention programmes for adolescent girls and young women.
Almost one quarter (23%) of new HIV infections were in Asia and the Pacific where new infections are rising alarmingly in some countries. Steep increases in new infections are continuing in eastern Europe and central Asia (a rise of 49% since 2010) and in the Middle East and North Africa (a rise of 61% since 2010). These trends are due primarily to a lack of HIV prevention services for marginalized and key populations and the barriers posed by punitive laws and social discrimination.
Funding for HIV also declined in 2022 from both international and domestic sources, falling back to the same level as in 2013. Funding amounted to US$ 20.8 billion in 2022, far short of the US$ 29.3 billion needed by 2025.
There is an opportunity now to end AIDS by increasing political will by investing in a sustainable response to HIV through financing what matters most: evidence-based HIV prevention and treatment, health systems integration, non- discriminatory laws, gender equality, and empowered community networks.
“We are hopeful, but it is not the relaxed optimism that might come if all was heading as it should be. It is, instead, a hope rooted in seeing the opportunity for success, an opportunity that is dependent on action,” said Ms Byanyima. “The facts and figures shared in this report do not show that as a world we are already on the path, they show that we can be. The way is clear.”
In 2022, an estimated:
- 39.0 million people globally were living with HIV
- 29.8 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy
- 1.3 million people became newly infected with HIV
- 630 000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.