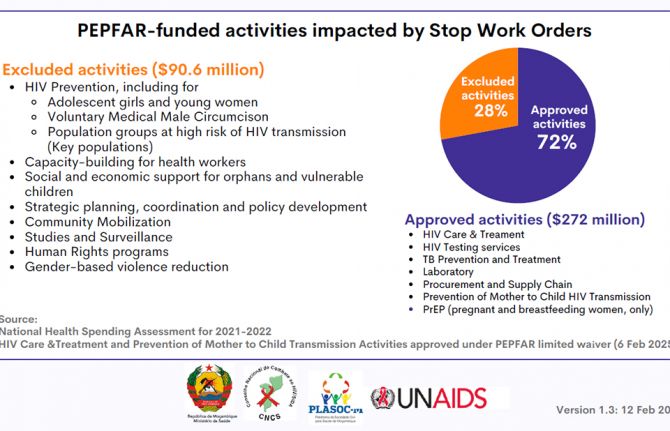
HIV Prevention



Feature Story
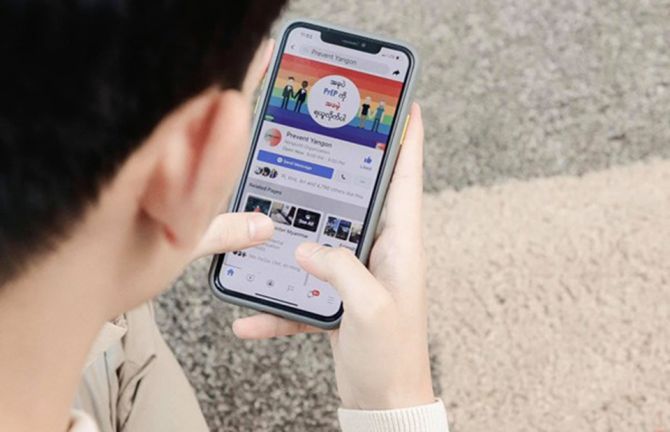
PrEParing for the next chapter of HIV prevention in Myanmar
19 September 2022
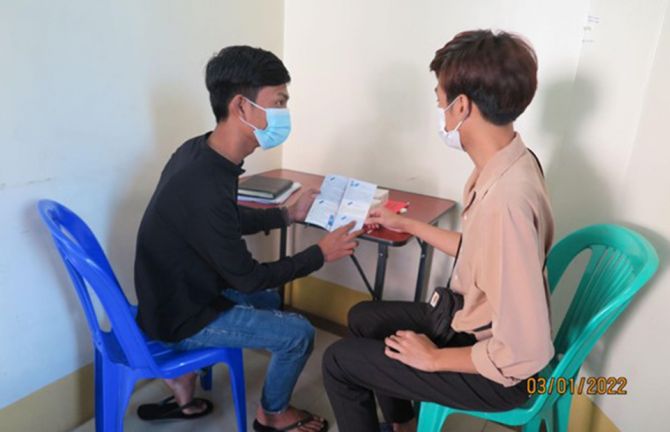
19 September 2022 19 September 2022Two young men are sitting on a couch scrolling on their phones when May Oo, a famous makeup artist and lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) activist in Myanmar, joins them wearing a face mask and carrying a bag of drinks. He announces that a friend who works at an HIV clinic in Yangon told him that pre-exposure prophylaxis, or PrEP, is now available in Myanmar. As one friend is unaware of PrEP, May Oo shares his knowledge, also informing anyone else wo would like to listen in.
This scene, from a video shared on the Facebook pages of implementing partners of the USAID HIV/AIDS Flagship (UHF) Project, is one of several to raise awareness and demand PrEP as a prevention tool for men who have sex with men and transgender women in Myanmar. In these videos by celebrated members of the LGBTQ community and other educational posts, questions covered include what PrEP is, why it should be taken, and where to get it. As May Oo’s friend in the video puts it, ‘PrEP is a drug that can prevent HIV.’
Since 2016, PrEP has been included as a priority intervention in Myanmar’s National Strategic Plan on HIV/AIDS following recommendation by the World Health Organization that it be used as an essential part of HIV prevention services. It was also an objective of the UHF Project to introduce PrEP in Myanmar and integrate it into existing HIV services, since the project’s inception in August 2017.
The UHF Project, overseen by UNAIDS Myanmar and the non-governmental organisation Community Partners International, aims to develop, implement, and scale up innovative, cost-effective approaches to the HIV care cascade in Myanmar. As one of the innovative HIV prevention activities under the National Strategic Plan IV (2020-2025), the initial 18-month PrEP demonstration project began in July 2020 at three clinics in Yangon for men who have sex with men and transgender people.
Along with the pilot was a plan to expand the project for people who inject drugs in Kachin State since the UHF Project’s overarching goal is to foster interventions such as PrEP for Myanmar’s four key populations at highest risk for HIV—people who inject drugs, men who have sex with men, transgender people, and female sex workers in the five states and regions with the highest burden of HIV—Kachin and Shan States and Mandalay, Sagaing, and Yangon.
Formative assessments conducted prior to the inception of these PrEP services indicated that PrEP awareness in Myanmar was very low. Fewer than a quarter of focus group participants—comprised of men who have sex with men, transgender women, and people who inject drugs—had heard of PrEP prior to the assessment. Service providers interviewed as part of the assessments also described low PrEP awareness among their clients.
Once educated about PrEP, however, most study participants agreed that PrEP would benefit their communities and that people at risk would be interested and willing to take PrEP. Awareness raising and community education have been one of the UHF Project’s focuses to increase PrEP uptake in Myanmar.
That is where videos such as May Oo’s are important. By using celebrities, private chat groups, and informational posts alongside interactive follow up by service providers for recruitment of PrEP clients, implementing partners not only educate people at risk for HIV on PrEP as a prevention option but also address the stigma around it.
Respondents to a midterm analysis conducted one year into the PrEP project reported that Facebook was the primary source of PrEP information and education, as the potentially more effective approach of fully-fledged in-person outreach is not feasible in the country’s current situation.
‘There are many in rural areas who do not have access to or use social media platforms,’ reports Ma Shin Thant, a PrEP client and activist currently based in Mandalay for her work with transgender women. As PrEP is currently only available in Yangon, Ma Shin Thant is fortunate that she can afford access to required testing and PrEP delivery in Mandalay.
‘The next chapter of PrEP in Myanmar calls for greater political commitment, more resources, a decentralised and simplified delivery system, and innovative community-centred approaches to ensure access by populations who need PrEP,’ concurs Rangaiyan Gurumurthy, UNAIDS Myanmar Country Director. ‘Moving from the demonstration phase to reaching scale with epidemic impact is now necessary.’
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
Documents
UNAIDS Executive Director's remarks at AIDS 2022 satellite session - A new global road map for combination HIV prevention
14 September 2022
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
55th meeting of the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board
10 December 2024




Feature Story
Successfully expanding the rollout of PrEP in Indonesia
01 September 2022
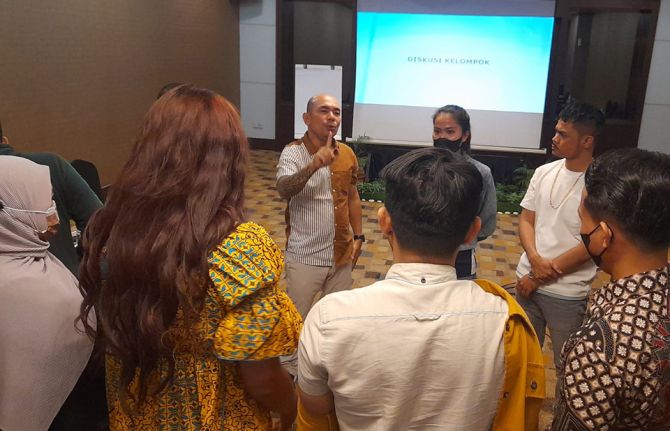
01 September 2022 01 September 2022While the number of new HIV infections in Indonesia decreased by 3.6% in 2021 to around 27 000, the country remains one of the countries with the highest number of new infections in the Asia and the Pacific region. Pre-exposure prophylaxis or PrEP is a medication that is highly effective at preventing HIV infection so making it available to groups of people most vulnerable is a key priority.
“In the past, I independently searched for information about PrEP because a client asked about it. I am glad there is a PrEP training that allows me to receive comprehensive information that I can then share with other people,” said Temmy a community outreach worker who participated in a training course in Bekasi.
PrEP was rolled out in Indonesia in 2021 as a pilot project to provide a new HIV prevention option which may be more convenient for people at risk of HIV, and to reduce new HIV infections among key populations such as sex workers and gay men and other men who have sex with men. It began in 12 districts, before expanding to 21 districts in 2022, with the aim of getting 7000 people on to PrEP.
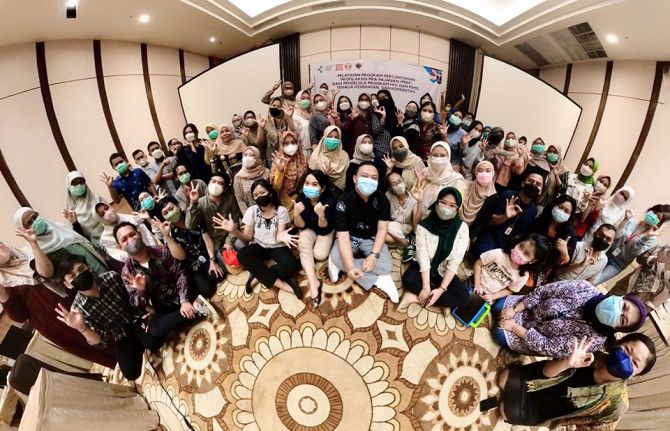
As part of the expansion, a second round of training sessions was conducted in August across nine cities in Indonesia: Bogor City, Bogor Regency, Depok, Bekasi, Tangerang, Batam, Balikpapan, Samarinda, and Sidoarjo. Over 120 services providers from 24 hospitals and 47 outreach workers from local communities took part.
The PrEP training for health providers and community outreach workers was conducted by the Ministry of Health of Indonesia in partnership with Kerti Praja Foundation, Padjajaran University, and the national MSM-TG Network (GWL-INA). It was supported by donors, including the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, USAID-PEPFAR and the Government of Australia’s Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT).
"With less than a decade to go before our goal of ending AIDS by 2030, we must prioritize efforts to scale up combination prevention programmes, such as PrEP. The piloting of PrEP is critical to kickstart policy and programme development on PrEP in Indonesia. The conduct of training for service providers and community outreach workers is an integral part of the pilot implementation to ensure adequate capacities to provide PrEP services to communities in need,” said Krittayawan Boonto, the UNAIDS Country Director for Indonesia.
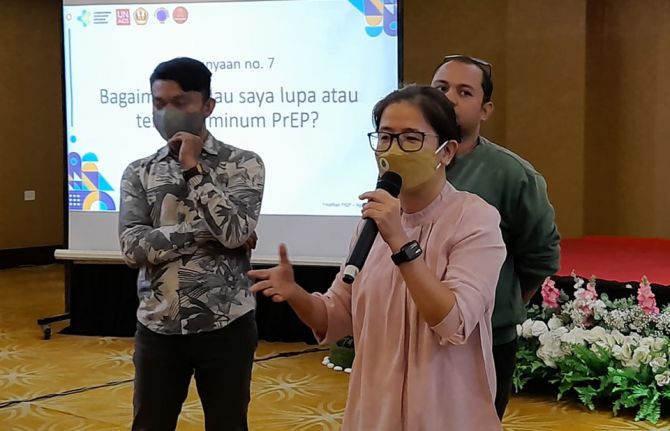
The PrEP training sessions are held over two days and include discussions between service providers and outreach workers. The aim is to equip and improve the capacity of the service providers and outreach workers to provide good quality PrEP services.
“This PrEP training has increased my knowledge of the alternative methods to prevent HIV. After this training, our health service office can now offer this new method of HIV prevention to our clients. We hope that this will contribute to the reduction of new infection risk. Thanks to this training, I have become more confident in providing PrEP services in the future,” said Doctor Elly from Lambuk Baja, Batam Province.
Unlike the first series of training sessions, the second was conducted in person and engagement was much higher. The enthusiasm also led to more active follow up after the training. One of the health centres in Bogor City started to provide PrEP services a couple of days after the end of the course. They also directly approached communities about the benefits of PrEP and within a month PrEP uptake had increased by 15%.
“As with all aspects of the HIV response, communities play a key role in the success of PrEP implementation. Contribution from the community is especially vital in the context of the pilot implementation in Indonesia, as communities of key populations with a substantial risk of HIV infection are the main beneficiaries of the programme,” said Muhammad Slamet, National Coordinator of the MSM-TG network (GWL Ina).
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
Documents
HIV prevention 2025 road map — Getting on track to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030
30 July 2022
This new Road Map charts a way forward for country-level actions to achieve an ambitious set of HIV prevention targets by 2025. Those targets emerged from the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS, which the United Nations General Assembly adopted in June 2021 and they are underpinned by the Global AIDS Strategy (2021–2026). The Strategy sets out the principles, approaches, priority action area and programmatic targets for the global HIV response. A Portuguese version is also available
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025




Feature Story
A beacon of hope in Guatemala
15 July 2022
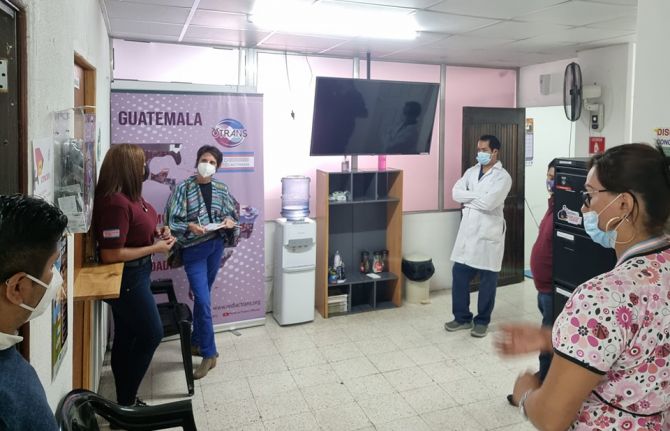
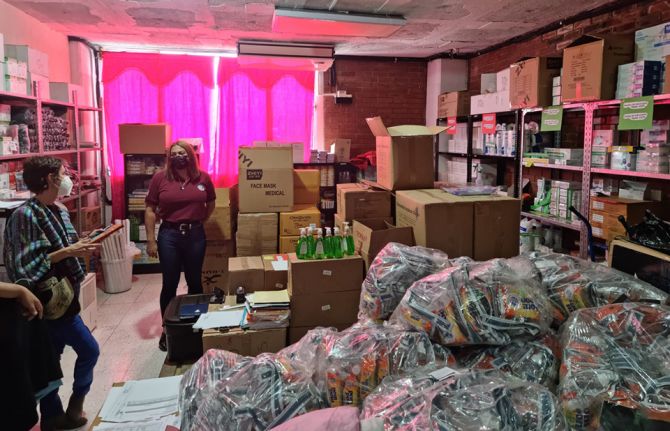
15 July 2022 15 July 2022It was a proud day for Stacy Velasquez the Executive Director of OTRANS Reinas de la Noche in June as she opened the doors to the community clinic that had just been officially approved as a health post by the Ministry of Public Health and Social Assistance. This meant that a full-time doctor was now in position.
Around 40 transgender women and sex workers have come to the clinic since the doctor's arrival. The clinic has existed for several years, but with the approval by the Ministry of Health and financial support from the Global Fund and OXFAM, patients now have access to comprehensive care: HIV prevention and diagnosis; prevention, diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted infections; psychosocial counselling; medical consultations including hormone therapy; a laboratory service for sexual health testing and a pharmacy.
The clinic offers pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a biomedical intervention within the combination prevention approach, which refers to the use of antiretroviral drugs by HIV-negative individuals to reduce the risk of contracting the virus.
"In 2016, a comprehensive health strategy for trans people was approved with technical support from UNAIDS. It includes a manual of guidelines for the health care of trans people,” said Stacy. “The community clinic and this strategy are the fruit of the work of almost 18 years of advocacy by the trans community."
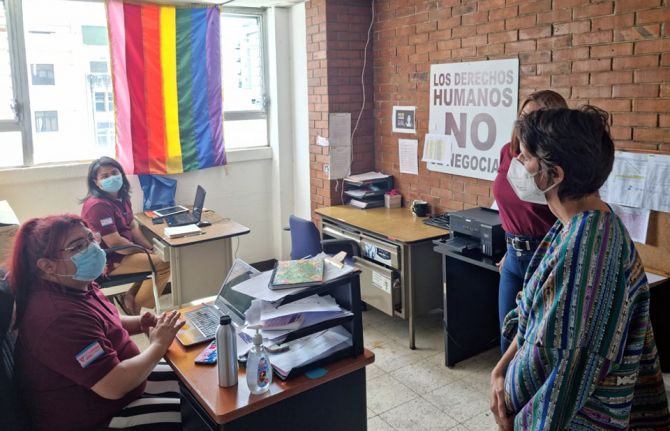
OTRANS contributes to the Centro de Documentación y Situación Trans de América Latina y el Caribe (CEDOSTALC), a community-based system for collecting information, monitoring and responding to human rights-related barriers faced by the transgender population in 26 countries in Latin American and the Caribbean.
In Guatemala, transgender women still face exclusion, discrimination, stigma, verbal and physical violence, criminalization, marginalization and a lack of recognition of their rights, resulting in a life expectancy of only 35 to 40 years old. The average life expectancy in the country is 74 years old.
During a visit to the clinic, UNAIDS country director, Marie Engel praised the work of the site and paid tribute to Andrea Gonzalez, the OTRANS legal representative who was murdered in 2021.
“In Guatemala, the HIV prevalence rate is 22.2% among the transgender population, compared to 0.2% for the general population,” said Ms Engel. “And although new HIV infections declined by 23% among all women between 2010 and 2019 globally, they have not declined among transgender women. And yet, transgender people have less access to HIV services than the rest of the population.”
Stigma and discrimination have a profound negative effect on the mental health of transgender people, which in turn can influence their vulnerability to HIV infection. Data reported to UNAIDS in recent years show that the percentage of transgender people who avoid seeking HIV testing due to stigma and discrimination ranges from 47% to 73%.
Region/country




Feature Story
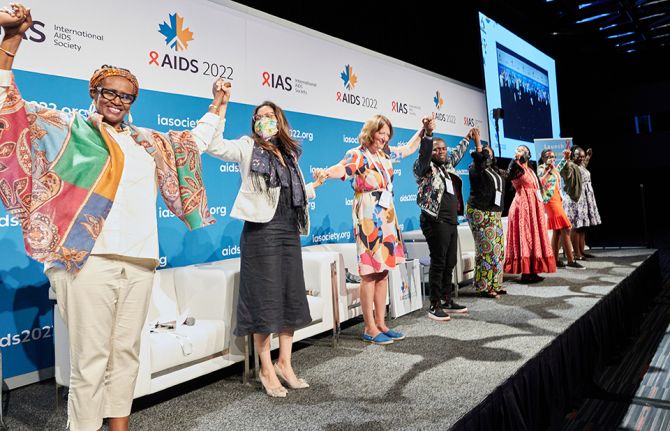
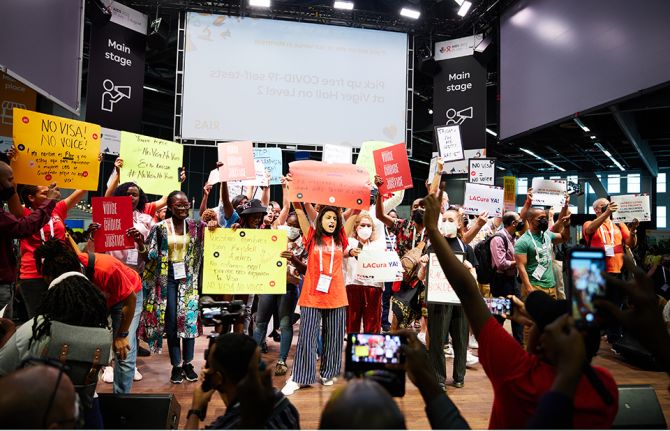
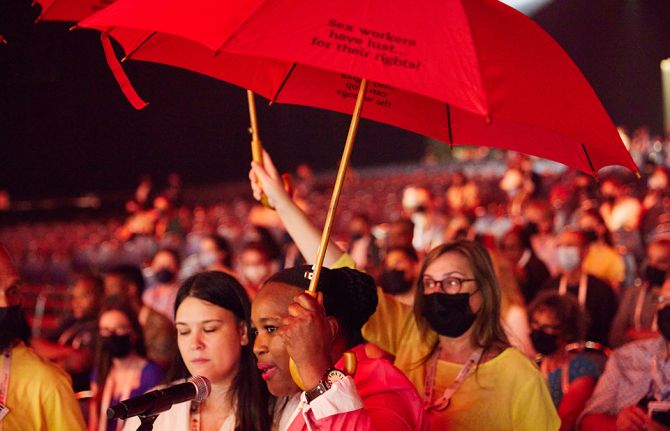
Pandemics are not fate: Concrete actions to tackle inequalities can overcome AIDS, Monkeypox and COVID-19
10 August 2022
10 August 2022 10 August 2022We do not need to accept pandemics as fate, experts gathered at the International AIDS Conference concurred. By taking specific, well-evidenced, concrete actions to tackle the inequalities driving them, today’s health threats can all be overcome.
As the latest data reveals that progress in the HIV response is stalling, putting millions of lives in danger, as the COVID-19 crisis drags on, and as Monkeypox presents new risks, all are being held back by inequalities, and all three viruses are in turn further exacerbating those inequalities. However, a focus on tackling underlying drivers of pandemic risk can enable a successful response, scientists, economists and heads of AIDS programmes concurred.
“There are Monkeypox vaccine doses in Europe but none in Africa. Most people at risk of dying from COVID-19 in lower-income countries have still not received a COVID-19 vaccine. New game changing prevention medicines for HIV will not be widely available in lower income counties for years unless there is a dramatic course correction,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director, UNAIDS, and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations. “An effective response to disease outbreaks and pandemics means tackling inequalities. That means empowering women and girls to shift power relations between men and women. It means tackling inequalities in access to health services between rich and poor. And it means removing punitive laws that push away from life-saving services LGBTQI+ people, people who use drugs, and sex workers.”
The application of scientific advancements is currently being undermined by inequalities, delegates at the International AIDS Conference noted. They recalled how, at the turn of the millennium, civil society and generic manufacturers teamed up to demand access to antiretrovirals for people living with HIV and their victory against the odds helped save millions of lives. But whilst that battle was won, delegates highlighted that the overall process of research and development, innovation and how that translates into manufacturing, pricing and distribution has remained untransparent and heavily skewed to the interests of rich countries. This played out during the COVID-19 pandemic as tests, vaccines and now antivirals are widely available in rich countries while still scarce in lower-income countries. And now this is repeating again with Monkeypox.
Inequality is not only about differential risks but is about cycles of power, the imbalance in how laws and policies are implemented, who is empowered by these policies, and who is disempowered.
“The AIDS movement is one of the best examples of how groups of people experiencing intersecting inequalities can unite to overcome them, leading to millions of lives being saved,” said Professor Joseph Stiglitz, Nobel laureate in economics. “But those gains were not permanent. Now a heating world combined with systemic inequalities mean that new disease outbreaks are becoming more frequent and while technological advancement is important, if there’s not a serious move to tackle inequality, the pattern of prolonged pandemics will only continue.” Professor Stiglitz was speaking at the AIDS Conference’s flagship session entitled “How Inequalities Perpetuate Pandemics: Why We Need a New Approach to End AIDS.”
New HIV infections occurred disproportionately among young women and adolescent girls, with a new infection every two minutes in this population in 2021. The gendered HIV impact, particularly for young African women and girls, occurred amidst disruption of key HIV treatment and prevention services, millions of girls out of school due to pandemics, and spikes in teenage pregnancies and gender-based violence. In sub-Saharan Africa, adolescent girls and young women are three times as likely to acquire HIV as adolescent boys and young men.
Worldwide, only half (52%) of children living with HIV have access to life-saving medicine, and the inequality in HIV treatment coverage between children and adults is increasing rather than narrowing.
Racial inequalities drive HIV too. In the United Kingdom and the United States, declines in new HIV diagnoses have been smaller among Black populations than among White. In Australia, Canada and the United States, HIV acquisition rates are higher in Indigenous communities than in non-Indigenous communities.
Sbongile Nkosi, Co-Executive Director of the Global Network of PLHIV stated “Our experiences to date remind us that responding to pandemics such as HIV and COVID-19 is not just about dealing with a medical condition, it’s also about the environment in which we live and how my social status will determine the care I receive. It means centering interventions around the needs of people, listening to people. When we talk about key populations, we tend to group people. But then we misunderstand inequalities. People live intersecting lives and inequalities affect them differently.” During the disruptions of the last few years, key populations have been particularly affected in many communities – with rising prevalence in many locations. UNAIDS data have shown increasing risk of new infections faced by gay men and other men who have sex with men (MSM) globally. As of 2021, UNAIDS key populations data show MSM have 28 times the risk of acquiring HIV compared to people of the same age and gender identity while people who inject drugs have 35 times the risk, sex workers 30 times the risk, and transgender women 14 times the risk.
Just as tackling inequalities has been key to progress in tackling HIV, so it is in tackling COVID-19. But too many COVID-19 responses have ignored this. “We have failed to learn a lot of the lessons from HIV/AIDS in the way we responded to COVID-19. And we need to be honest about that and reflect on where we go from here,” noted Executive Director of the Global Fund, Peter Sands.
“It's time not only to know your gaps but to close those gaps,” said Ambassador John Nkengasong, US Global AIDS Coordinator and Special Representative for Global Health Diplomacy.
Today’s inequalities are bleak. But the most important message is a hopeful one. We know how to end AIDS by 2030 and also how to overcome Monkeypox, COVID-19 and other current and future health threats: when we tackle the inequalities which drive health risks, we can keep everyone safe.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
Executive summary — In Danger: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2022
27 July 2022
Progress in prevention and treatment is faltering around the world, putting millions of people in grave danger. Eastern Europe and central Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East and North Africa have all seen increases in annual HIV infections over several years. In Asia and the Pacific, UNAIDS data now show new HIV infections are rising where they had been falling. Action to tackle the inequalities driving AIDS is urgently required to prevent millions of new HIV infections this decade and to end the AIDS pandemic. See also: Full report | Fact sheet | Epi slides | Microsite | Press release | Arabic translation of the report summary
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
Innovate, Implement, Integrate: Virtual interventions in response to HIV, sexually transmitted infections and viral hepatitis
29 July 2022
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025





Feature Story
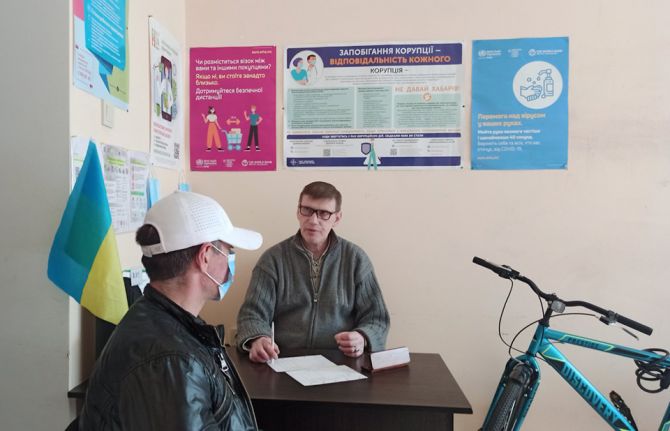
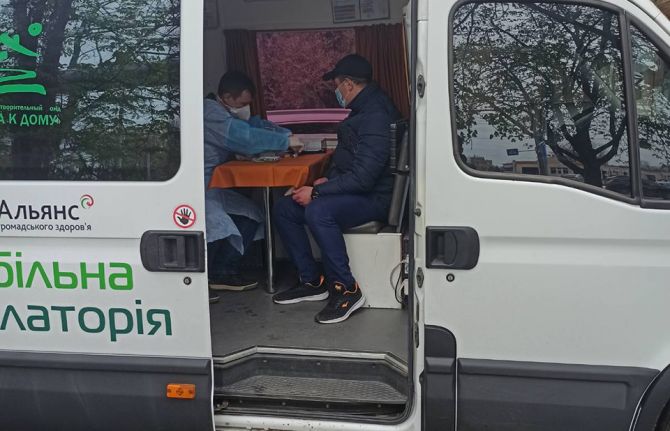
Sustaining HIV services for people who use drugs in Odesa
22 April 2022
22 April 2022 22 April 2022Odesa is a major Black Sea port, with a substantial drug use. In the 1990s, Odesa saw the outbreak of HIV infection in Ukraine. But more recently it has successfully developed one of the world’s most effective systems of harm reduction services for people who use drugs. The system is funded by the state and local budgets and implemented jointly with non-governmental and community organizations. Odesa was one of the first cities in Eastern Europe and Central Asia that signed the Paris Declaration. Last year, it reported a reduction of new HIV cases among people who use drugs.
Natalia Kitsenko is head of the public health department of the Road to Home Foundation, one of Odesa’s oldest organizations providing services to people who use drugs. UNAIDS spoke with her about how her organization has been managing to continue to help people in need, even during this war.
Question: Did many people flee Odesa?
Answer: Yes, many left, mostly women and children. The people in our organisation are an exception. Of 60 employees, 4 people left because they have small children. The rest stayed and we are actively continuing our usual work and also providing emergency assistance to women with children and elderly people fleeing from other cities—Mykolaiv, Kherson, Mariupol and Kharkiv. We mostly provide transportation to the Moldova border and connect them with volunteers who then help them in the country or in another destination depending on their needs.
We also prepare food such as pies and dumplings for people in need. This whole situation has united us; I have seen a lot of mutual support around.
Question: How many people from your harm reduction program have left the city?
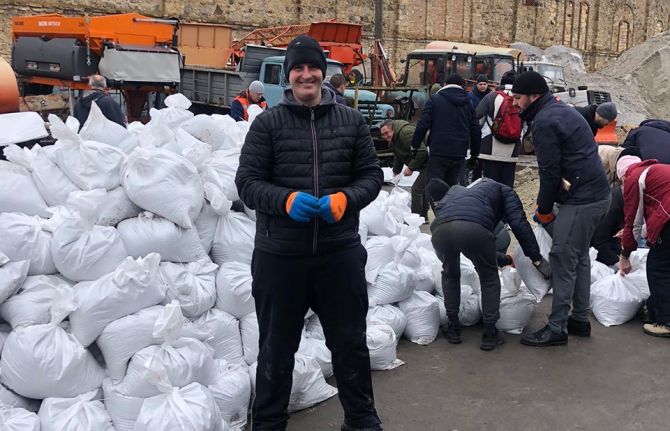
Answer: Our coverage in Odesa and surrounding region includes about 20,000 people per year. As far as we know only 7 clients have fled abroad. Some clients have gone into the local territorial defense groups. Others have taken part in building protective structures, which involves collecting bags of sand and transporting them to protect streets and monuments. Others reside with us for the services they need. We had an influx of people who use drugs from other regions of Ukraine where conditions are far worse.
Question: What services does your organization offer to people who use drugs?
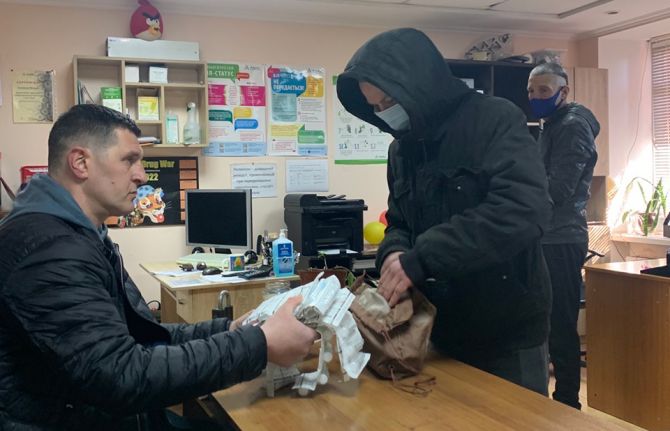
Answer: First of all the basic harm reduction package which we provide under the state budget includes consultations, HIV prevention (syringes, condoms, wipes, lubricants, etc.); HIV testing, and TB screening. Among clients who have used these services for a long time, the detection rate of HIV infection is 0.02%. Among new clients who have just joined the programme, it reaches up to 7%. We set up a client recruitment model with the Alliance for Public Health coordination using the Global Fund Grant and ECDC support. We encourage people who use drugs to bring their close friends to our community centres for testing. This is an important aspect because new clients, especially young people, those who recently started using drugs, can be a very difficult group to reach. Many hide their use and try to stay invisible. This recruitment system allows us to attract them to our harm reduction services, and first of all to testing. Management of new cases, support for diagnosis and receiving antiretroviral therapy, screening, and follow-up for tuberculosis is also provided through donor funding, in particular the PEPFAR project.
Question: Have you gotten additional funds?
Answer: Yes. We just received additional funding from the UNAIDS Emergency Fund to purchase medicines, dressings and hygiene products for our clients. This is a very timely and essential help because many medical products like Fluconazole (antibiotic) are not affordable to our clients and they are not widely available anymore.
Question: Natalia, you have been working in the HIV field for more than 20 years, have public attitudes changed regarding people living with HIV and drug users?
Answer: We have seen a welcome dramatic reduction in the level of stigma and discrimination and the overall attitude towards our clients in medical settings. However, we still experience problems with prejudices. Many people say that they do not want to have our syringe exchange points and community centers near their homes, and that they don't want to see people who use drugs near them as they fear that they might threaten their comfort, well-being and safety. We understand these fears, and we try to explain to concerned people why we are here, how these syringe exchange points and community centers work. We organise outings and sessions to explain to people the reality that people who use drugs face. We work to continually demonstrate our contribution and show how we help keep the epidemics of HIV, TB and hepatitis under control.
Since the war started we have also provided shelter to people who live by our centres. As our syringe exchange points are usually in basements, when the sirens sound the neighbors come to us; and that means for some their first time being in close contact with people living with HIV or people who use drugs.
Question: What are the most pressing issues for you now?
Answer: At the moment we are experiencing difficulties in providing our customers with Naloxone, which can prevent drug overdoses. Although we are constantly working on counseling and informing people about signs of overdosing, with the war going on, overdoses have increased. And because Naloxone is manufactured in the heavily bombed city of Kharkiv we have no more. We need it in any form, preferably ready-made, intranasal or injectable, as this would save many lives. And we need to sustain HIV services for people who use drugs together with providing them with urgent humanitarian aid.
Region/country
Related
 Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery
Three Years On: From crisis to prospective recovery

20 February 2025




Feature Story
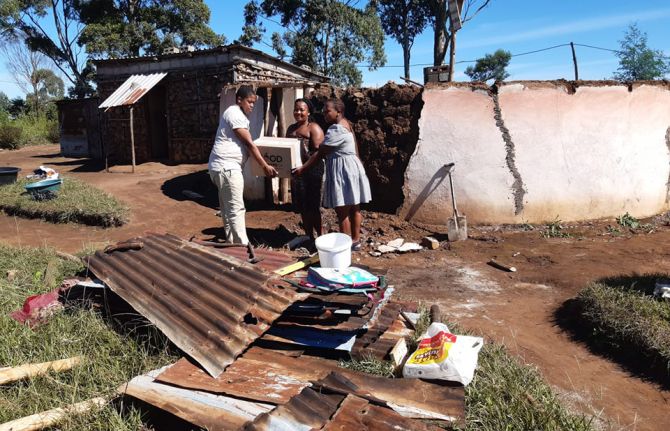
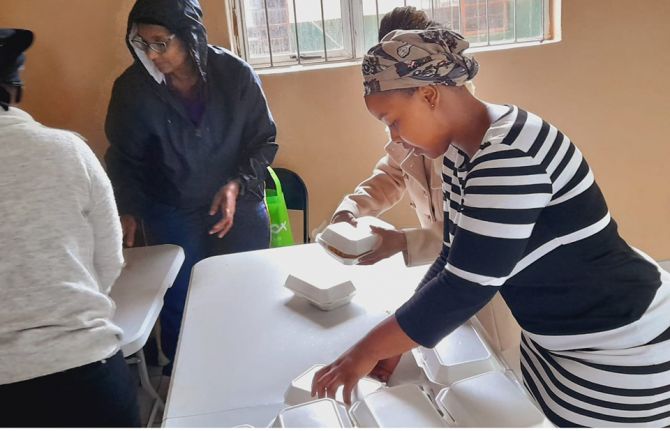
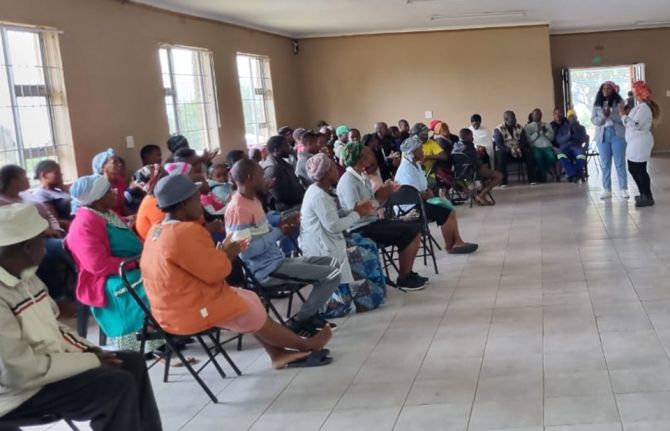
Supporting HIV services for flood survivors in KwaZulu-Natal
23 April 2022
23 April 2022 23 April 2022Since floods killed 440 people and left many thousands more homeless last week in KwaZulu-Natal (KZN), South Africa, UNAIDS has been working with communities, civil society and government leaders to respond.
Together with the UN system in South Africa, donors and other partners, UNAIDS has been urgently evaluating the needs of thousands of people living with HIV who were directly impacted by the flash flooding. Swollen rivers and landslides damaged more than 600 schools and 66 health care facilities, while many homes have been left without running water or electricity. The government health facilities that can operate, say that they are being overwhelmed, with their staff – themselves affected by the flooding - being further stretched by the scale of demand for health services.
“It is a very tense and stressful time for everyone,” said Miriam Chipimo, UNAIDS Fast-Track Adviser based in KZN. “Major roads are damaged or flooded, food supplies are disrupted. People are struggling for electricity, water and shelter while worrying about security. Some are having to dig through the mud, looking for friends and family members on their own.”
Using lessons learned from the Covid-19 pandemic and other humanitarian situations around the world, UNAIDS has prioritised a rapid assessment of flood-affected people living with HIV, to make sure their urgent needs are met.
South Africa has the largest HIV epidemic in the world, and KZN has the country’s largest provincial burden, with an estimated two million people living with HIV, including 76 000 children (December 2020). The floods have particularly impacted eThekwini district, which is home to Africa’s largest port in Durban. In 2020, eThekwini had an estimated 641 000 adults and 21 000 children living with HIV.
It is understood that many people living with HIV are among the thousands left homeless, and many saw their medication washed away with their other belongings. UNAIDS Country Director for South Africa, Eva Kiwango, said: “Our response to these terrible floods is to ensure that people living with HIV, TB and STIs can continue to access treatment and related services. Our starting point has been to engage with as many relevant parties as possible, to find ways to meet the immediate, practical needs of people living with HIV. It is important that our response is coordinated, reflects community priorities and upholds the principle of the greater involvement of people living with HIV/AIDS (GIPA).”
The Government has declared the floods to be a national state of disaster and has sent 10 000 troops to assist. UNAIDS staff are collaborating on the ground and remotely with the Office of the Mayor of eThekwini, the Office of the Premier of KZN, and the KZN Provincial Department of Health, to help coordinate responses. UNAIDS is also working with the National Association of Child Care Workers which has a large presence in the communities focused on children and young people living with HIV who are particularly vulnerable.
An ongoing project facilitated by UNAIDS has already redirected eight young peer educators to conduct outreach visits to emergency shelters and affected communities to locate people in need, including those who need urgent replenishment of their lifesaving medication. A further 20 child and youth care workers, who are registered health professionals, are distributing medication and providing counselling to affected community members, as well as working with NGOs and others to help distribute donated food, water and clothing.
UNAIDS is working with the UN Country Team through the UN Resident Coordinators office and convening the country-level Joint Team on AIDS, to explore ways to re-programme AIDS funding in support of related emergency measures. UNAIDS is also pursuing similar opportunities with international donors that are already supporting projects overseen by UNAIDS in the province.