Epidemiology
Documents
Evaluating the Evidence for Historical Interventions Having Reduced HIV Incidence: A Retrospective Programmatic Mapping Modelling Analysis
08 February 2017
As the HIV epidemic continues to mature alongside the increasing scope and coverage of treatment and prevention programmes, inferring trends in incidence from available prevalence data and subsequently identifying drivers behind epidemic trends will become increasingly complex.25 The availability of prospectively collected programmatic and epidemic surveillance data at a greater sub-national spatial resolution will greatly improve the robustness of future impact evaluations.
Related
 Building country-led sustainable HIV responses
Building country-led sustainable HIV responses

20 December 2024
Joint Evaluation of the Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-being for All (SDG 3 GAP)
16 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
 Resilience amid crisis: strengthening the HIV response for displaced communities in Ethiopia
Resilience amid crisis: strengthening the HIV response for displaced communities in Ethiopia

02 December 2024
 Women living with HIV in China unite to confront discrimination
Women living with HIV in China unite to confront discrimination
14 October 2024
 UNAIDS calls for a rapid international response to mpox based on rights and an equitable access to vaccines and treatments
UNAIDS calls for a rapid international response to mpox based on rights and an equitable access to vaccines and treatments

19 August 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
Documents
Get on the Fast-Track — The life-cycle approach to HIV
21 November 2016
In this report, UNAIDS is announcing that 18.2 million people now have access to HIV treatment. The Fast-Track response is working. Increasing treatment coverage is reducing AIDS-related deaths among adults and children. But the life-cycle approach has to include more than just treatment. Tuberculosis (TB) remains among the commonest causes of illness and death among people living with HIV of all ages, causing about one third of AIDS-related deaths in 2015. These deaths could and should have been prevented. Download slide deck
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024
Documents
AIDS by the numbers — AIDS is not over, but it can be
21 November 2016
Huge progress has been made since 2000 and millions of lives have been saved. But there are still important milestones to reach, barriers to break and frontiers to cross. The world has agreed to meet a set of global targets by 2020 as part of UNAIDS Fast-Track strategy to end the AIDS epidemic as a public health threat.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
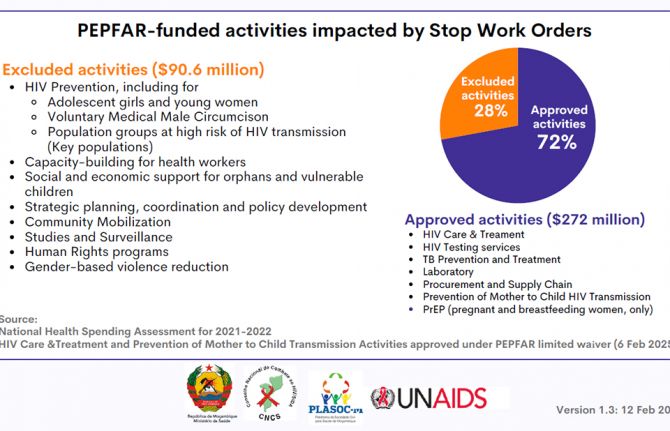
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Documents
Prevention gap report
11 July 2016
Efforts to reach fewer than 500 000 new HIV infections by 2020 are off track. This simple conclusion sits atop a complex and diverse global tapestry. Data from 146 countries show that some have achieved declines in new HIV infections among adults of 50% or more over the last 10 years, while many others have not made measurable progress, and yet others have experienced worrying increases in new HIV infections. More on the Prevention Gap report | Slides are also available for download | Download summary
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Documents
How AIDS changed everything — MDG6: 15 years, 15 lessons of hope from the AIDS response
14 July 2015
We have reached a defining moment in the AIDS response. Against all odds, we have achieved the AIDS targets of Millennium Development Goal 6. AIDS changed everything. In these pages are valuable insights and ground-breaking and heart-warming experiences from the innovative and exciting work that partners, communities and countries have done and are doing in the AIDS response. There are also heart-breaking stories about the challenges that still remain. More on How AIDS changed everything
You can also view the report on Issuu Report with no annexes Annexes only
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
 UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid
UNAIDS urges that all essential HIV services must continue while U.S. pauses its funding for foreign aid

01 February 2025
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024
Documents
Fact sheet - Latest global and regional statistics on the status of the AIDS epidemic.
22 July 2024
Fact sheet - Latest global and regional statistics on the status of the AIDS epidemic. Also available in Portuguese (Brazil)
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024
Documents
Methods for deriving UNAIDS estimates
08 June 2016
UNAIDS annually provides revised global, regional and country-specific modelled estimates to track the HIV epidemic, using the best available epidemiological and programmatic data. Modelled estimates are required because it is impossible to count the exact number of people living with HIV, people who are newly infected with HIV or people who have died from AIDS-related causes in any country. Knowing this for certain requires testing every person for HIV regularly and investigating all deaths, which is logistically impossible and ethically problematic. Modelled estimates and the lower and upper bounds around these estimates provide a scientifically appropriate way to describe HIV epidemic levels and trends.
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024