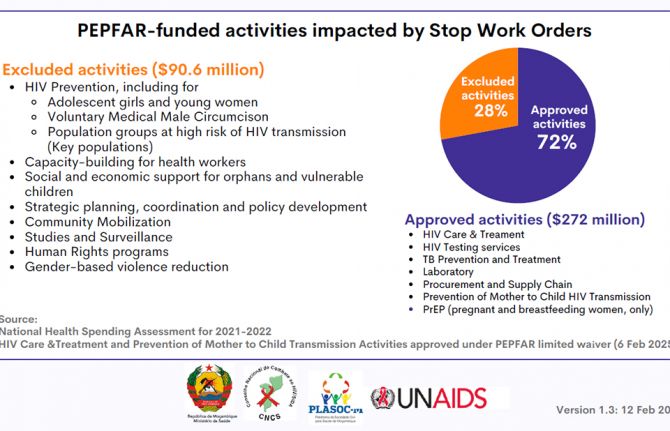
Data

Feature Story
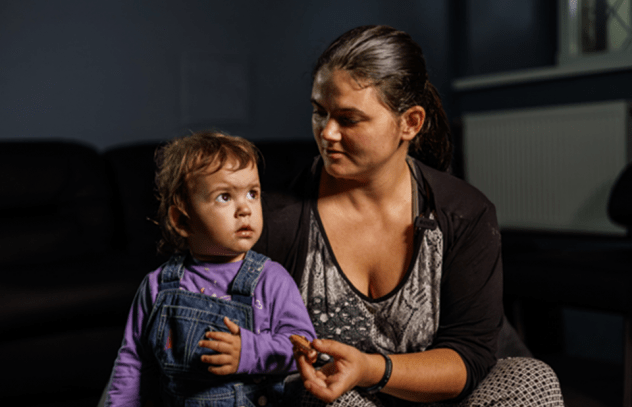
Study shows how COVID-19 is impacting access to HIV care in the Russian Federation
27 November 2020
27 November 2020 27 November 2020A new study shows the negative impact that the COVID-19 pandemic is having on access to HIV care in the Russian Federation and shows that people living with HIV in the country are more susceptible to COVID-19 but less likely to seek testing or treatment.
More than a third of people living with HIV who were surveyed reported some impact on HIV services, including about 4% who reported that they had missed taking antiretroviral therapy because they could not get the medicine and nearly 9% who reported that they had missed taking medicine for tuberculosis prevention. However, the majority of respondents (about 70% of people living with HIV) did not experience problems obtaining antiretroviral therapy and about 22% reported that antiretroviral medicines were delivered to their home. More than 900 respondents from 68 regions of the Russian Federation, including people living with HIV and those who are not, were reached by the study.
“This study answers some of the most important questions about the impact of COVID-19 on people living with HIV in our country,” said Natalya Ladnaya, Principal Investigator and Senior Researcher at the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of the Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing (Rospotrebnadzor).
According to Ms Ladnaya, the study confirmed that it is crucial for people living with HIV to protect themselves against the new coronavirus. The authors of the study also note the need to provide uninterrupted HIV treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Encouraging results were obtained on how the pandemic affected access to HIV treatment—many specialized institutions have been able to adapt to the new reality,” said Alexey Mikhailov, Head of the Monitoring Department of the Treatment Preparedness Coalition, who took part in the study.
According to the study, the number of people living with HIV with COVID-19 markers was four times higher than that of HIV-negative respondents. At the same time, they were half as likely, compared with HIV-negative respondents, to be tested for coronavirus infection and were less likely to seek medical help, even if they had symptoms.
The majority of respondents with HIV and COVID-19 coinfection had a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 due to the significant number of local cases of COVID-19 and the low level of use of personal protective measures, as well as an underestimation of the real personal risk of COVID-19 disease.
Although more than two thirds of the study participants were women, among people living with HIV and having had COVID-19 the majority of respondents were men who had lived with HIV for more than 10 years.
The authors of the study point to the need for further investigation into the causes of the increased incidence of COVID-19 and the low demand for medical care to treat the symptoms of COVID-19 among people living with HIV.
“The COVID-19 pandemic continues to affect all areas of our lives. We need to closely monitor the colliding pandemics of COVID-19 and HIV and provide support so as not to lose the gains in the response to HIV that have been achieved,” said Alexander Goliusov, Director, a.i., UNAIDS Regional Support Team for Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
The study was conducted by the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor together with the Treatment Preparedness Coalition with the support of UNAIDS and Rospotrebnadzor.
Our work
Region/country
Related


Press Release
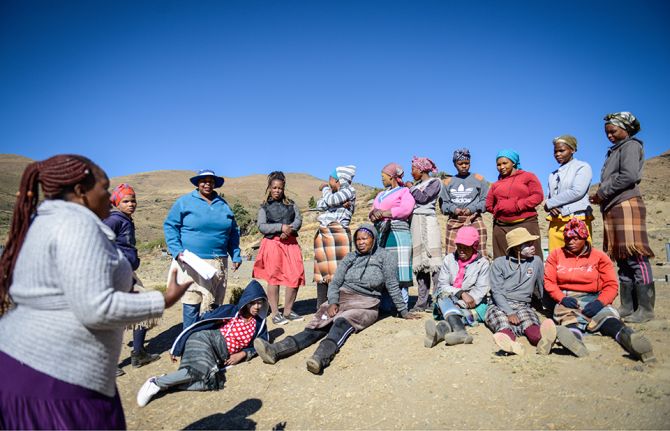
UNAIDS calls on countries to step up global action and proposes bold new HIV targets for 2025
26 November 2020 26 November 2020As COVID-19 pushes the AIDS response even further off track and the 2020 targets are missed, UNAIDS is urging countries to learn from the lessons of underinvesting in health and to step up global action to end AIDS and other pandemics
GENEVA, 26 November 2020—In a new report, Prevailing against pandemics by putting people at the centre, UNAIDS is calling on countries to make far greater investments in global pandemic responses and adopt a new set of bold, ambitious but achievable HIV targets. If those targets are met, the world will be back on track to ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
The global AIDS response was off track before the COVID-19 pandemic hit, but the rapid spread of the coronavirus has created additional setbacks. Modelling of the pandemic’s long-term impact on the HIV response shows that there could be an estimated 123 000 to 293 000 additional new HIV infections and 69 000 to 148 000 additional AIDS-related deaths between 2020 and 2022.
“The collective failure to invest sufficiently in comprehensive, rights-based, people-centred HIV responses has come at a terrible price,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Implementing just the most politically palatable programmes will not turn the tide against COVID-19 or end AIDS. To get the global response back on track will require putting people first and tackling the inequalities on which epidemics thrive.”
New targets for getting back on track
Although some countries in sub-Saharan Africa, such as Botswana and Eswatini, have done remarkably well and have achieved or even exceeded the targets set for 2020, many more countries are falling way behind. The high-performing countries have created a path for others to follow. UNAIDS has worked with its partners to distil those lessons into a set of proposed targets for 2025 that take a people-centred approach.
The targets focus on a high coverage of HIV and reproductive and sexual health services together with the removal of punitive laws and policies and on reducing stigma and discrimination. They put people at the centre, especially the people most at risk and the marginalized—young women and girls, adolescents, sex workers, transgender people, people who inject drugs and gay men and other men who have sex with men.
New HIV service delivery targets aim at achieving a 95% coverage for each sub-population of people living with and at increased risk of HIV. By taking a person-centred approach and focusing on the hotspots, countries will be better placed to control their epidemics.
The 2025 targets also require ensuring a conducive environment for an effective HIV response and include ambitious antidiscrimination targets so that less than 10% of countries have punitive laws and policies, less than 10% of people living with and affected by HIV experience stigma and discrimination and less than 10% experience gender inequality and violence.
Prevailing against pandemics
Insufficient investment and action on HIV and other pandemics left the world exposed to COVID-19. Had health systems and social safety nets been even stronger, the world would have been better positioned to slow the spread of COVID-19 and withstand its impact. COVID-19 has shown that investments in health save lives but also provide a foundation for strong economies. Health and HIV programmes must be fully funded, both in times of plenty and in times of economic crisis.
“No country can defeat these pandemics on its own,” said Ms Byanyima. “A challenge of this magnitude can only be defeated by forging global solidarity, accepting a shared responsibility and mobilizing a response that leaves no one behind. We can do this by sharing the load and working together.”
There are bright spots: the leadership, infrastructure and lessons of the HIV response are being leveraged to fight COVID-19. The HIV response has helped to ensure the continuity of services in the face of extraordinary challenges. The response by communities against COVID-19 has shown what can be achieved by working together.
In addition, the world must learn from the mistakes of the HIV response, when millions in developing countries died waiting for treatment. Even today, more than 12 million people still do not have access to HIV treatment and 1.7 million people became infected with HIV in 2019 because they did not have access to essential HIV services.
Everyone has a right to health, which is why UNAIDS has been a leading advocate for a People’s Vaccine against COVID-19. Promising COVID-19 vaccines are emerging, but we must ensure that they are not the privilege of the rich. Therefore, UNAIDS and partners are calling on pharmaceutical companies to openly share their technology and know-how and to wave their intellectual property rights so that the world can produce successful vaccines at the huge scale and speed required to protect everyone.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 68 96
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025

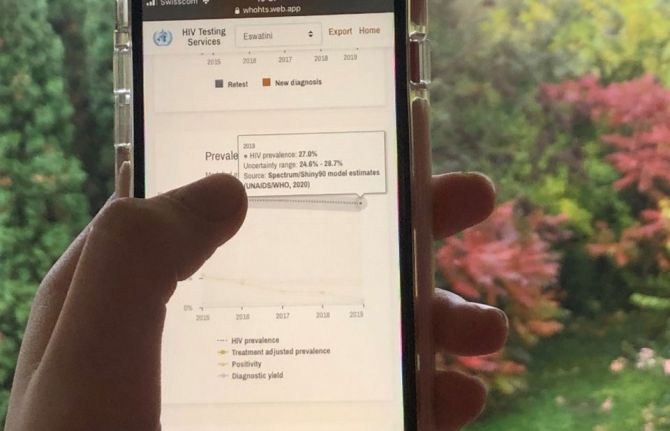
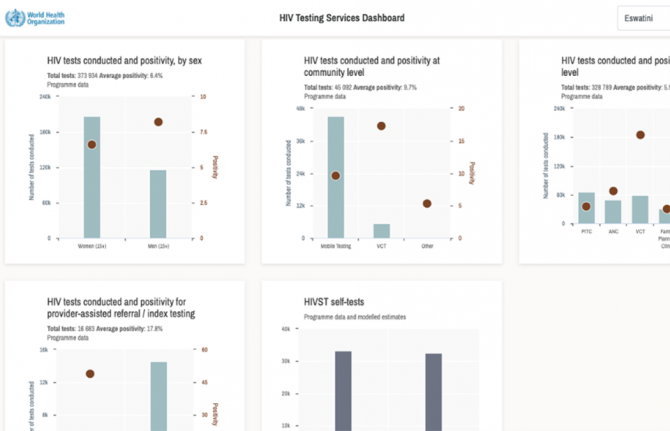

Feature Story
Updated dashboard supports differentiated HIV testing services
12 November 2020
12 November 2020 12 November 2020The World Health Organization (WHO), in coordination with UNAIDS, has updated its HIV Testing Services dashboard with new data for 2020, ahead of this year’s World AIDS Day.
The interactive dashboard gives users a wide range of information on HIV testing from countries worldwide on, for example, HIV prevalence, the number of people testing positive for HIV and the number of people testing for HIV for the first time or repeating a test. Data are given in charts and tables and are differentiated by age, sex and other characteristics.
“It is critical to have differentiated HIV testing data at this stage in the epidemic,” said Cheryl Johnson, WHO Technical Officer. “Having such data will help programmes to implement the World Health Organization’s guidelines so that they may reach the remaining people living with HIV who do not know their status. We look forward to working with countries on how they can use their data to guide efficient and effective HIV testing services.”
Countries need to have a range of testing approaches to reach people living with HIV who do not know their status and others at risk of acquiring HIV. The dashboard will help countries to develop the best mix of testing services—such as self-testing, index testing and various forms of community and facility-based testing services—suitable for their settings. Countries can also monitor the progress of the number of people who newly learn their HIV status.
“We are using data to intensify our efforts to reach the remaining people living with HIV who don’t know their status and to facilitate linkage to care by prioritizing and differentiating testing so we can reach underserved geographies and populations in Uganda. The dashboard is a useful tool to help guide decision-making and our national strategy moving forward,” said Geoffrey Taasi, Programme Officer, HIV Testing Services, Ministry of Health, Uganda.
The information on the dashboard is a mixture of WHO and UNAIDS data, national programme data, modelled estimates and population survey data—it also includes the implementation status of testing services and national policies. The data used were selected in consultation with representatives of ministries of health, research partners, local and international implementing partners and donors.
In addition to the website, the dashboard can be accessed through the WHO HTS Info app using a smartphone or tablet.
“Expansion of relevant HIV testing approaches is critical for Viet Nam to achieve the 90–90–90 targets. With support from the World Health Organization and other partners, we have successfully piloted community-based HIV testing, including lay provider testing and self-testing. We are now working to scale up these approaches nationwide,” said Nguyen Hoang Long, Director-General of the Viet Nam Authority of HIV/AIDS Control, Ministry of Health, Viet Nam.
HIV Testing Services Dashboard
Our work

Update
New HIV infections: men outnumber women
12 October 2020
12 October 2020 12 October 2020Men living with HIV are less likely to access HIV testing and antiretroviral therapy, and they also experience higher levels of new HIV infections.
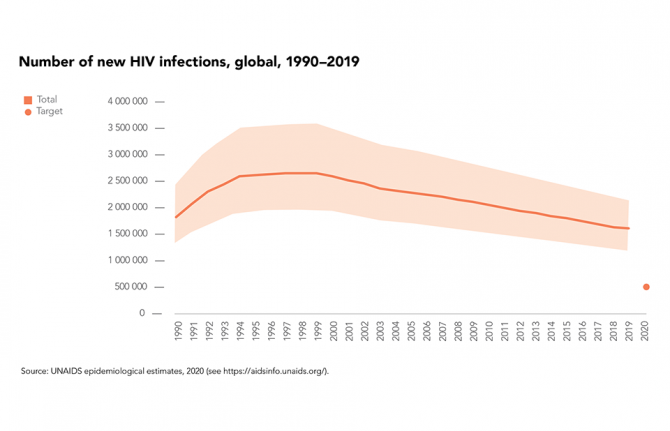
In 2019, the estimated 1.7 million people who acquired HIV worldwide marked a 23% decline in new HIV infections since 2010, although progress on HIV prevention remains far too slow, with the estimated total number of new infections in 2019 more than three times higher than the milestone of 500 000 that was set for 2020.
There were fewer new HIV infections in 2019 worldwide among women and girls (48% of total infections) than among men and boys (52%) in 2019—globally the annual number of new infections has been falling more rapidly among women and girls (a 27% decrease since 2010) than among men and boys (an 18% decrease).
Number of new HIV infections by sex, global, 2019-2019. Source: UNAIDS epidemiological estimates, 2020
RESOURCES

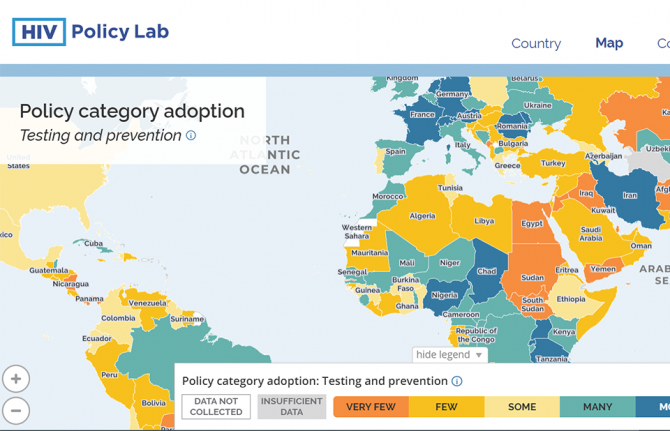
Press Release
New HIV Policy Lab uses law and policy data in the HIV response
29 September 2020 29 September 2020WASHINGTON, D.C./GENEVA, 29 September 2020—Despite decades of scientific advance in the HIV response, progress remains uneven, with some countries rapidly reducing AIDS-related deaths and new HIV infections and others seeing increasing epidemics. Laws and policies are driving a significant part of that divergence.
Launched today, the HIV Policy Lab is a unique initiative to gather and monitor HIV-related laws and policies around the world.
“Laws and policies are life or death issues when it comes to HIV. They can ensure access to the best that science has to offer and help people to realize their rights and live well, or they can be barriers to people’s well-being. Like anything that matters, we need to measure the policy environment and work to transform it as a key part of the AIDS response,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director.
The HIV Policy Lab is a data visualization and comparison tool that tracks national policy across 33 different indicators in 194 countries around the world, giving a measure of the policy environment. The goal is to improve transparency, the ability to understand and use the information easily and the ability to compare countries, supporting governments to learn from their neighbours, civil society to increase accountability and researchers to study the impact of laws and policies on the HIV pandemic.
According to Matthew Kavanagh, Director of the Global Health Policy & Politics Initiative at Georgetown University’s O’Neill Institute, “Policy is how governments take science to scale. If we want to improve how policy is used to improve health outcomes, it is essential to monitor and evaluate the policies that comprise it.”
“Reducing stigma and making care easier to access are fundamental for improving the lives of people living with HIV—and those are all consequences of policy choices. Tracking these choices is a key tool for improving them, and ensuring justice and equity for people living with HIV,” said Rico Gustav, Executive Director of the Global Network of People Living with HIV.
The HIV Policy Lab draws information from the National Commitments and Policy Instrument, legal documents, government reports and independent analyses to create data sets that can be compared across countries and across issues. The goal of the HIV Policy Lab is to help identify and address the gaps between evidence and policy and to build accountability for a more inclusive, effective, rights-based and science-based HIV policy response.
The HIV Policy Lab is a collaboration between Georgetown University and the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law, UNAIDS, the Global Network of People Living with HIV and Talus Analytics.
About the Georgetown University O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law
The O’Neill Institute, housed at Georgetown University, was established to create innovative solutions to the most pressing national and international health concerns, with the essential vision that the law has been, and will remain, a fundamental tool for solving critical health problems. The Georgetown University Department of International Health is home to scholarship in public health, economics, political science, and medicine. Georgetown’s Global Health Initiative serves as a university-wide platform for developing concrete solutions to the health challenges facing families and communities throughout the world. Read more at oneillinstitute.org and connect with us on Twitter and Facebook.
About UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
About GNP+
GNP+ is the global network for and by people living with HIV. GNP+ works to improve the quality of life of all people living with HIV. GNP+ advocates for, and supports fair and equal access to treatment, care and support services for people living with HIV around the world. Learn more at gnpplus.net and connect with GNP+ on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
Contact
O’Neill InstituteLauren Dueck
Lauren.Dueck@Georgetown.edu
UNAIDS
Sophie Barton-Knott
bartonknotts@unaids.org
GNP+
Lesego Tlhwale
ltlhwale@gnpplus.net
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
Documents
2020 Global AIDS Update — Seizing the moment — Tackling entrenched inequalities to end epidemics
06 July 2020
UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic shows that 2020 targets will not be met because of deeply unequal success; COVID-19 risks blowing HIV progress way off course. Missed targets have resulted in 3.5 million more HIV infections and 820 000 more AIDS-related deaths since 2015 than if the world was on track to meet the 2020 targets. In addition, the response could be set back further, by 10 years or more, if the COVID-19 pandemic results in severe disruptions to HIV services.
Visit the special page to read this report interactively and access all related materials
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
Related
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
Slide deck - 2024 global AIDS update
22 July 2024
Core epidemiology slides
22 July 2024


Press Release
UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic shows that 2020 targets will not be met because of deeply unequal success; COVID-19 risks blowing HIV progress way off course
06 July 2020 06 July 2020Missed targets have resulted in 3.5 million more HIV infections and 820 000 more AIDS-related deaths since 2015 than if the world was on track to meet the 2020 targets. In addition, the response could be set back further, by 10 years or more, if the COVID-19 pandemic results in severe disruptions to HIV services.
GENEVA, 6 July 2020—A new report by UNAIDS shows remarkable, but highly unequal, progress, notably in expanding access to antiretroviral therapy. Because the achievements have not been shared equally within and between countries, the global HIV targets set for 2020 will not be reached. The report, Seizing the moment, warns that even the gains made could be lost and progress further stalled if we fail to act. It highlights just how urgent it is for countries to double down and act with greater urgency to reach the millions still left behind.
“Every day in the next decade decisive action is needed to get the world back on track to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, the Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Millions of lives have been saved, particularly the lives of women in Africa. The progress made by many needs to be shared by all communities in all countries. Stigma and discrimination and widespread inequalities are major barriers to ending AIDS. Countries need to listen to the evidence and step up to their human rights responsibilities.”
Fourteen countries have achieved the 90–90–90 HIV treatment targets (90% of people living with HIV know their HIV status, of whom 90% are on antiretroviral treatment and of whom 90% are virally supressed), including Eswatini, which has one of the highest HIV prevalence rates in the world, at 27% in 2019, and which has now surpassed the targets to achieve 95–95–95.
Millions of lives and new infections have been saved by the scale-up of antiretroviral therapy. However, 690 000 people died of AIDS-related illnesses last year and 12.6 million of the 38 million people living with HIV were not accessing the life-saving treatment.
“We cannot rest on our successes, nor be discouraged by setbacks. We must ensure that no one is left behind. We must close the gaps. We are aiming for 100–100–100,” said Ambrose Dlamini, the Prime Minister of Eswatini.
The world is far behind in preventing new HIV infections. Some 1.7 million people were newly infected with the virus, more than three times the global target. There has been progress in eastern and southern Africa, where new HIV infections have reduced by 38% since 2010. This is in stark contrast to eastern Europe and central Asia, which has seen a staggering 72% rise in new HIV infections since 2010. New HIV infections have also risen in the Middle East and North Africa, by 22%, and by 21% in Latin America.
Seizing the moment shows unequal progress, with too many vulnerable people and populations left behind. Around 62% of new HIV infections occurred among key populations and their sexual partners, including gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, people who inject drugs and people in prison, despite them constituting a very small proportion of the general population.
Stigma and discrimination, together with other social inequalities and exclusion, are proving to be key barriers. Marginalized populations who fear judgement, violence or arrest struggle to access sexual and reproductive health services, especially those related to contraception and HIV prevention. Stigma against people living with HIV is still commonplace. At least 82 countries criminalize some form of HIV transmission, exposure or non-disclosure, sex work is criminalized in at least 103 countries and at least 108 countries criminalize the consumption or possession of drugs for personal use.
Women and girls in sub-Saharan Africa continue to be the most affected and accounted for 59% of all new HIV infections in the region in 2019, with 4500 adolescent girls and young women between 15 and 24 years old becoming infected with HIV every week. Young women accounted for 24% of new HIV infections in 2019, despite making up only 10% of the population in sub-Saharan Africa.
However, where HIV services are comprehensively provided, HIV transmission levels are reduced significantly. In Eswatini, Lesotho and South Africa, a high coverage of combination prevention options, including social and economic support for young women and high levels of treatment coverage and viral suppression for previously unreached populations, have narrowed inequality gaps and driven down the incidence of new HIV infections.
The COVID-19 pandemic has seriously impacted the AIDS response and could disrupt it more. A six-month complete disruption in HIV treatment could cause more than 500 000 additional deaths in sub-Saharan Africa over the next year (2020–2021), bringing the region back to 2008 AIDS mortality levels. Even a 20% disruption could cause an additional 110 000 deaths.
“Those of us who survived HIV and fought for life and access to treatment and care cannot afford losing the gains that took so much effort to win. In some Latin American countries we are seeing how HIV resources, medicines, medical staff and equipment are being moved to the fight against COVID-19,” said Gracia Violeta Ross, President of the Bolivian Network of People Living with HIV. “Some good lessons and practices of the HIV response, such as meaningful participation and accountability, are being ignored. We will not allow HIV to be left behind.”
To fight the colliding epidemics of HIV and COVID-19, UNAIDS and partners are leading a global call for a People’s Vaccine for COVID-19, which has been signed by more than 150 world leaders and experts demanding that all vaccines, treatments and tests be patent-free, mass produced and distributed fairly and free for all.
UNAIDS is also urging countries to increase investments in both diseases. In 2019, funding for HIV fell by 7% from 2017, to US$ 18.6 billion. This setback means that funding is 30% short of the US$ 26.2 billion needed to effectively respond to HIV in 2020.
“We cannot have poor countries at the back of the queue. It should not depend on the money in your pocket or the colour of your skin to be protected against these deadly viruses,” said Ms Byanyima. “We cannot take money from one disease to treat another. Both HIV and COVID-19 must be fully funded if we are to avoid massive loss of life.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 22 791 1697 / +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
tel. +41 22 791 4237
communications@unaids.org
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)
Documents
UNAIDS data 2020
06 July 2020
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025