Stigma and discrimination
Documents
End inequalities — Zero Discrimination Day brochure
25 February 2021
On Zero Discrimination Day this year, UNAIDS is highlighting the urgent need to take action to end the inequalities surrounding income, sex, age, health status, occupation, disability, sexual orientation, drug use, gender identity, race, class, ethnicity and religion that continue to persist around the world.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
 Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”
Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”

01 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024


Feature Story
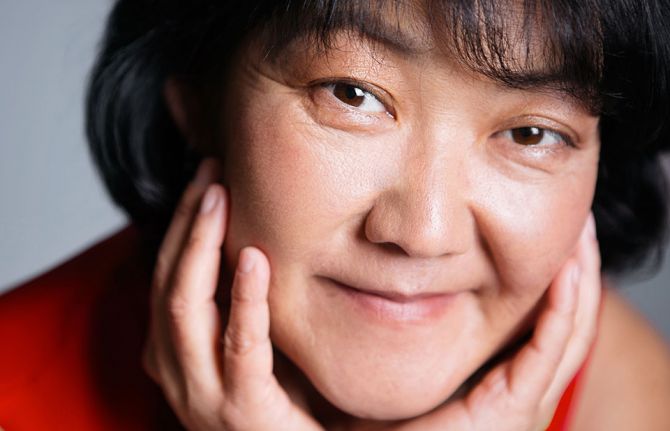
People living with HIV in Kyrgyzstan have won the right to adopt
12 February 2021
12 February 2021 12 February 2021At the end of January 2021, the Kyrgyzstan Constitutional Court decided to exclude HIV from the list of diseases that prevent people from adopting children or becoming guardians or foster parents. The barrier to parenting for people living with HIV in the country had been in effect for many years.
The change—brought about by a joint effort of activists, lawyers and human rights defenders, but primarily by people who personally suffered from discrimination and fought for their rights—is a victory against stigma and discrimination against people living with HIV in Kyrgyzstan.
Baktygul Israilova, pictured above and who leads the Country Network of Women Living with HIV, is one of those who were affected. Several years ago, she wanted to adopt a child. “At that time, I did not fully understand the depth of the problem. I thought that if I prepared all the necessary documents, submitted them to the right department, they would consider me and make a positive decision,” Ms Israilova said. “I am a mother of two wonderful girls, I have a job, a stable job, so at that time it seemed that everything should be on my side.”
When she found out that she could not adopt a child because of her HIV status, she was shocked. “I’m used to the fact that people living with HIV are constantly discriminated against, but why can’t they become parents and give their love and care to a child from an orphanage?” she said.
At that time, Ms Israilova was starting on her path in HIV activism. “Until that time I was always afraid of something, at first my HIV status. I was worried for my girls, I was worried that I would not find a job, I was afraid that people would not understand me, I was worried that I would not achieve anything in my life. But then I became tired of being afraid. It was a turning point in my life. It was then that I openly declared my HIV status and became the first woman in the country openly living with HIV.”
According to the Kyrgyzstan National Statistical Committee, in 2019 there were more than 2000 children and adolescents under the age of 18 years who were left without parental care, of which 592 were orphans.
In 2018, Ms Israilova met Svetlana Izambayeva, pictured above, an activist from the Russian Federation who is living with HIV and who became one of the first women in the Russian Federation to declare her HIV status openly. Ms Izambayeva had extensive and successful experience in the struggle for the right to adopt in her home country and helped and advised the women in Kyrgyzstan in their battle.
A similar case was being considered by the Kyrgyzstan courts in which the Kyrgyz lawyer Ainura Osmonalieva and lawyers from the Adilet legal clinic were trying to help a woman living with HIV to get custody of her nephew after the death of his mother.
The activists joined forces and resources and studied the entire existing legal framework, international obligations, ratified conventions and the United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS, which the country had committed to implement. The process lasted for two years. Activists from other countries, particularly from the Eurasian Women’s Network on AIDS, helped to collect evidence. The activists highlighted examples of changes in legislation in three eastern European countries—the Republic of Moldova, the Russian Federation and Ukraine. The UNAIDS Country Office in Kyrgyzstan supported the advocacy efforts of the Country Network of Women Living with HIV at all stages and provided technical support to strengthen its organizational and advocacy capacity.
Ms Israilova said that when she had to speak and defend her position before the Constitutional Court judges, she was ready for any developments. “Even if we were given a negative decision, we would not have given up, but tried again and again to achieve a result where every person living with HIV can adopt or become a guardian of a child.”
“When we received a positive decision, I came home and told my girls about what we had achieved. They have long dreamed of a brother and even came up with a name for him. My girls are my light, which illuminates my path. I have managed to achieve a lot in life thanks to the fact that I have them. Now I must prepare all the necessary documents to give happiness to another child,” said Ms Israilova.
Photos: November 2019. Credit: UNAIDS
Region/country
Related


Update
Discriminatory attitudes towards people living with HIV declining in some regions, rebounding in others
25 January 2021
25 January 2021 25 January 2021Among 151 reporting countries, 92 continue to criminalize HIV exposure, transmission and nondisclosure—all grave violations of the rights of people living with HIV that also frustrate efforts to control HIV epidemics. These laws reinforce stigma and discrimination against people living with HIV and those more vulnerable to HIV infection, they disregard up-to-date knowledge on the science of HIV-related risks and harms, and they have adverse impacts on public health.
The most recent data from population-based surveys show that while discriminatory attitudes towards people living with HIV are declining consistently in some regions, they are rebounding in others. In eastern and southern Africa, for instance, discriminatory attitudes have been reduced to historically low levels in some countries. Elsewhere, however, disconcertingly large proportions of adults continue to hold discriminatory attitudes towards people living with HIV. In 25 of 36 countries with recent data on a composite indicator that includes two types of discriminatory attitudes, more than 50% of people aged 15 to 49 years reported having discriminatory attitudes towards people living with HIV.
Our work
Related


Feature Story
Challenge the stigma, pursue your right to health
20 January 2021
20 January 2021 20 January 2021Adolescent girls and young women must boldly and unapologetically seek sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services. The stigma and harmful gender norms associated with sexual and reproductive health and rights are not going anywhere, says Nyasha Phanisa Sithole, a Zimbabwean sexual and reproductive health and rights leader.
“If you are afraid of stigma, then you will not be able to access these services because we are not going to have a stigma-free environment any time soon,” she says.
Working as a sexual and reproductive health and rights advocate and a regional lead for young women’s advocacy, leadership and training at the Athena Network, Ms Sithole believes everyone has a role to play in changing the status quo and influencing decision-making.
“My story is common. It is that of a 16-year-old adolescent girl who needed access to HIV prevention commodities, but only had condoms available and, in rare cases, pre-exposure prophylaxis,” Ms Sithole says, reflecting on her experience as an adolescent.
Despite this common story, the need for comprehensive HIV, sexual and reproductive health and rights and sexual and gender-based violence services in the eastern and southern African region is critical.
Adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years account for 29% of new HIV infections among adults aged 15 years and older in the eastern and southern African region, when they only comprise 10% of the population. This means that there are 3600 new HIV infections per week among adolescent girls and young women in the region, which is more than double that of their male peers (1700 weekly).
The stigma and discrimination that young people face, particularly adolescent girls and young women, to access sexual and reproductive health and rights services creates barriers at various levels, including the individual, interpersonal, community and societal levels.
Furthermore, documented health rights abuses include the unauthorized disclosure of health status, being denied sexual and reproductive health and rights services and related psychological violence.
In 2014, Ms Sithole went undercover as a secret client at a youth-friendly health centre in Harare, Zimbabwe’s capital city, in a district with residential areas and schools. The first person she encountered at the centre was a nosy security guard.
“He asked me: ‘What do you need?’ A health screening, I replied. Then he asked, “Asi wakarumwa?” Meaning, “Have you been bitten?” In Shona, this is street language for someone who has a sexually transmitted infection,” she recalls.
Had she not been well-informed, Ms Sithole says she would have felt scared. “It’s something that can scare you or put you off to say, “It’s just a security guard, why are they mocking me or my situation?” Because imagine if I really had a condition that I wanted to manage, what would happen then?”
Ms Sithole said health-care workers sometimes look at adolescent girls and young women accessing sexual and reproductive health and rights services with disdain and judgement and ask, “How old are you and what do you need the condom or contraception for?”
Considering the stigma attached to accessing sexual and reproductive health and rights services, community organizations play a critical role for adolescent girls and young women. Organizations empower them with sexual and reproductive health and rights information and service referrals.
However, COVID-19 greatly impacted how these organizations work in Zimbabwe, which enforced lockdown restrictions to curb the spread of the virus.
“I think all governments weren’t fair when they clamped down restrictions on each and every organization that was working in communities,” Ms Sithole says, adding that it negatively impacted young people’s access to sexual and reproductive health and rights services.
To mitigate these risks, the Global HIV Prevention Coalition, co-convened by UNAIDS and the United Nations Population Fund, came on board to provide financial and technical support to the Athena Network in 10 countries, including Zimbabwe, to establish What Girls Want focal people in each country. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the focal people, who are adolescent girls and young women, mobilized their peers to conduct dialogues via WhatsApp to discuss the issues they face and seek peer support.
Ms Sithole says governments should invest in policy change and development to create an enabling environment where adolescent girls and young women can access sexual and reproductive health and rights and HIV information and services.
Despite the stigma and discrimination attached to seeking sexual and reproductive health and rights services, Ms Sithole says adolescent girls and young women should realize their power and use their agency to get what they need.
“Think about your life because your life is more important than anything else. So, no matter what happens, if you know there is a service you can access, go for it,” she advises.
Region/country
Related

Update
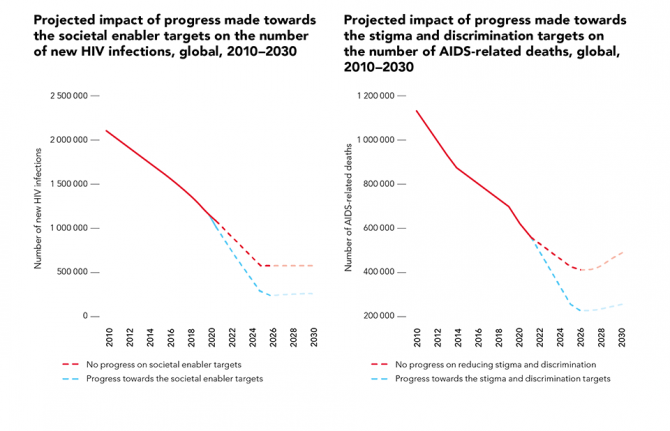
Attaining UNAIDS’ proposed societal and legal barrier targets could stop 440 000 AIDS-related deaths
11 January 2021
11 January 2021 11 January 2021UNAIDS has called on countries to make far greater investments in global pandemic responses and adopt a new set of bold, ambitious but achievable HIV targets for 2025.
An analysis was performed focused on available studies that have quantitatively measured the negative impact that stigma and discrimination and the criminalization of sex work, drug use and same-sex sexual relationships would have on HIV prevention, testing and treatment efforts.
The analysis suggests that failure to make any progress on HIV-related stigma and discrimination would undermine efforts to reach the HIV testing, treatment and viral suppression targets, resulting in an additional 440 000 AIDS-related deaths between 2020 and 2030, and that failure to make any progress across all societal enablers would undermine efforts to reach HIV prevention targets, resulting in 2.6 million additional new HIV infections over the same period.
Our work
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025


Feature Story
Hope from Tiraspol
06 January 2021
06 January 2021 06 January 2021Nadezhda Kilar’s battles with her health service providers began several years ago. “I did not agree with how obstetrics services for women living with HIV are provided in our city,” said Ms Kilar. “From admission to discharge, there was a constant violation of rights.”
Ms Kilar, who lives in Tiraspol, in the Republic of Moldova, has been living with HIV for several years. Her antiretroviral therapy has suppressed her viral load to undetectable levels, but during pregnancy and childbirth she was isolated. She was kept in an isolation ward, gave birth in a separate delivery room and after giving birth was placed in a special room for women living with HIV—a room with bars on the window.
“All the other women leave through the front door, where relatives meet them with flowers and a photographer. But I was let out through the back exit, where there are garbage cans,” she said.
And the discrimination did not stop with her. “Although my son does not have HIV, in the maternity hospital he was alone in a separate special room, under a sign with “HIV contact” written on. Why should a child feel this stigma?” Ms Kilar said.
“I want to give birth to my next child in a normal maternity hospital. And I do not doubt that it will be so. For something to change, a lot still needs to be done, but the main thing is I must defend my rights,” she said.
Ms Kilar’s relationship with her husband started to break down after he became violent towards her. For a long time, she didn’t do anything about it, as she thought that violence was the norm. “My father often beat my mother; I myself was twice in hospital after his beatings.” Not knowing what to do, she sank deeper and deeper into depression. “I didn’t want to live,” she said.
But change slowly came about. When she realized that she could not cope with her financial problems, the violence and her depression, on the advice of a peer consultant at the HIV clinic she attends in Tiraspol she joined the Women’s Mentoring Programme, along with 20 other women living with HIV from different communities in the area. The Women’s Mentoring Programme, a joint project of UN Women and UNAIDS and supported by the Government of Sweden, works through peer consultants and mentors to help women living with HIV to understand and identify their problems, learn about their rights and get support in the fight against violence and discrimination.
“I understood that it would not be the same as before. I realized that I would not tolerate the beatings,” Ms Kilar said.
Since 2019, Ms Kilar has been working in a sales job and has been studying at the university to become a teacher. “It’s not easy for me. I do not sleep much at night, but I have gained confidence that I can solve problems on my own,” she said.
Iren Goryachaya, the Programme Coordinator for the Women’s Mentoring Programme, explained that the programme provides a range of services. “We not only deal with the issues of discrimination in a health-care institution or the fight against violence—we see a woman as a person from different perspectives. First, it is important to help women accept their HIV status and overcome self-stigma. Without this, it is impossible to achieve a different attitude towards herself either from doctors or men.”
“Often, women in the Republic of Moldova have insufficient access to reliable information about HIV. They still cannot defend their right to safe sex. Various forms of violence, including sexual violence, the widespread violation of women’s rights and the controlling behaviour of men further aggravate the situation. All this deprives women of the opportunity to defend their right to health,” said Svetlana Plamadeala, the UNAIDS Representative for the Republic of Moldova.
Ms Kilar looks to the future with confidence. “I see myself as a free woman. I do what I want. My children are growing up in a safe environment. I don't worry about my HIV diagnosis. If I decide to have another child, I will give birth in a normal hospital.”
Our work
Region/country
Related


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes Suki Beavers as UNAIDS Director of Gender Equality, Human Rights and Community Engagement
16 November 2020 16 November 2020GENEVA, 16 November 2020—UNAIDS is delighted to announce the appointment of Suki Beavers to the position of Director, Gender Equality, Human Rights and Community Engagement in UNAIDS Programme Branch.
Ms Beavers will be joining from the National Association of Women and the Law in Canada, where in her position as Executive Director, she led efforts to develop high quality feminist legal analysis and law reform strategies to advance the rights and empowerment of women in all their diversity.
“With a wealth of experience in women’s rights and empowerment, sexual and gender-based violence, sexual and reproductive health, and human rights Ms Beavers will be a huge asset to UNAIDS,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Her passion and dedication in standing up for the rights of women and the most vulnerable will be invaluable in advancing UNAIDS work in these critical areas.”
In her new role Ms Beavers will be leading UNAIDS work to address human rights challenges, including stigma and discrimination, inequality and violence against women and girls, misuse of criminal law and punitive approaches which remain among the main barriers to effective HIV responses. She will also oversee UNAIDS work on achieving gender equality, advancing women’s empowerment and fulfilling the sexual and reproductive health and rights of women and girls. In addition, she will be leading work to support the critical role of community action in advocacy, participation and coordination of AIDS responses and service delivery.
“I am honoured to be joining UNAIDS, especially now as we work to scale up the global, regional, national and local efforts required to advance the rights of women and girls, end stigma and discrimination, and strengthen and expand community engagement as critical components of the HIV response,” said Ms Beavers.
UNAIDS would also like to thank Luisa Cabal for assuming the role of interim Director of the Department since June 2019.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Feature Story
Interactive TV series about HIV launched in Kyrgyzstan
13 November 2020
13 November 2020 13 November 2020A new television series for young people in the Kyrgyz language, School Elections, was launched online last week. During six 15–20-minute episodes, a girl, Ayana, who is living with HIV, tells her story of bullying, friendship and the fight for human dignity. The producers of the series hope that Ayana’s example will give hope to young people who face similar challenges.
“We have a simple idea to promote: you may differ from others in your health, appearance or level of wealth. But regardless of this, we all deserve respect, friendship, love and happiness. This series is about kindness and acceptance of others as they are,” said Azim Azimov, Head of Production at the Media Kitchen production studio and the main screenwriter of the series.
Starting on 6 November, new episodes will be aired weekly on YouTube and will also be broadcast on television, Instagram and the teens.kg youth project website. Additionally, each series has one to three interactive episodes—the leading actors invite the viewers to look at the problems raised in the series through the viewers’ eyes, experience each situation for themselves and make their own decisions.
According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), more than 30% of students around the world experience various forms of bullying at the hands of their classmates. Students who are perceived as “different” are often subjected to bullying for reasons of appearance, health status, including HIV status, sexual orientation and gender identity, social status or the economic situation of the family.
“This series tells people about the complex issue in simple and understandable language, to show how strong-willed and honest young people can overcome ignorance, indifference, cruelty and injustice, inspire others and change life for the better,” said Tigran Yepoyan, UNESCO Regional Adviser on HIV, Education and Health.
“This series is a powerful new instrument for reducing stigma in our society, it not only shows the difficulties of living with HIV, discrimination and bullying but also motivates our adolescents not to be afraid to fight for dignity and justice and move forward towards their dreams,” said Meerim Sarybaeva, UNAIDS Country Director for Kyrgyzstan.
The official soundtrack of the series, which was supported by the UNESCO Institute for Information Technologies in Education and UNAIDS, was performed by the singer Ayim Ayilchieva.
Our work
YouTube 1 st series
Soundtrack
Interactive episodes
Region/country
Related
Documents
Evidence for eliminating HIV-related stigma and discrimination — Guidance for countries to implement effective programmes to eliminate HIV-related stigma and discrimination in six settings
24 April 2020
This report reviews the latest evidence on what works to reduce HIV-related stigma and discrimination through key programmes to reduce stigma and discrimination and increase access to justice in the six settings of focus for the Global Partnership. It includes guidance for national governments and key stakeholders on how stigma and discrimination harm; how the stigmatization process operates and how we can stop it; key principles of stigma- and discrimination-reduction efforts; an overview of common intervention approaches; recommendations based on the latest evidence for reducing HIV-related stigma and discrimination in the six settings; and an overview of considerations for monitoring the success of the programmatic interventions recommended for each setting.
Related
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
 Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”
Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”

01 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024