Stigma and discrimination
Documents
UNAIDS data 2022
20 January 2023
Every year UNAIDS provides revised global, regional and country-specific modelled estimates using the best available epidemiological and programmatic data to track the HIV epidemic. Modelled estimates are required because it is not possible to count the exact number of people living with HIV, people who are newly infected with HIV or people who have died from AIDS-related causes in any country: doing so would require regularly testing every person for HIV and investigating all deaths, which is logistically infeasible and ethically problematic. Modelled estimates—and the lower and upper bounds around these estimates—provide a scientifically appropriate way of describing HIV epidemic levels and trends.


Press Statement
UNAIDS congratulates Barbados on its decision to repeal colonial-era laws that criminalised same sex sexual relations
13 December 2022 13 December 2022GENEVA, 13 December 2022—UNAIDS welcomes the judgement by the High Court in Barbados to strike down the country’s colonial-era gross indecency and buggery laws that criminalised consensual same-sex relations.
“This historic decision is a significant step towards protecting the human rights and dignity of LGBT people in Barbados,” said Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. “It will also strengthen the country’s HIV response by helping to reduce stigma and discrimination faced by LGBT people and increasing the uptake of HIV testing, treatment and prevention services.”
Under section 9 of the Barbados Sexual Offences Act, punishment could lead to life imprisonment for men engaging in same-sex sexual activity. Under section 12, both men and women were criminalised and liable to up to 10 years imprisonment. Laws that punish consensual same sex relations, in addition to contravening the human rights of LGBT people, act as a barrier to improving health outcomes, including in the HIV response. Such laws sustain stigma and discrimination against LGBT people and stop LGBT people seeking and receiving healthcare for fear of being punished or detained. Decriminalisation saves and changes lives and builds stronger societies.
Barbados becomes the third Caribbean country this year to announce the repeal of such discriminatory legislation. The case was filed by two Barbadian LGBT advocates with local organisation Equals Barbados providing community support, and the regional LGBT umbrella organisation, the Eastern Caribbean Alliance for Diversity and Equality, convening the process.
Earlier this year, courts in Antigua and Barbuda and St Kitts and Nevis also struck down as unconstitutional laws that criminalised gay men and other men who have sex with men. There now remain six countries in the Caribbean that criminalize gay sex between consenting adults, all of them former British colonies. They are Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, St. Lucia, and St. Vincent and the Grenadines.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the recent decision of the government of the Republic of Kazakhstan to remove the remaining legal barriers for people living with HIV to adopt children
07 December 2022 07 December 2022The 2020 Kazakhstan Code on Public Health and Health Care System guaranteed the right of people living with HIV to adopt children. However, certain bylaw regulations remained that created barriers for people living with HIV to enjoy the right to adopt children. On 1 December 2022, the day the world commemorated World AIDS Day, the Ministry of Health removed this remaining barrier.
UNADS welcomes this progressive action as reaffirmation of Kazakhstan’s continuing commitment to eliminate stigma and discrimination against people living with and affected by HIV.
UNAIDS Country Director in Kazakhstan Gabriela IONASCU said, “Living with HIV is no longer seen as an impediment to adopting and raising children. By excluding HIV from the list of diseases that prevent people from adopting children or becoming guardians or foster parents, Kazakhstan is taking bold steps to advance in the right direction: ensuring human rights for all, including for people living with HIV.”
It furthermore underlines Kazakhstan’s commitment to guaranteeing human rights for all leaving no one behind, including activities under the framework of the Global Partnership for Action to Eliminate All Forms of HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination which the Republic of Kazakhstan joined in 2021 among 30 other pilot countries.
“Similar changes in legislation were made in other eastern European and central Asian countries, including the Kyrgyz Republic, the Republic of Moldova, the Russian Federation, and Ukraine. UNAIDS reaffirms its commitment to provide technical assistance and expert support to advance progress to end AIDS in Kazakhstan and support all people living with and affected by HIV across the region,” said Eamonn Murphy, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director and Regional Director for Eastern Europe and Central Asia
Note: The decree of the Ministry of Health of The Republic of Kazakhstan
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS again urges Russia to repeal 'LGBTQ propaganda' law
25 November 2022 25 November 2022Responding to the decision of the Russian Duma to pass a further extension of the so-called “LGBTQ propaganda law”, UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima reiterated her deep concern about the damaging consequences of such laws for public health.
“In addition to violating the rights of people to autonomy, dignity and equality, and harming the security and general wellbeing of LGBTQ individuals, this decision will seriously hurt public health. It will undermine Russia’s efforts to end AIDS by 2030. Punitive and restrictive laws increase the risk of acquiring HIV and decrease access to services, reduce the ability of service providers, including peer networks, to provide critical sexual and reproductive health information and services, and increase stigma related to sexual orientation. Such laws make it harder for people to protect their health and that of their communities. We urge the repeal of this harmful law.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS urges Russia to repeal 'LGBTQ propaganda' law
28 October 2022 28 October 2022GENEVA, 29 October 2022—Responding to the statement by the Russian government that it intends to extend the so-called “LGBTQ propaganda” law, UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima has joined with UN High Commissioner for Human Rights in expressing deep concern.
“Extension of this law,” said Ms Byanyima, “is a further violation of the rights of people to autonomy, dignity and equality. Not only will it harm the security and general wellbeing of LGBTQ individuals, it will have a serious negative impact on people’s health outcomes. The evidence is clear that punitive and restrictive laws, including those restricting free speech, increase the risk of acquiring HIV and decrease access to services. Such laws reduce the ability of service providers, including peer networks, to provide critical sexual and reproductive health information and services, and increase stigma related to sexual orientation, making it harder for people to protect their health and that of their communities. This will undermine Russia’s efforts to end AIDS by 2030. Our call to the Parliament and Government of Russia is to withdraw these harmful proposals and indeed to repeal the existing law. Stigmatising approaches damage public health, perpetuate pandemics and hurt everyone. Social solidarity, inclusion and protecting every person’s human rights are key to ending AIDS and ensuring health for all.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights
Region/country


Feature Story
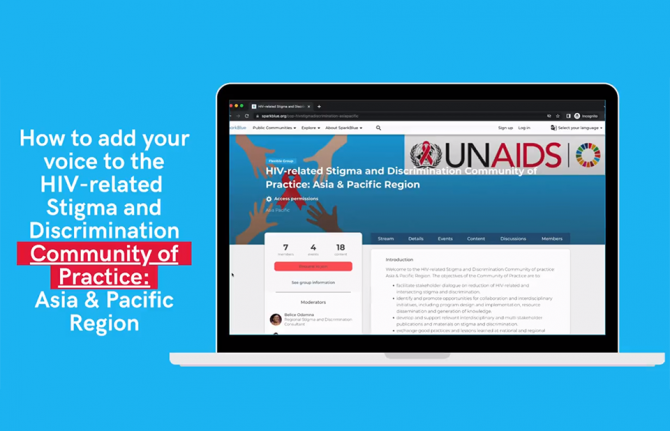
UNAIDS launches new platform on ending HIV-related stigma and discrimination in the Asia and Pacific region
07 September 2022
07 September 2022 07 September 2022Despite decades of advances in prevention and treatment, stigma and discrimination towards people living with HIV and key populations are a persistent barrier to addressing the epidemic. To encourage innovative approaches to address HIV-related stigma and discrimination in the region, UNAIDS has launched a new tool: the HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination Community of Practice: Asia and Pacific Region.
HIV-related stigma and discrimination significantly impacts the health, lives and well-being of people living with or at risk of HIV, especially key populations. The Global AIDS Strategy 2021-2026 has prioritized the realization of human rights and elimination of stigma and discrimination by including new global targets that UN Member States have committed to as part of the 2021 Political Declaration. Yet, people living with HIV and key populations continue to face unfair treatment, rejection, abuse and even violence in various settings, including in their communities, healthcare, workplace, justice and education systems.
In Asia and the Pacific, which is the world’s most populous region, there were 6 million people living with HIV in 2021 and 86% of people living with HIV knew their status. Furthermore, amongst young people almost all new HIV infections are among key populations (gay men and other men who have sex with men, transgender people, sex workers, people who use drugs) and their sex partners who face many barriers in accessing HIV prevention and treatment services.
The online community of practice platform will capture and disseminate knowledge, experiences and innovative ideas and approaches to inform programming to reduce stigma and discrimination across the region.
“Relevant stakeholders working in the HIV response in Asia and the Pacific region are welcome to join the interactive platform and engage on the issues,” said Taoufik Bakkali, UNAIDS Regional Director for Asia and the Pacific. “Academics and researchers, communities of people living with or affected by HIV and of key populations, representatives of government ministries and other relevant government agencies, and civil society groups working on the HIV response are all encouraged to join and shape the conversation.”
The initiative is expected to foster south-south stakeholder dialogue and collaboration on interdisciplinary initiatives on programme design and implementation, the development and knowledge management of HIV-related stigma and discrimination and the creation of opportunities for peer learning and exchange of good practices and lessons learned.
“This platform provides an opportunity for all stakeholders to engage and shape responses to HIV-related stigma and discrimination while engaging communities in the process,” noted Harry Prabowo, the APN+ Program Manager. “This is an opportunity to link the science and evidence to innovative programming.”
Region/country
Related
 Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia
Status of HIV Programmes in Indonesia

24 February 2025
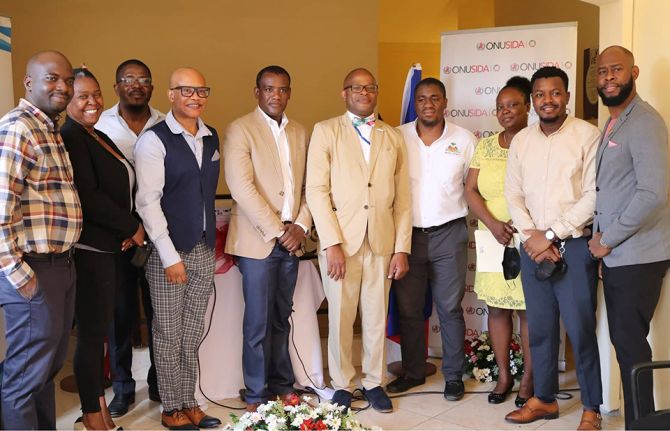








Feature Story
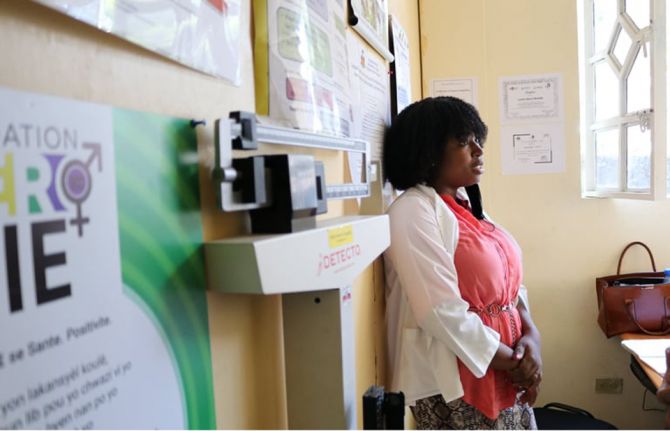
A model for serving key populations from Haiti
16 August 2022
16 August 2022 16 August 2022Imagine being widely blamed for tragedies that befall your country. Earthquakes. Hurricanes. Floods.
Now imagine being excluded from disaster response efforts because of this.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Haiti face profound prejudice. Discrimination often undermines life chances. Education and employment opportunities erode. Even accessing healthcare can be difficult.
Founded in 1999, the SEROvie Foundation pairs health promotion for the LGBT community with human rights advocacy and socioeconomic empowerment. Today the organization operates projects in nine geographical departments.
UNAIDS supports SEROvie to ensure that the needs of key population communities are addressed during disaster responses. This intervention ensures people living with HIV continue to receive HIV treatment and have timely access to aid. Beyond the emergency phase, beneficiaries get support to resume generating incomes and reintegrate into their homes. They also receive psychosocial support to cope with grief and trauma.
In 2016 SEROvie founded the J.C Ménard Clinic in Port au Prince. This clinic serves LGBT people and other key populations including female sex workers and their clients. Here SEROvie has distilled more than two decades' experience in providing health and social support into a complete service package.
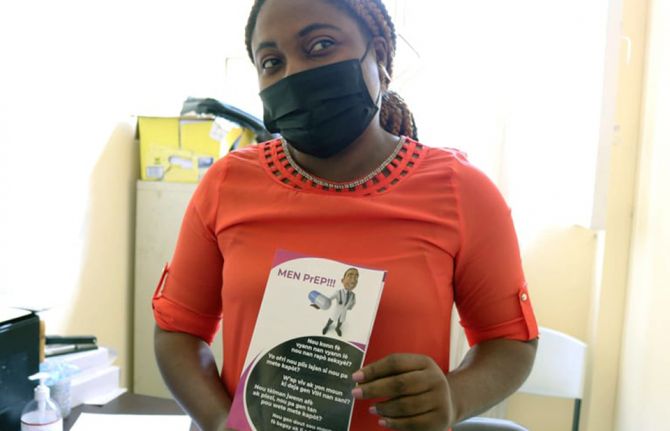
With the assistance of several collaborators including the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), J.C Ménard offers a range of free-to-user services addressing gender-based violence, stigma and discrimination, family planning and HIV prevention, including PrEP. It also provides HIV, STI and TB treatment and care.
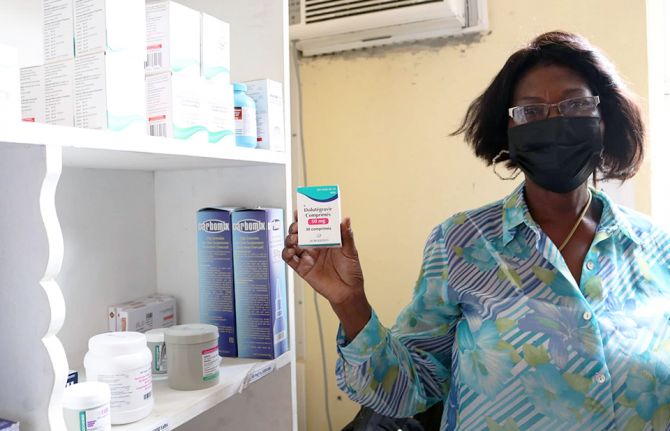
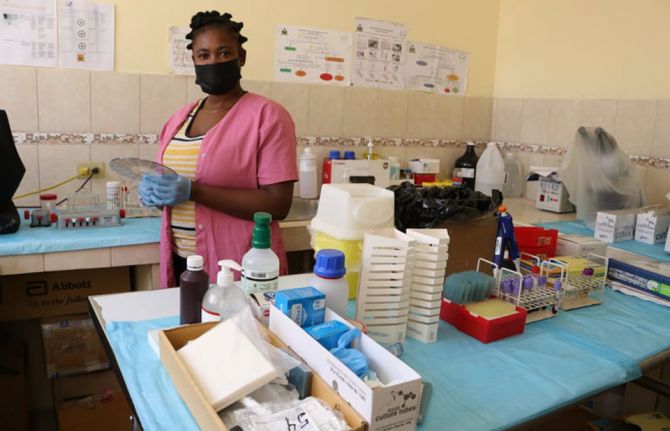
At the in-house laboratory, technicians manage both diagnostics and treatment monitoring. They track individual journeys from positive test to viral suppression. Over the last year the clinic provided facility-based HIV testing for 6,000 people and supported HIV treatment management for over 1,500 clients. Apart from dispensing patients' medicines, the clinic coordinates with other treatment facilities to ensure there are no stockouts and drugs do not expire.
Social workers conduct individual assessments to determine clients' needs. Psychologist, Darline Armand says the most important moment in her work is the first interaction after someone has been diagnosed.
"They need to feel safe," she says.
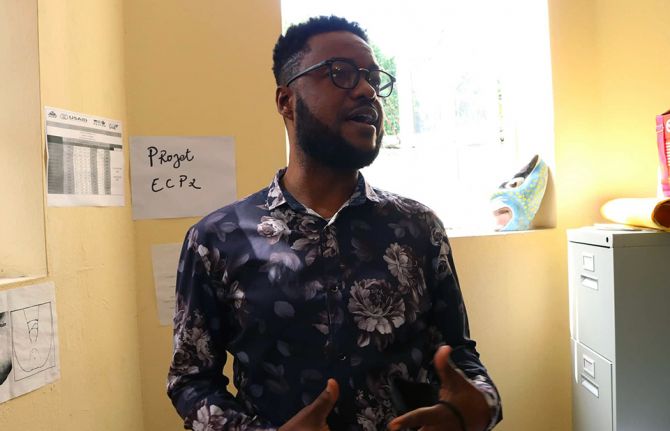
Peer Supervisor, Gregory Jacques, explained that the clinic employs both peer education and peer navigation as strategic approaches. Educators engage clients about relationships, risk and safety, providing accurate information. Navigators are themselves people living with HIV who walk others through the treatment and care process.
"The thing that makes a difference is that they know you are just like them," one navigator explains.
In the community room clients learn about health and relationships through fun activities. This is also where they meet for support groups and dialogues.
The Monitoring and Evaluation team measures programme performance with painstaking detail. They track everything from the number of people living with HIV identified through index testing to the number of sensitization sessions conducted with Voodoo priests. Over the past year more than 15,000 people received awareness-raising messages on HIV, GBV, stigma and discrimination from the clinic. Over 1,500 people benefit from comprehensive HIV care and treatment services while more than 1,500 are on PrEP.
Steeve Laguerre, SEROvie's co-founder, reflects on the organization’s journey with both awe and clarity.
"The services we provide are entirely determined by the needs of the people we serve," he says. "We seek funding that aligns with their demands. The work is always client-driven."
This client-centred approach is valuable for the wider Caribbean. According to the 2022 Global AIDS Update, In Danger, last year four of five new infections in the region were linked to key population communities and their sexual partners. At the same time, most of the funding for regional combination prevention activities with key populations comes from international sources.
“Community-led strategies for patient care help reduce late diagnosis and loss to follow-up while improving treatment outcomes,” said Dr. Christian Mouala, UNAIDS Country Director for Haiti. “These approaches must be adequately resourced and integrated into the national response.”
Region/country
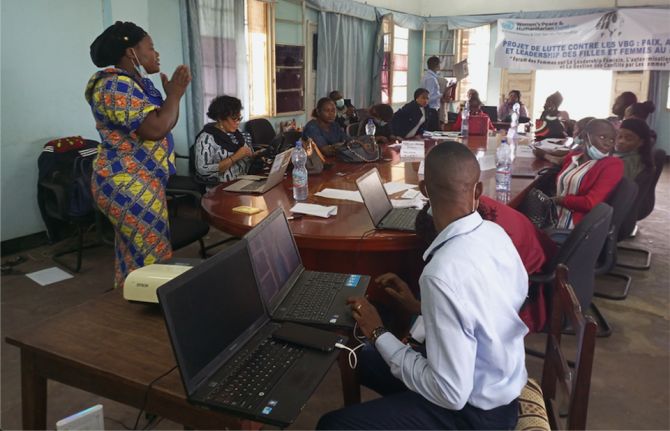




Feature Story
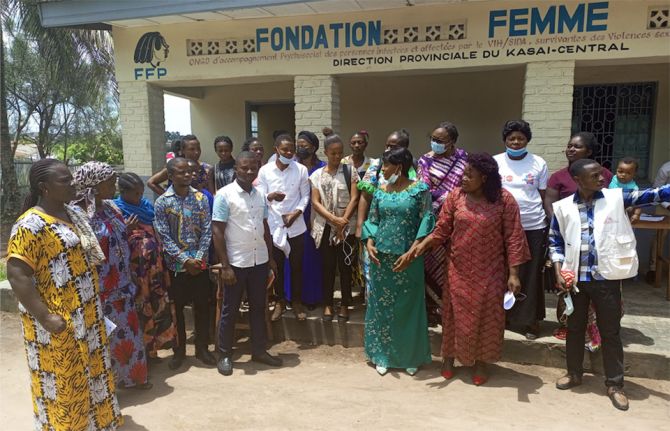
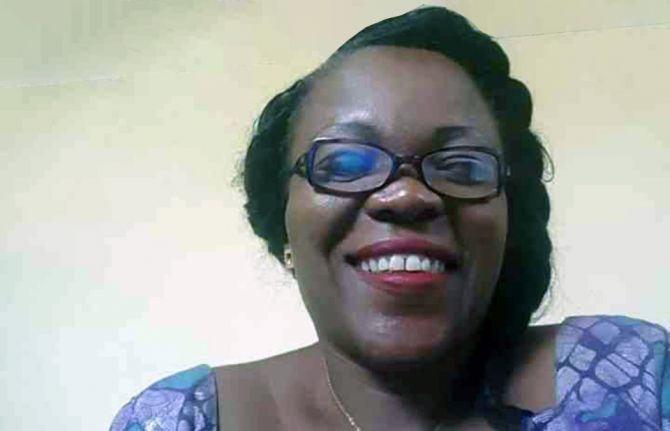
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, Thérèse Omari maintains her commitment to ending AIDS and providing a fulfilling and harmonious life for people living with HIV
28 July 2022
28 July 2022 28 July 2022"We are here, we are not giving up". These are the encouraging words of Thérèse Omari, an activist who has been involved in the fight against AIDS for more than 20 years within the Femme Plus organisation, of which she is the co-founder and National Director in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Femme Plus, true to its motto "Positive Life", works to improve the quality of life of people living with HIV. "The objective is for our beneficiaries to live in harmony with themselves, with their environment and with their beliefs," explains Ms Omari.
To this end, the organisation provides psychosocial support to people living with or affected by HIV through counselling, care and support services. Femme Plus also carries out numerous activities in communities to free people living with HIV from the burden of stigma. "There is still a lot to be done to change behaviours towards people living with HIV," says Ms Omari. In the Democratic Republic of Congo, HIV-related stigma is still very present, especially in community settings. "Many people living with HIV say they no longer participate in family gatherings and other events fearing discrimination. It is therefore essential that people who come to Femme Plus feel that they are considered normal people with rights and obligations," she explains. In order to raise awareness, the organisation runs workshops to provide communities with the knowledge to better support people living with HIV, without isolating them or treating them differently.
Ms Omari also deplores the persistence of stigma and discrimination in health care settings despite the numerous HIV-related trainings for health care workers. In particular, she receives testimonies from pregnant women who have tested positive for HIV in one facility and wish to give birth in another, fearing of being stigmatised and treated differently. This is problematic as it can be detrimental to the provision of appropriate care for the mother and baby.
Ending discrimination and ensuring that the rights of people living with HIV are protected is therefore one of Femmes Plus' priorities to help them assert themselves and make the right choices about their health. "We encourage people living with HIV to empower themselves, to speak up about their condition, for their own well-being," says Ms Omari.
Ms Omari also raises other obstacles to the AIDS response. The lack of access to prevention and treatment, and the low rate of people with an undetectable viral load, are among the shortcomings of the fight against HIV in the Democratic Republic of Congo. "Not everyone has access to testing. There are still people with HIV who live in anonymity," warns Ms Omari.
To overcome this gap, Femme Plus works with community leaders to teach them how to stay healthy with HIV. Among other activities, it also engages with pregnant and breastfeeding women, providing them with the knowledge to protect their babies and thereby stop vertical transmission.
"As long as there are people who do not know their HIV status, who do not have access to treatment and who have not reached an undetectable viral load, the fight of Femme Plus will remain meaningful," insists Ms Omari.
She concludes by pointing out that the fight against AIDS in the Democratic Republic of Congo is taking place in a context where resources are limited. "The local population must be involved in psychosocial care and prevention activities to make HIV an electoral issue," she explains. While waiting for more substantial funding from the State and better traceability of funds, community-led services have a crucial role to play with people living with HIV. They are at the heart of the fight against AIDS, advocating for access to prevention and life-saving care, calling for respect for human rights and addressing the specific needs of their beneficiaries. Their support is therefore pivotal in meeting the challenges of the HIV response and ending AIDS by 2030.
Region/country
Related
Documents
So what's stopping us from ending AIDS?
10 July 2022
What if I told you we could end the AIDS epidemic by 2030? So what's stopping us? Well, we're stopping ourselves.
Related
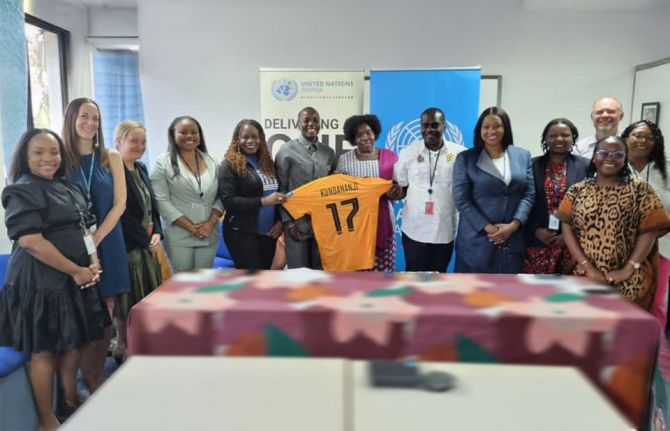 Zambian football star Racheal Kundananji named UNAIDS Goodwill Ambassador for Education Plus in Zambia
Zambian football star Racheal Kundananji named UNAIDS Goodwill Ambassador for Education Plus in Zambia

23 January 2025
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024
 Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”
Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”

01 December 2024
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
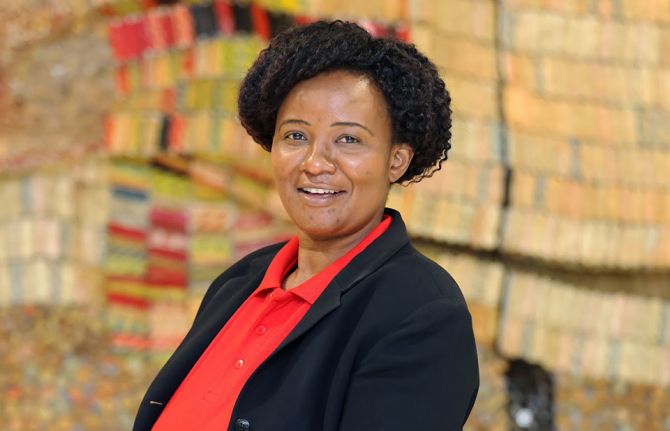 Evelyn Siula: A journey of strength and solidarity
Evelyn Siula: A journey of strength and solidarity
18 November 2024
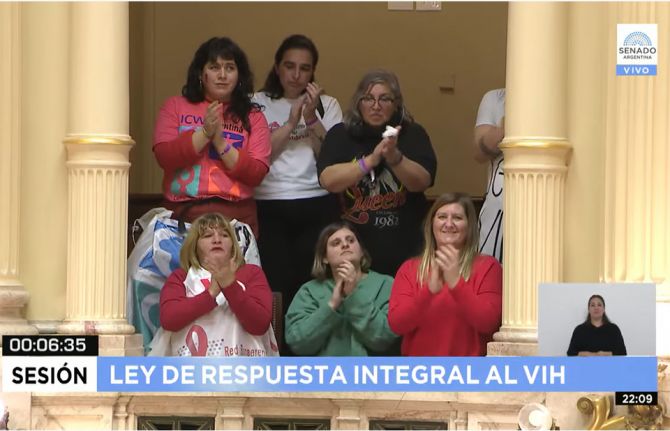




Press Statement
UNAIDS applauds Argentina for the approval of its new human rights-based HIV law
04 July 2022 04 July 20224 July 2022—UNAIDS congratulates the Argentinian Congress on the approval of a new law on a comprehensive response to HIV, viral hepatitis, tuberculosis and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The bill, which has had input from a number of civil society organizations, replaces 30-year-old legislation and changes the country’s health approach from a biomedical approach to an approach more focused on gender and human rights. The new law calls for an end to stigma and discrimination against people living with HIV or STIs and aims to stop criminalization of HIV exposure or transmission.
By prohibiting mandatory testing for HIV and other STIs as part of pre-employment exams, the new law also seeks to protect against discrimination in all areas (with emphasis on the workplace) and ensures the privacy of the diagnosis.
“We join the civil society and community movements in this important celebration. The new law is evidence-based and written from the perspective of human rights,” celebrates Alberto Stella, UNAIDS Country Director for Argentina, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay. “The HIV response in the country now counts on a broad framework of social protection, very much in line with the Global AIDS Strategy (2021-2026), which focuses on ending inequalities to end the AIDS epidemic.”
Besides eradicating discriminatory practices, the new legislation also includes the possibility of early retirement at 50 years old for people who have been living with the virus for ten years and who have paid at least 20 years of pension contributions. It also allows access to a non-contributory pension for life in cases of social vulnerability.
The new bill pays a historical debt for dozens of activists who occupied the balconies of Congress in recent voting sessions and the thousands of people living with HIV they represent. “We are one step closer to eliminating barriers to the implementation of self-testing and promoting prevention strategies such as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)”, celebrated Fundación Huesped, an Argentinian organization with a regional reach that has advocated for the right to health since 1989.
The new law also recognizes specific rights of women, guarantees the right to health of their children and ensures compliance with the rights recognized in the law for the Integral Protection of Women.
“This is the result of the articulated work conducted by civil society who not only led its elaboration but who also did excellent and hard work on advocacy,” says Stella. “Along with the National HIV, TB, Hepatitis and STI department of the Ministry of Health, UNAIDS was able to contribute with advocacy efforts and the facilitation of dialogues, providing evidence and the informing on international guidelines.”
The new bill also proposes the national production of medication and supplies.
The latest estimates from the UNAIDS 2021 Global AIDS Update report show that 140 000 people are living with HIV in Argentina and 65% of whom are on antiretroviral treatment. Every year 5600 people are newly infected with HIV, and 1400 people die from AIDS-related illnesses.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.