Punitive laws


Press Release
Ahead of World AIDS Day UNAIDS is calling for urgent support to Let Communities Lead in the fight to end AIDS
30 November 2023 30 November 2023A new report by UNAIDS demonstrates the critical role communities play, and how underfunding and harmful barriers are holding back their lifesaving work and obstructing the end of AIDS.
LONDON/GENEVA, 28 November 2023—As World AIDS Day (1 December) approaches, UNAIDS is urging governments across the world to unleash the power of grassroots communities across the world to lead the fight to end AIDS. A new report launched today by UNAIDS, Let Communities Lead, shows that AIDS can be ended as a public health threat by 2030, but only if communities on the frontlines get the full support they need from governments and donors.
“Communities across the world have shown that they are ready, willing and able to lead the way. But they need the barriers obstructing their work to be pulled down, and they need to be properly resourced,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Too often, communities are treated by decision-makers as problems to be managed, instead of being recognised and supported as leaders. Communities are not in the way, they light the way to the end of AIDS.”
The report, launched in London during a World AIDS Day event organized by the civil society organization STOPAIDS, shows how communities have been the driving force for progress.
Community advocacy from the streets to the courtrooms to parliaments has secured groundbreaking changes in policy. Communities’ campaigning helped open up access to generic HIV medicines, leading to sharp, sustained reductions in the cost of treatment from US$ 25 000 per person per year in 1995 to less than US$ 70 in many countries most affected by HIV today.
Let Communities Lead shows that investing in community-led HIV programmes delivers transformational benefits. It sets out how programmes delivered by community-based organizations in Nigeria were associated with a 64% increase in access to HIV treatment, a doubling of the likelihood of HIV prevention service utilization, and a four-fold increase in consistent condom use among people at risk of HIV. It also notes how, among sex workers reached by a package of peer-based services in the United Republic of Tanzania, the HIV incidence rate was reduced to below half (5% vs 10.4%).
“We are the vehicle for change that can end systematic injustices that continue to fuel HIV transmission. We have seen groundbreaking developments with U=U, improved access to medicines, and have made great strides in decriminalisation," said Robbie Lawlor, Co-Founder of Access to Medicines Ireland. “Yet, we are expected to move mountains without being financially supported. We are supposed to fight for a more equitable world and are tasked with dismantling stigma yet are side-lined in crucial discussions. We are at a tipping point. Communities can no longer be relegated to the periphery. The time for leadership is now.”
The report highlights how communities are at the forefront of innovation. In Windhoek, Namibia, a self-funded project by the youth Empowerment Group is using e-bikes to deliver HIV medicines, food and adherence support to young people who often cannot attend clinics due to their schooling hours. In China, community organizations developed smartphone apps that link people to self-testing which contributed to a more than four-fold increase in HIV tests across the country from 2009 to 2020.
The report reveals how communities are also holding service providers to account. In South Africa five community networks of people living with HIV inspected 400 sites across 29 districts and conducted more than 33 000 interviews with people living with HIV. In the Free State province, these findings led provincial health officials to implement new appointment protocols to reduce clinic wait times and three- and six-month dispensing of antiretroviral medicines.
“I am extremely concerned about the exclusion from health services of key populations like the LGBT+ community,” said Andrew Mitchell, Minister of State for Development and Africa. “The UK champions the rights of such communities, and we will continue to protect them, working closely with our partners in civil society. I thank UNAIDS for keeping us focused on the inequities driving the pandemic and I look forward to working with our partners to champion the voice of people living with HIV and end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.”
Despite the clear evidence of community-led impact, community-led responses are unrecognized, under-resourced and in some places even under attack. Crackdowns on civil society and on the human rights of marginalized communities are obstructing communities from providing HIV prevention and treatment services. Underfunding of community-led initiatives is leaving them struggling to continue operating and holding them back from expansion. If these obstacles are removed, community-led organizations can add even greater impetus to end AIDS.
In the 2021 Political Declaration on ending AIDS, United Nations member states recognized the critical role communities play in HIV service delivery, particularly to people most at risk of HIV. However, whereas in 2012, when over 31% of HIV funding was channelled through civil society organizations, ten years later, in 2021, only 20% of funding for HIV was available—an unprecedented backsliding in commitments which has cost and is continuing to cost lives.
“At this time, community-led action is the most important countermeasure in the AIDS response,” said Solange Baptiste, Executive Director of the International Treatment Preparedness Coalition. “Yet, shockingly, it isn’t a cornerstone of global plans, agendas, strategies, or financing mechanisms for improving pandemic preparedness and health for all. It is time to change that.”
Every minute, a life is lost to AIDS. Every week, 4000 girls and young women become infected with HIV, and out of the 39 million people living with HIV, 9.2 million do not have access to lifesaving treatment. There is a Path that Ends AIDS and AIDS can be ended by 2030, but only if communities lead.
UNAIDS is calling for: Communities’ leadership roles to be made core in all HIV plans and programmes; Communities’ leadership roles to be fully and reliably funded; And for barriers to communities’ leadership roles to be removed.
The report features nine guest essays from community leaders, in which they share their experience on the achievements they have secured, the barriers they face, and what the world needs to end AIDS as a public health threat.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDS GenevaSophie Barton Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS Media
communications@unaids.org
UNAIDS Geneva
Michael Hollingdale
tel. +41 79 500 2119
hollingdalem@unaids.org
World AIDS Day message
World AIDS Day 2023
Watch the launch
World AIDS Day report
World AIDS Day videos


Press Release
New report from UNAIDS shows that AIDS can be ended by 2030 and outlines the path to get there
13 July 2023 13 July 2023GENEVA, 13 July 2023—A new report released today by UNAIDS shows that there is a clear path that ends AIDS. This path will also help prepare for and tackle future pandemics and advance progress towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. The report, ‘The Path that Ends AIDS’, contains data and case studies which highlight that ending AIDS is a political and financial choice, and that the countries and leaders who are already following the path are achieving extraordinary results.
Botswana, Eswatini, Rwanda, the United Republic of Tanzania, and Zimbabwe have already achieved the “95-95-95” targets. That means 95% of the people who are living with HIV knowing their HIV status, 95% of the people who know that they are living with HIV being on lifesaving antiretroviral treatment, and 95% of people who are on treatment being virally suppressed. A further 16 other countries, eight of them in sub-Saharan Africa, the region which accounts for 65% of all people living with HIV, are also close to doing so.
“The end of AIDS is an opportunity for a uniquely powerful legacy for today’s leaders,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “They could be remembered by future generations as those who put a stop to the world’s deadliest pandemic. They could save millions of lives and protect the health of everyone. They could show what leadership can do.”
The report highlights that HIV responses succeed when they are anchored in strong political leadership. This means following the data, science, and evidence; tackling the inequalities holding back progress; enabling communities and civil society organizations in their vital role in the response; and ensuring sufficient and sustainable funding.
Progress has been strongest in the countries and regions that have the most financial investments, such as in eastern and southern Africa where new HIV infections have been reduced by 57% since 2010.
Thanks to support for and investment in ending AIDS among children, 82% of pregnant and breastfeeding women living with HIV globally were accessing antiretroviral treatment in 2022, up from 46% in 2010. This has led to a 58% reduction in new HIV infections among children from 2010 to 2022, the lowest number since the 1980’s.
Progress in the HIV response has been strengthened by ensuring that legal and policy frameworks do not undermine human rights, but enable and protect them. Several countries removed harmful laws in 2022 and 2023, including five (Antigua and Barbuda, the Cook Islands, Barbados, Saint Kitts and Nevis, and Singapore) that have decriminalized same-sex sexual relations.
The number of people on antiretroviral treatment worldwide rose almost fourfold, from 7.7 million in 2010 to 29.8 million in 2022.
However, the report also sets out that ending AIDS will not come automatically. AIDS claimed a life every minute in 2022. Around 9.2 million people still miss out on treatment, including 660 000 children living with HIV.
Women and girls are still disproportionately affected, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. Globally, 4,000 young women and girls became infected with HIV every week in 2022. Only 42% of districts with HIV incidence over 0.3% in sub-Saharan Africa are currently covered with dedicated HIV prevention programmes for adolescent girls and young women.
Almost one quarter (23%) of new HIV infections were in Asia and the Pacific where new infections are rising alarmingly in some countries. Steep increases in new infections are continuing in eastern Europe and central Asia (a rise of 49% since 2010) and in the Middle East and North Africa (a rise of 61% since 2010). These trends are due primarily to a lack of HIV prevention services for marginalized and key populations and the barriers posed by punitive laws and social discrimination.
Funding for HIV also declined in 2022 from both international and domestic sources, falling back to the same level as in 2013. Funding amounted to US$ 20.8 billion in 2022, far short of the US$ 29.3 billion needed by 2025.
There is an opportunity now to end AIDS by increasing political will by investing in a sustainable response to HIV through financing what matters most: evidence-based HIV prevention and treatment, health systems integration, non- discriminatory laws, gender equality, and empowered community networks.
“We are hopeful, but it is not the relaxed optimism that might come if all was heading as it should be. It is, instead, a hope rooted in seeing the opportunity for success, an opportunity that is dependent on action,” said Ms Byanyima. “The facts and figures shared in this report do not show that as a world we are already on the path, they show that we can be. The way is clear.”
In 2022, an estimated:
- 39.0 million people globally were living with HIV
- 29.8 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy
- 1.3 million people became newly infected with HIV
- 630 000 people died from AIDS-related illnesses
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Watch: roundtable discussion
Quote sheet for media
Social media assets


Press Statement
Uganda’s new Anti-Homosexuality Bill would harm public health
03 May 2023 03 May 2023GENEVA/JOHANNESBURG, 3 May 2023—Responding to the passing of the Anti-Homosexuality Bill by the Ugandan Parliament, UNAIDS has warned that its passing into law would undermine Uganda’s efforts to end AIDS by 2030, by violating fundamental human rights including the right to health and the very right to life.
UNAIDS East and Southern Africa Director Anne Githuku-Shongwe said:
“Uganda has made excellent progress in tackling the AIDS pandemic. This new Bill, if passed into law, would undercut that progress.
It would drive communities away from life-saving services, and obstruct health workers, including civil society groups, from providing HIV prevention, testing and treatment.
The evidence is crystal clear: the institutionalization of discrimination and stigma will further push vulnerable communities away from life-saving health services. Research in sub-Saharan Africa shows that in countries which criminalize homosexuality HIV prevalence is five times higher among men who have sex with men than it is in countries without such laws.
By undermining public health, this law would be bad for everyone.
The harmful Bill stands in marked contrast to a positive wave of decriminalization taking place in Africa and across the world, in which harmful punitive colonial legislation is being removed in country after country. Decriminalization saves lives and benefits everyone.
Public health organizations welcomed the President’s rejection of the earlier Bill. As this new Bill, like the earlier Bill, would hurt public health, it too should not be enacted.”
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS urges the Government of Uganda to not enact harmful law that threatens public health
22 March 2023 22 March 2023GENEVA/JOHANNESBURG, 22 March 2023 — Responding to the passing of the Anti-Homosexuality Bill by the Ugandan Parliament, UNAIDS has warned that, if the Bill is enacted into law, it will have extremely damaging consequences for public health, by curtailing the human rights of people living with HIV and some of the most vulnerable people of Uganda to access life-saving services.
UNAIDS East and Southern Africa Director Anne Githuku-Shongwe said:
“If enacted, this law will undermine Uganda’s efforts to end AIDS by 2030, by violating fundamental human rights including the right to health and the very right to life.
It will drive communities away from life-saving services, and obstruct health workers, including civil society groups, from providing HIV prevention, testing and treatment.
The evidence is crystal clear: the institutionalization of discrimination and stigma will further push vulnerable communities away from life-saving health services. Research in sub-Saharan Africa shows that in countries which criminalize homosexuality HIV prevalence is five times higher among men who have sex with men than it is in countries without such laws.
By undermining public health, this law will be bad for everyone.
This law, if enacted, will hurt Ugandans. It will cost lives and it will drive up new HIV infections. We urge Government to not enact this harmful law.”
The law would impose a penalty of life imprisonment for homosexual acts and the death penalty for so-called “aggravated offences”. It even includes a duty to report acts of homosexuality, with failure to do so punishable by up to 6 months in prison.
The harmful Bill stands in marked contrast to a positive wave of decriminalization taking place in Africa and across the world, in which harmful punitive colonial legislation is being removed in country after country. Decriminalisation saves lives and benefits everyone.
Although the Anti-Homosexuality Bill has been passed by parliament, it is not yet enacted as a law and can, in the interest of promoting public health and equal rights of Ugandan citizens, be rejected by the President. It is not too late for this Bill to be rejected and lives to be saved.
Region/country

Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the repeal of laws that criminalise and discriminate against LGBT people in Antigua and Barbuda
07 July 2022 07 July 2022Geneva, July 7, 2022— UNAIDS applauds the ruling of the Antigua and Barbuda High Court of Justice that effectively decriminalises consensual same-sex sexual activity by holding that sections 12 and 15 of the Caribbean country’s 1995 Sexual Offences Act are unconstitutional. The court held that the criminalisation of consensual sexual acts between same-sex, adult partners infringes the rights to liberty, legal protection, freedom of expression, privacy and protection from discrimination based on sex. This ruling is an important step toward creating a more equitable context for lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Antigua and Barbuda to exercise their rights to dignity, justice and health.
“This ruling will save lives and will help advance the end of AIDS. It will benefit everyone in the country, and will inspire countries across the world to take the same vital step forward for health and human rights. By creating a more supportive legal environment we can accelerate progress around reducing stigma and discrimination and ensuring everyone can enjoy lives free of fear, shame and injustice,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “We congratulate the courageous litigants, civil society organizations and their legal team who have earned this landmark win for equality in Antigua and Barbuda.”
The case was brought by Mr Orden David, President of Meeting Emotional and Social Needs Holistically (MESH), an organization serving the LGBT community and Women against Rape (WAR)—a group that provides counselling and psychosocial support to gender-based violence survivors as well as marginalized and vulnerable groups.
They argued that the criminalization of same-sex sexual relations contributed to hostile healthcare settings where LGBT people often faced verbal abuse and confidentiality breaches. Among other things, this blocked their access to HIV testing, treatment and follow-up care.
“I have seen first-hand the pain, frustration and anger that the LGBT community experiences when trying to access services,” said Ms Alexandrina Wong, WAR’s Executive Director. “This judgment… is saying to us that changes must be made to ensure that human rights are assured, and discrimination is eliminated in time.”
“This is a clear statement that we must stop the stigma and discrimination against our community, and we will continue to support each other and advocate for our rights,” Mr David said.
Criminal laws drive and sustain public health inequalities. They legitimize stigma, discrimination and violence against LGBT people, increasing their risk of contracting HIV while reducing access to life-saving care. Gay men and other men who have sex with men who live in countries that criminalize same-sex relations are more than twice as likely to be living with HIV as those living in countries without such penalties. In countries with extreme criminal penalties, this increases to more than five times as likely
This case was part of an initiative spearheaded by the Eastern Caribbean Alliance for Diversity and Equality (ECADE). In 2020 ECADE also launched legal challenges to similar laws in four other countries: Barbados, Grenada, St. Kitts and Nevis and St. Lucia.
“Our government has sworn to uphold the rights of all, and this action tells us we are on the right road,” said Kenita Placide, ECADE’s Executive Director. She acknowledged the state attorneys who supported the final position.
In the Caribbean, strategic litigation is emerging as an effective strategy for challenging punitive, colonial-era laws. There were successful challenges of laws discriminating against LGBT people in Belize in 2016 as well as Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago in 2018.
“The marginalization and criminalization of entire communities are fuelling the Caribbean HIV epidemic,” said Luisa Cabal, UNAIDS Regional Support Team Director for Latin America and the Caribbean. “This decision shows that change is possible and UNAIDS remains committed to support law reform in the region.” She emphasized that judicial review is a key component of a broader approach that includes national dialogue around social justice and equity, as well as the deepened engagement of policymakers and health professionals.
UNAIDS is contributing to community conversations around these issues, including by supporting public forums and sensitizing journalists reporting on key population communities and law reform in the region.
Consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized in 70 countries globally, including seven in the Caribbean.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country




Press Statement
UNAIDS applauds Argentina for the approval of its new human rights-based HIV law
04 July 2022 04 July 20224 July 2022—UNAIDS congratulates the Argentinian Congress on the approval of a new law on a comprehensive response to HIV, viral hepatitis, tuberculosis and sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The bill, which has had input from a number of civil society organizations, replaces 30-year-old legislation and changes the country’s health approach from a biomedical approach to an approach more focused on gender and human rights. The new law calls for an end to stigma and discrimination against people living with HIV or STIs and aims to stop criminalization of HIV exposure or transmission.
By prohibiting mandatory testing for HIV and other STIs as part of pre-employment exams, the new law also seeks to protect against discrimination in all areas (with emphasis on the workplace) and ensures the privacy of the diagnosis.
“We join the civil society and community movements in this important celebration. The new law is evidence-based and written from the perspective of human rights,” celebrates Alberto Stella, UNAIDS Country Director for Argentina, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay. “The HIV response in the country now counts on a broad framework of social protection, very much in line with the Global AIDS Strategy (2021-2026), which focuses on ending inequalities to end the AIDS epidemic.”
Besides eradicating discriminatory practices, the new legislation also includes the possibility of early retirement at 50 years old for people who have been living with the virus for ten years and who have paid at least 20 years of pension contributions. It also allows access to a non-contributory pension for life in cases of social vulnerability.
The new bill pays a historical debt for dozens of activists who occupied the balconies of Congress in recent voting sessions and the thousands of people living with HIV they represent. “We are one step closer to eliminating barriers to the implementation of self-testing and promoting prevention strategies such as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)”, celebrated Fundación Huesped, an Argentinian organization with a regional reach that has advocated for the right to health since 1989.
The new law also recognizes specific rights of women, guarantees the right to health of their children and ensures compliance with the rights recognized in the law for the Integral Protection of Women.
“This is the result of the articulated work conducted by civil society who not only led its elaboration but who also did excellent and hard work on advocacy,” says Stella. “Along with the National HIV, TB, Hepatitis and STI department of the Ministry of Health, UNAIDS was able to contribute with advocacy efforts and the facilitation of dialogues, providing evidence and the informing on international guidelines.”
The new bill also proposes the national production of medication and supplies.
The latest estimates from the UNAIDS 2021 Global AIDS Update report show that 140 000 people are living with HIV in Argentina and 65% of whom are on antiretroviral treatment. Every year 5600 people are newly infected with HIV, and 1400 people die from AIDS-related illnesses.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes parliament’s decision to repeal the law that criminalizes HIV transmission in Zimbabwe
18 March 2022 18 March 2022GENEVA, 18 March 2022—UNAIDS congratulates Zimbabwe’s parliament for repealing section 79 of the Criminal Law Code, which criminalizes HIV transmission. A new marriage bill adopted by parliament that repeals the criminal code section is to be signed into law by the president. The criminalization of HIV transmission is ineffective, discriminatory and undermines efforts to reduce new HIV infections. Such laws actively discourage people from getting tested for HIV and from being referred to the appropriate treatment and prevention services.
“Public health goals are not served by denying people their individual rights and I commend Zimbabwe for taking this hugely important step,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “This decision strengthens the HIV response in Zimbabwe by reducing the stigma and discrimination that too often prevents vulnerable groups of people from receiving HIV prevention, care and treatment services.”
UNAIDS has worked closely with Zimbabwe’s National AIDS Council, Zimbabwe Lawyers for Human Rights, parliamentarians, civil society activists and communities to advocate for the repeal of the law criminalizing HIV. Overly broad and inappropriate application of criminal law against people living with HIV remains a serious concern across the globe. More than 130 countries worldwide still criminalize HIV non-disclosure, exposure and transmission through either specific or general criminal legislation.
In 2019, Zimbabwe completed a legal environment assessment, which identified the criminalization of HIV transmission as a barrier to health care and a driver of stigma and discrimination for people living with HIV and other key populations. Since then, the United Nations Development Programme has worked with key populations and other stakeholders, convening meetings with parliamentarians and other partners to advance the recommendations of the legal environment assessment.
In 2018, UNAIDS, the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care and the International AIDS Society convened an expert group of scientists who developed an Expert Consensus Statement on the Science of HIV in the Context of Criminal Law. The statement calls on the criminal justice system to ensure that science informs the application of the law in criminal cases related to HIV.
Zimbabwe has made great progress in the response to HIV over the past decade. It is estimated that 1.2 million of the 1.3 million people living with HIV in the country are now on life-saving medicines. AIDS-related deaths have decreased by 63% since 2010, with new HIV infections down by 66% over the same period.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country


Feature Story
The case for anti-discrimination legislation in Jamaica
01 March 2022
01 March 2022 01 March 2022Michael James (not his real name) was shell-shocked when he was fired. He scanned the dismissal letter. It cited his performance and tardiness as reasons for the job loss. But years of performance appraisals told a different story. He’d consistently received positive evaluations and there were no memos about late-coming or substandard work on his file. The only reason he could discern was that colleagues recently learned that he was living with HIV.
HIV-related prejudice remains rife in Jamaica. One third of people living with HIV responding to the 2020 Jamaica People Living with HIV Stigma Index reported experiencing stigma and discrimination. Verbal harassment, gossip and discriminatory remarks were the most common violations. But one in 10 said they were refused employment or lost a source of income because of their HIV status. No legislation prohibits a Jamaican employer from discriminating on the basis of HIV status.
This has marked implications for the HIV response. Twenty-one per cent of respondents were worried about mistreatment or confidentiality breaches by health-care workers. Thirty-eight per cent delayed testing and 29% delayed starting treatment because of concerns about how they would be treated.
Shelly John (not her real name) recounts hopping from one treatment site to another before landing at Jamaica AIDS Support for Life. At other facilities she overheard nurses gossiping about patients’ medical histories.
“I felt uncomfortable. If I am hearing about other clients, other clients can come inside and hear about me as well,” she reasoned.
“The fear of stigma drives some persons underground and away from much needed health services. Owing to stigma and discrimination, some persons delay accessing needed services and, as a result, some are diagnosed with HIV at an advanced stage,” acknowledged State Minister in the Health and Wellness Ministry and Chair of the Jamaica Partnership to Eliminate HIV-Related Stigma and Discrimination, Juliet Cuthbert Flynn.
Jamaica’s testing and treatment outcomes bear this out. While an estimated 86% of people living with HIV were aware of their status in 2020, just 40% of people living with HIV were on HIV treatment.
While the Jamaica Charter of Fundamental Rights and Freedom guarantees protection against discrimination, it is limited in scope. The protected grounds are race, sex, place of origin, social class, colour, religion and political opinions. There are piecemeal anti-discrimination provisions in different pieces of legislation, such as the 2014 Disabilities Act and the 1975 Employment Act. But neither the constitution nor ordinary legislation make discrimination on other grounds unlawful.
Since 2020, UNAIDS and the United Nations Development Programme have been providing technical and financial support to local nongovernmental organizations, including Jamaica AIDS Support for Life, to support the rollout of a national survey on the public’s perspectives and experiences with stigma and discrimination in Jamaica and on the need to have more adequate protections in the law. The results of the survey will be used to advocate for legislation to adequately deal with discrimination experienced by vulnerable and marginalized groups.
The proposed legislation should provide protection across areas including discrimination based on health status, pregnancy or childbirth, hiring or termination decisions and the denial of services to minority groups. It should also address discriminatory conduct based on assumptions about a person’s competence, capabilities, age, self-expression, income level, the neighbourhood in which they live or their educational background.
“Comprehensive anti-discrimination legislation will strengthen the legal framework for the protection of human rights towards achieving equality for all,” Manoela Manova, the UNAIDS Country Director for Jamaica, explained.
In real terms, this means that duty-bearers will have to consider how their policies, programmes and services will affect people with the protected characteristics. Critically, the focus on markers related to poverty would mean that for the first time public bodies will have a duty to consider socioeconomic disadvantage when making strategic decisions about how to exercise their functions and when proposing to use public funds.
“Our overarching finding has been that regardless of health status, sex, age or sexual orientation, the factor that fuels discrimination and makes people more vulnerable is poverty. Moving forward, it is critical that we don’t treat HIV as a stand-alone concern but address the full picture of what makes people marginalized and vulnerable in Jamaica,” said UNAIDS Community Support Adviser for Jamaica, Ruben Pages Ramos.
Region/country
Related

Update
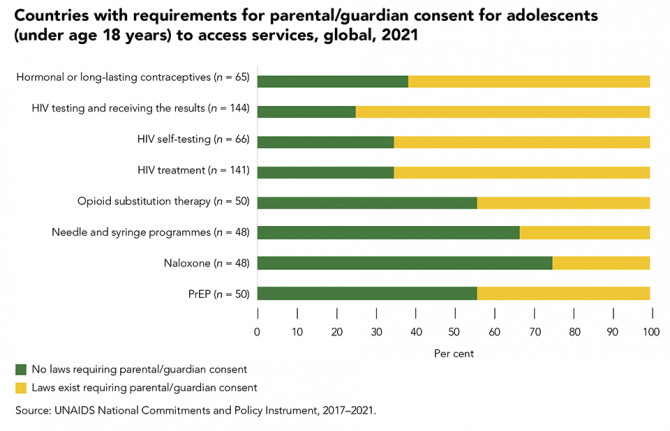
Parental consent laws leave adolescents vulnerable to HIV
14 February 2022
14 February 2022 14 February 2022Sexual activity often starts during adolescence. Many countries have age of consent laws in relation to sexual activity that are inconsistent with minimum age laws for accessing sexual and reproductive health information and services without parental permission. This means that adolescents may legally have sex before they can legally access any information or services relating to safer sex practices or contraception, leaving them at greater risk of HIV, other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unwanted pregnancy.
The removal of laws that require parental permission to access services for sexual and reproductive health and HIV prevention, testing and treatment has been shown to improve health-seeking behaviours. That effect is even stronger when schools can provide age-appropriate comprehensive sexuality education to young people so they can protect themselves from HIV, STIs, unwanted pregnancy and gender-based and sexual violence.
Forty countries reported to UNAIDS in 2021 that they have laws requiring parental/guardian consent for adolescents to access hormonal or long-lasting contraceptives, 108 reported that this consent is required for an HIV test, 43 for HIV self-testing, 92 for HIV treatment and 22 for PrEP. Among these countries, some provide exceptions based on demonstrated maturity: 10 for hormonal or long-lasting contraceptives, 15 for HIV testing, eight for self-testing and nine for HIV treatment. The age cut-off of parental consent laws varied by service. The majority of countries that reported having requirements for parental/guardian consent had an age cut-off of 18 years, with exceptions in a few countries where adolescents as young as 14 years could access a service without parental/guardian consent, which varied by service.
Our work
Documents
Still not welcome — HIV-related travel restrictions
27 June 2019
Mandatory HIV testing and bans on entry, stay and residence based on HIV status not only do not protect public health but undermine HIV prevention and treatment efforts. For millions of people living with HIV around the world, these are repeated violations of their right to privacy, equality and non-discrimination and a constant reminder of HIV-related stigma. In 2016, United Nations Member States agreed to eliminate HIV-related travel restrictions. In 2019, around 48 countries and territories still maintain some form of HIV-related travel restriction.
Related
 U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how
U=U can help end HIV stigma and discrimination. Here’s how

27 February 2025
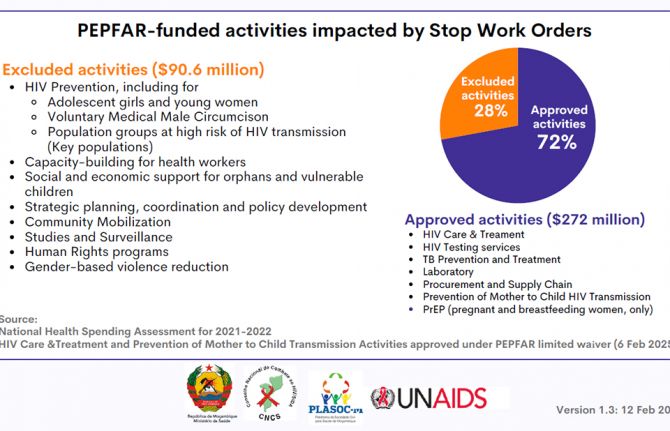
 How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them
How the shift in US funding is threatening both the lives of people affected by HIV and the community groups supporting them

18 February 2025
Impact of community-led and community-based HIV service delivery beyond HIV: case studies from eastern and southern Africa
30 January 2025
 Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment
Lost and link: Indonesian initiative to find people living with HIV who stopped their treatment

21 January 2025
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Indicators and questions for monitoring progress on the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV and AIDS — Global AIDS Monitoring 2025
17 December 2024
UNAIDS data 2024
02 December 2024