Education


Feature Story
Tanzania commits to invest in secondary education as part of efforts to keep boys and girls free from HIV
16 December 2022
16 December 2022 16 December 2022Tanzania became the 13th African country to join the Education Plus Initiative, committing to provide greater investments to ensure boys and girls complete secondary school.
Education Plus is an initiative spearheaded by UNAIDS to accelerate action and investments in education to prevent HIV. Evidence shows that completing secondary education reduces the risk of HIV infection and early pregnancy and improves their livelihoods and prosperity for girls and young women. The education Plus initiative is centred on empowering adolescent girls and young women and achieving gender equality in sub-Saharan Africa.
On 30 November 2022, during the HIV week commemoration, the Office of the Prime Minister, led by the Minister of State for Policy, Coordination and Parliamentary Affairs, Mr George Simbachawene, alongside the Deputy Minister of Health Dr Godwin Mollel, launched the initiative in Lindi region, Tanzania.
"Young people aged 15-24 years make up one of the largest groups of new infections, among all new infections every year, approximately 30% are among people aged 15–24. That means for every 10 new infections, three are from this age group,'" said Mr. Simbawachane
The launch of Education Plus in Tanzania will accelerate the ongoing country's adolescent education, health and wellbeing agenda. Tanzania has been particularly affected by HIV. In 2021 around 1.7 million people were living with HIV; 74% of new HIV infections among young people aged between 15 and 24 were among young women, showing the disproportionate impact HIV is having on young women and girls.
Minister Simbachawene said the country would increase primary education opportunities for adolescents and enable them to stay in school by removing all barriers to completion of primary and secondary school education. Through the initiative, Tanzania will strengthen efforts to bring HIV education, reproductive health, and life skills to adolescents inside and outside of school.
The initiative comes at a time when Tanzania has made good progress in adopting global treaties and agreements to address gaps in education and health rights and increase opportunities for girls and boys. Most commitments have been translated into national policies and strategies, as demonstrated by the government’s commitment to offering free basic and secondary education. Tanzania has also adopted policy decisions to implement a re-entry program for children who drop out and to include comprehensive sexuality education into the curriculum. The country has also amended the HIV and AIDS Act to lower the age of consent for HIV testing and allow HIV self-testing.
The minister also pledged to do more to eliminate gender-based and sexual violence by providing youth-friendly education, skills building, and enhancing referrals by connecting youth to health and community services.
However, key gaps remain, with national surveys showing increased rates of teenage pregnancy, school dropouts, and high levels of gender-based violence. Around 27% of young women aged between 15 and 19 years already have a child or are pregnant and 50% of ever-married women aged between 15 and 49 report experiencing physical, sexual, or emotional violence.
The total number of students enrolled in secondary education is still below 50%, and for those in school, there is a high dropout rate, and some do not complete their schooling. The country has a low completion rate in secondary schools at 11.3%, and dropout in secondary schools due to pregnancy was reported at 4% in 2020.
Despite increased political will and significant achievements, women's and girls' vulnerabilities remain very high. Adolescent girls and young women in Tanzania continue to shoulder the burdens of domestic work, gender inequality in education, and harmful norms. Many are entrenched in cycles of poverty and extreme vulnerabilities.
At the launch, the government committed to strengthening policies to facilitate the provision of education and essential skills to prepare and equip young people for employment and other economic opportunities.
The launch was attended by key partners including Dr Leonard Maboko, the Executive Director for Tanzania Commission for AIDS (TACAIDS) youth representative Pudensiana Mbwiliza; Permanent secretary office of the Prime Minister, Dr John Jingu and Hon Judith Nguli from Lindi Regional Commissioner’s office and Tanzania PEPFAR coordinator Jessica Greene; representatives from UNAIDS, UNESCO, International Labour Organisation (ILO), UNICEF and the World Health Organisation (WHO).
The event brought together civil society organisations, young people’s networks, and representatives of people living with HIV and partners. Co-lead by five United Nations agencies working with governments, women’s and youth movements; the initiative is of even greater urgency as the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed millions of African girls out of school.
Region/country


Press Release
School saves lives: World leaders back a courageous goal, “Education Plus”, to prevent new HIV infections through education and empowerment
19 September 2022 19 September 2022NEW YORK/GENEVA, 19 September 2022—At the Transforming Education Summit in New York it was announced that 12 African countries* have committed to Education Plus, a bold initiative to prevent HIV infections through free universal, quality secondary education for all girls and boys in Africa, reinforced through comprehensive empowerment programmes.
Speaking on the Leaders Day of the Summit on behalf of the Education Plus movement, the Executive Director of UNAIDS, Winnie Byanyima said, “School saves lives. We are coming together to champion the right for a girl to be in a classroom and in a safe classroom. Keeping girls in school helps ensure their rights and prevents HIV. We know that if a girl completes secondary education, the risk of infection reduces by 50%. That's why we've teamed up with UNESCO, UNFPA, UNICEF and UN Women, with governments and with civil society, to champion the education and empowerment of adolescent girls in Africa to stop new HIV infections.”
Through Education Plus, champion countries across Africa are bringing sectors together to fight inequalities by ensuring access to and completion of secondary school, protecting girls and young women from HIV infection, sexual violence, teenage pregnancies and early marriages, and creating opportunities for access to education, health, and jobs.
Sierra Leone, an Education Plus champion, has been reforming its education system since 2018, enrolling an additional one million learners in four years. Speaking at the Summit President Julius Madda Bio said, “We have adopted a radical inclusion policy and have achieved gender parity in school enrollment. Girls can now be educated from primary through to university free of tuition fees, and pregnant girls can once again go to school. Education is not a luxury, it is a right. We must rally the international community behind the global initiatives being launched.”
International partners shared their backing for the initiative. Franz Fayot, Minister for Development Cooperation and Humanitarian Affairs, Luxembourg said, “The risks of acquiring HIV and the challenges in accessing services in sub-Saharan Africa are very real and are compounded by stigma and discrimination, as well as legal and financial barriers. Financing to support education systems to deliver gender-transformative education is urgent. It will save lives and have a hugely positive impact on economies.”
Joyce Ouma, a young leader from the Education Plus hub, shared why young women’s movements are backing the initiative: “Some of us are still denied sexual and reproductive health information and services and sexuality education because of our age and this has a devasting impact on our lives. As young women living with HIV, we face discrimination, stigma and violence perpetrated within school environments and cannot easily seek essential medical care. Transforming education means we face these gloomy statistics head on. I urge leaders to listen and act on our collective concerns for better systems.”
UNAIDS latest report, In Danger, released in July this year showed that in sub-Saharan Africa 4 900 young women and girls (15-24 years old) acquired HIV every week in 2021. Once a person contracts HIV they require life-long treatment. In 2021 in sub-Saharan Africa, 22 000 adolescent girls and young women died of AIDS-related illnesses.
Fostering investments in access to health, education and jobs gives results. Girls—and their communities and countries—reap multiple social and economic benefits from their completion of secondary school. An extra year of secondary school can increase women’s wages by 15-25%. Educating adolescent girls and young women in Africa could add US$ 316 billion or 10% to GDP in the period to 2025 if each country makes advances in gender parity in schooling.
The United Nations Secretary-General recognized girls’ education and empowerment as crucial for development, "Girls’ education is among the most important steps to deliver peace, security, and sustainable development everywhere," said Antonio Guterres.
*The 12 African Education Plus champion countries are Benin, Cameroon, Eswatini, Gabon, Gambia, Lesotho, Malawi, Senegal, Sierra-Leone, South Africa, Uganda and Zambia.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.




Press Release
African leaders launch the Education Plus initiative – a huge step forward for girls’ education and empowerment in Africa
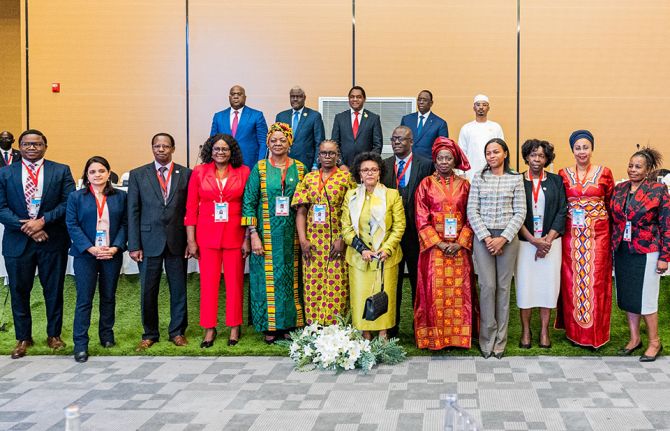
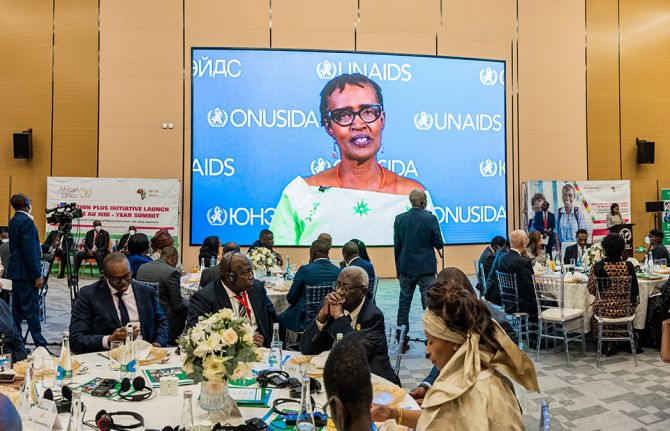
18 July 2022 18 July 2022LUSAKA, ZAMBIA / GENEVA, SWITZERLAND, 18 July 2022—Leaders meeting at the Africa Union summit in Lusaka, Zambia, have pledged their support for the Education Plus initiative at its continental launch, commiting to take action to keep adolescent girls in school, which will dramatically reduce their vulnerability to HIV.
Every week, around 4200 adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa acquire HIV. In 2020, six in seven adolescents aged between 15—19 years old acquiring HIV in the region were girls. More than 23000 young women died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2020, making it the second leading cause of death among women aged 15—29 after maternal mortality in sub-Saharan Africa.
Keeping girls in secondary school and providing them with life skills, training and employment opportunities is key to ending the AIDS pandemic in Africa. Research shows that ensuring that girls complete secondary education reduces their risk of acquiring HIV by up to half, and that combining this with a package of services and rights for girls’ empowerment reduces their risk further still.
Education Plus calls for free and quality secondary education for all girls and boys in sub-Saharan Africa by 2025; universal access to comprehensive sexuality education; fulfilment of sexual and reproductive health and rights; freedom from gender-based and sexual violence; school-to-work transitions, and economic security and empowerment.
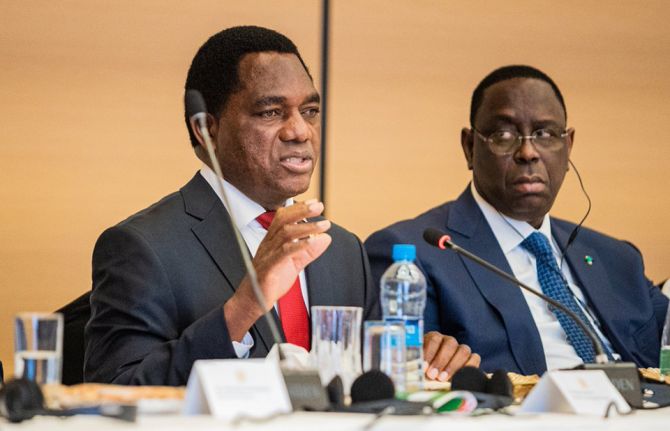
“My government has committed to the provision of free primary and secondary education for all,” said President Hakainde Hichilema of Zambia, who hosted the summit. “Education is the greatest equalizer and with appropriate education, everyone is given an opportunity to explore their full potential and be able to participate in the development process. Access to education empowers both girls and boys as it enhances their ability to access decent jobs and other means of production thus alleviating poverty.”
The President of Senegal and current chair of the African Union, Macky Sall, launched the initiative flanked by three other presidents and the Chairperson of the African Union Commission Moussa Faki Mahamat.
“It is my pleasure to join you on the occasion of the ceremony to launch the continental “Education Plus Initiative” under the leadership of the Organisation of African First Ladies (OAFLAD) in support to children and young girls in particular,” said President Sall. “There is need for action to promote women’s rights and autonomy, to fight against the discrimination and violence which girls and women face. We must address gender inequality at all stages of life. At the continental level, AU Member States are committed to accelerating the implementation of gender-specific economic, social, and legal measures aimed at combating the HIV/AIDS pandemic by adopting various policy and legal frameworks including the Maputo Protocol.”
The launch was held in partnership with the Organisation of African First Ladies for Development, convened by the First Lady of Zambia, H.E Mutinta Hichilema.
“I am confident that Education Plus will enable us all to protect, provide and preserve the lives of adolescent girls and young women by enhancing education standards and preventing new HIV infections by use of various interventions,” said Ms Hichilema.
“We lend our voice to the transformative call for gender-inclusive education in Africa,” said Leyla Gozo, Executive Secretary of the Organisation of African First Ladies for Development, “First ladies are uniquely positioned to amplify this inititiative.”
The Education Plus initiative has taken on even greater urgency as the COVID-19 pandemic pushed millions of girls out of school. Even before the pandemic, almost 34 million adolescent girls aged 12—17 years old in the sub-Saharan Africa region were not in secondary school. Evidence also shows that girls are less likely to restart school once they have dropped out.
Ten African countries – Benin, Cameroon, Eswatini, Gabon, Gambia, Lesotho, Malawi, Sierra Leone, South Africa and Uganda – have so far committed to the initiative which is jointly convened by five United Nations agencies, UNAIDS, UNESCO, UNFPA, UNICEF and UN Women, and brings together governments, civil society and international partners.
“We are making progress in Africa but not fast enough,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima in her address to the launch. “We need to urgently address the gender inequalities that still plague the continent, with devastating impacts on poor girls and young women. We don’t have a minute to wait. Working together, we can all end discriminatory laws and harmful social norms, so that our girls are healthy, educated and empowered and can lead our continent, Africa, forward.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Watch: Education Plus Initiative
Watch: video message by Winnie Byanyima
Our work
Region/country




Feature Story
Young women leaders in Senegal push for more education for their peers
24 May 2022
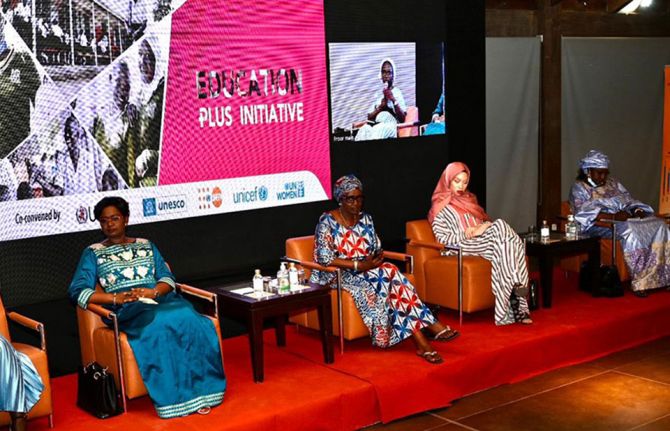
24 May 2022 24 May 2022As part of the Education Plus initiative, young women advocates in Senegal have met with key female figures in the region to discuss the education of girls in sub-Saharan Africa and the challenges they face.
A social work student in her second year of professional training said young women like her who are living with HIV still face stigma and economic marginalization in most spheres of life “Sometimes, the medicines are not in stock, and young women living with HIV often have to share their medication with each other while waiting for a new supply.” According to her, education guarantees a better future for young people, as it did for her in helping her to overcome the challenges she faces because of her HIV status and her difficult upbringing.
Another participant, Maah Koudia Keita (known as Lady Maah Keita), a Senegalese woman with albinism, and a musician, said that women with albinism are victims of harassment and the majority of them have experienced rape and sexual violence.
She is one of three professional female bass players in Africa and the only one in Senegal. She said, “People like me who were lucky to get an education now have to do the work of dispelling myths around women with albinism that drive the violence.” According to Ms Keita, the more educated and aware the community is, the better women and people with albinism can defend themselves.
Adama Pouye, a feminist activist and member of the Senegalese feminist collective that led the Buul Ma Risu (Don’t Mess with Me) movement, spoke at length during the meeting about raising awareness on sexual assault on public transport.
“Every day, you hear violent words and women come to believe that’s what they deserve,” she said. “You are told how far you can go by standards put in place by a patriarchal society, by men, and by religious standards, but our religious interpretations cannot be about oppressing women,” Ms Pouye said.
Young women are key advocates who the Education Plus initiative is working with to rally political leadership, development partners and communities in order to fulfil every adolescent girl’s right to education and health by enabling all girls to complete a quality secondary education in a violence-free environment.
As UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima stressed at the meeting, “In this region of western and central Africa, the vulnerability of girls is high.”
She also said that four out of 10 young women are married before the age of 18 years, saying that children becoming brides is a gross violation and a failure to harness the full potential of girls.
“Keeping girls in a classroom, if she stays and completes secondary school, has a protective effect for girls from HIV. What we fought and won for primary school is what is needed for secondary education,” Ms Byanyima said.
Fatou Nar Mbaye Diouf, the Deputy Executive Secretary of the National AIDS Council, Senegal, could not agree more. “We know that allowing girls to complete secondary education protects them from HIV and improves many other health and development factors,” she said.
Sharing key data from Senegal, Ms Nar said the level of comprehensive knowledge about HIV increases with the level of education. “Among young women, it is 10% among those with no education and 41% among those with secondary education or higher, while among young men knowledge of HIV varies from 9% among those with no education to 51% with education,” she said. “Education is key.”
The Regional Director for West and Central Africa for UN Women, Oulimata Sarr, concluded the intergenerational dialogue by saying that girls’ education is not a threat, nor should it be seen as that. “We want to move the needle and move it together with young women,” she said.
Ms Sarr wants the next generation to be supported as they seek more space in decision-making. “We need to pass the baton to young people, who organize differently from us, create an intergenerational legacy with young people holding us to account.”
Learn more
Region/country
Related
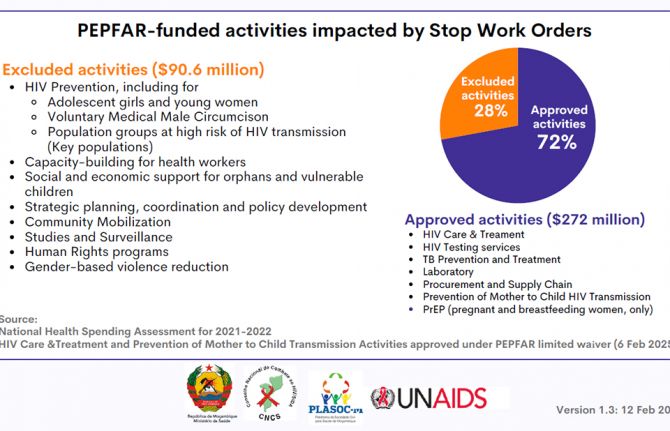
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025


Feature Story
Leaders from Eastern and Southern Africa recommit to the education, health and well-being of adolescents and young people
08 December 2021
08 December 2021 08 December 2021Ministers of education, health, gender, and youth in Eastern and Southern Africa (ESA), expressed overwhelming support to continue their joint efforts towards creating a brighter future for adolescents and young people in the region by empowering the youth and protecting their health and well-being to achieve the common goals.
A high-level Ministerial Meeting held virtually on Monday, as part of the International Conference on AIDS and sexually transmitted infections (ICASA) 2021 reaffirmed and expanded the commitment first made in 2013.
Eight years ago, Ministries of Health and Education from 20 countries - supported by the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the East African Community (EAC) – joined forces with regional UN organisations to agree on a joint commitment, known as the ESA Commitment. They recognized the urgent need for more systematic scale up of sexuality education and youth-friendly SRH services in the region.
“Africa has a large population of young people, and we must do all in our power to make opportune of this demographic dividend. Our young people are our hope for the development of our continent, Africa. As leaders of today, we need to prioritise the health and wellbeing of young people for the betterment of Africa”
While important strides have been made toward improving sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) outcomes among adolescents and young people, significant gaps and barriers still exist to the realization of the ESA Commitment targets. An evaluation of the 2013 commitment revealed progress in reducing new HIV infections, increasing comprehensive HIV knowledge and creating a conducive policy environment. However, the evaluation also indicated that accelerated efforts are urgently needed to reduce early and unintended pregnancy, gender-based violence and curb the effect of humanitarian emergencies, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. This further underscored the need to renew the commitment, through expanding and aligning it with the SDG Agenda 2030.
“Young Africans must have the facts and confidence to stay safe and healthy, live a dignified life and contribute positively to their community and countries. They must trust us, their elders, to tell them the truth. Therefore, as Religious Leaders we pledge our support today to the ESA Commitment that seeks to enhance efforts in ensuring the health and wellbeing of our children and young people”
Extensive consultations at national and regional level with governments, adolescents and young people, communities and development partners across sectors led to a new updated regional commitment and targets for 2022-2030.
“The ESA Commitment has opened doors that were closed to us as young leaders. It has provided an opportunity for further advocacy on SRHR to change the lives of adolescents and young people. We strongly encourage and support an expansion and extension of the ESA Commitment towards Agenda 2030”
This commitment by the ministers of Health, Gender, Education and Youth is expected to accelerate investments to the education, health and well-being of adolescents and young people in ESA.
“Today we are putting a spotlight on adolescents and young people, and we are set to promote national and international inter-sectoral collaboration. We call on and rally all development partners and well-wishers to come on board and ride with us in the renewed ship that is headed to a land where our adolescents and young people are healthier, more productive, and continual to champion inclusive development of our societies”
Region/country
Related


Feature Story
The importance of comprehensive sexuality education for Africa’s young people
07 December 2021
07 December 2021 07 December 2021A message of support for the ESA Commitment from Professor Mbulelo Dyasi, Vice Chair, Board of Directors, INERELA+, delivered at ICASA 2021
As religious leaders, we have a trusting relationship between us and our congregations. As beholders of God’s truth and a belief system based on faith, our relationships with our congregants and communities are based on a strong basis of belief and as custodians of good values. This provides us with a platform to advocate and motivate for the betterment of our people from a faith perspective while we can also work together with our congregations in finding solutions to the challenges they face in their environments.
Today, we are in a situation where our nation and our continent are at the right place to advance in areas of economics, infrastructure and human resources. This is because we have young populations who are fast growing up to be productive citizens. These young people need direction and guidance to be able to make good decision, have positive family lives and be good citizens. And as religious leaders we play an important role in providing this guidance. Parents in our congregations know their role in providing this guidance. And we live in a modern society with modern education and health systems, so we need teachers, social workers and health workers to also provide this guidance. Each has a role to play in improving society.
We trust a government that acts in our best interests. Since 2000, the South African Government has been providing our children with the education and guidance they need. This education, called Life Orientation/Life Skills, where sexuality education is embedded, complements the values and direction that we provide as religious leaders through our sermons and that parents provide at home. We have to make sure that our children can negotiate issues of sexuality and relationships from a position of knowledge and power, rather than a position of ignorance and fear. From a position of truth and science, rather than a position of misinformation and helplessness.
There are those who try to spread fear and disinformation, creating panic and claiming to be the guardians of family values. The truth is that many of us who are believers, who are parents, who are teachers, are united on human dignity. And sexuality education promotes human dignity. Because sexuality education ensures that our children learn to treat each other with respect and dignity from an early age. It ensures that our children learn to think about what is right and safe for them, and how to avoid coercion, sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, and early and unintended pregnancies. It helps to keep our children safe from abuse by teaching them about their bodies.
Young Africans must have the facts and confidence to stay safe and healthy, live a dignified life and contribute positively to their community and countries. They must trust us, their elders, to tell them the truth. Therefore, as religious leaders we pledge our support today to the ESA Commitment, which seeks to enhance efforts in ensuring the health and well-being of our children and young people. We commit to work with our governments to accelerate action towards realizing the agreed upon targets so that in 2030 we can all see the vision of an AIDS-free generation.
As religious leaders we hereby endorse the ESA Commitment towards 2030 aiming to ensure that we close the gap of comprehensive knowledge of our young people to protect themselves from new HIV infections, early and unintended pregnancies and gender-based violence and early child marriages. We promise to engage with our constituencies to create an enabling environment for adolescents and young people to access sexual and reproductive health services and use our platforms to empower parents to be able to talk with their children on issues affecting their health and well-being. With the challenge of COVID-19, we also commit ourselves to work together with our communities in finding innovative ways to ensure access to information and essential services during times of crisis. Working together we will surely win the fight against HIV and other pandemics.
Thank you!
Professor Mbulelo Dyasi, Vice Chair, Board of Directors, INERELA+


Feature Story
Invest in adolescent girls’ and young women’s rights, education and health to end AIDS in Western and Central Africa
02 November 2021
02 November 2021 02 November 2021Leaders from governments, civil society and the United Nations have renewed their commitment to make urgent and strategic investments in adolescent girls’ and young women’s rights, education and health. At a three-day regional summit on HIV/AIDS held in Dakar, Senegal that concluded with a call to action, the Education Plus initiative was applauded as a timely intervention to address the high number of adolescent girls and young women acquiring HIV in the Western and Central Africa region.
The Education Plus Initiative, a high-level political advocacy drive to accelerate actions and investments to prevent HIV, was launched as a joint commitment of UNAIDS, UNESCO, UNFPA, UNICEF and UN Women at the Generation Equality Forum in July this year. The Education Plus initiative is centred on the empowerment of adolescent girls and young women and the achievement of gender equality in sub-Saharan Africa—with secondary education as the strategic entry point for providing the multi-sectoral plus package. The initiative calls for free and quality secondary education for all girls and boys in sub-Saharan Africa by 2025; universal access to comprehensive sexuality education; fulfilment of sexual and reproductive health and rights; freedom from gender-based and sexual violence; school-to-work transitions, and economic security and empowerment.
While the Western and Central Africa region has progressed in girls’ education over the last two decades, the UNICEF 2019 report found that “the region still has the highest gender gaps in education in the world”. One in four adolescent girls aged 15-19 who have ever been married or in union, has experienced emotional, physical, or sexual violence at the hands of a husband or partner.
HIV/AIDS remains a major public health threat in the Western and Central Africa where 4.7 million people are living with HIV—12% of those living with HIV globally—but experiences 22% of all AIDS deaths in the world. Adolescent girls and young women (aged 15-24) in West and Central Africa are twice as likely to acquire HIV than their male peers. Five in six new HIV infections (82% / 18,237 females) among adolescents 15-19 years are among females. Three-quarters (74%) of new HIV infections in the age group 15-24 in the region are in females (40,432 females / 13,860 males). Every week, approximately 800 adolescent girls and young women in WCA are newly infected with HIV.
Secondary education offers protection to adolescent girls and young women from HIV—with reductions in HIV incidence among girls who complete secondary education by as much as one-third to one half in some countries.
However, most countries in Western and Central Africa are falling short of meeting the target of allocating 20 percent of government resources to education as required under the African Union’s Dakar Commitment on Education for All. Before the COVID19 pandemic, only Burkina Faso, São Tome and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo allocated at least 20 percent of their national budgets to education. As a percentage of GDP, education spending varies from 1.1 percent in Central African Republic to 7.7 percent in Sierra Leone.
Before COVID-19 struck, around 34 million secondary school-aged girls in sub-Saharan Africa were being denied a full 12-years of education and an estimated 24% of adolescent girls and young women (15–24 years) in the region were not in education, training or employed, compared to 14.6% of young men. UNICEF estimates that in 2020 school closures due to COVID-19 impacted around 250 million students in the sub-Saharan Africa region, millions of whom may never return to the classroom-especially girls.
To date, five countries—Benin, Cameroon, Gabon, Lesotho and Sierra Leone—have signed on to champion the initiative with a wide range of commitments that will tackle the urgency of effectively addressing the alarming numbers of adolescent girls and young women acquiring HIV and dying from AIDS-related illnesses, among other threats to their survival, well-being, human rights and freedoms, including sexual and gender-based violence and teenage pregnancy.
The Education Plus initiative is committed to advancing young women’s leadership as key to ending AIDS as a public health threat and in rebuilding communities and countries during and post pandemic.
Quotes
“The lessons learned from the success in accelerating gender parity in primary education, need to be implemented for secondary education. Guaranteeing the completion of quality secondary education for every adolescent girl is a must-do. That is why we are excited about the ground-breaking Education Plus Initiative on the empowerment of adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa, that I am co-leading with my sister Executive Directors of UNESCO, UNICEF, UNFPA and UN Women.”
“The evidence has shown us that HIV epidemic in West and Central Africa is feminized with women and girls bearing the brunt of new HIV infections and care of people living with HIV. The disproportionately high HIV infection among women and girls is fuelled by the systematic, structural and institutionalized gender inequalities that put women and girls at a disadvantage throughout the life cycle.”
"In The Gambia we have a lot of government schools. Apparently, it’s free. But that just means not paying tuition. Some families are worried about buying three meals a day - and yet they need to worry about buying schoolbooks. To donors investing in secondary education and governments who are supposed to be doing that, I’d say you should be investing specifically in what students need. "
“One pathway to women’s empowerment is through Education Plus. If a woman is not educated, she will be unable to take up any of the 30% quota of leadership positions reserved for women in Gabon, who will in turn make decisions and pass laws that empower girls. The country is intensifying efforts to increase access to education, by breaking down barriers and enabling adolescent girls and young women to take advantage of all the measures put in place by the government for access to quality education.”
“To reduce girls’ vulnerability to HIV, there is need to leverage health sector funding to catalyze cross-sectoral impact in the education sector, particularly to ensure access to sexual and reproductive health services for adolescent girls and young women.”
"Benin is committed to increasing funding for secondary education for girls and training teachers to facilitate a supportive environment."
"We know the solutions; we have the means. Now leaders must be ready to take radical measures. This emergency requires radical measures!"
“Adolescent girls who reach upper primary and lower secondary school face multiple barriers. To address them, we need to take a multi-sectoral approach which not only addresses their education, but also their economic, protection, nutrition, menstrual health and hygiene and HIV prevention needs.”
Region/country
Related
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025


Press Release
Education Plus launched in response to alarming rates of HIV among adolescent girls and young women in Africa
06 July 2021 06 July 2021Unequal gender power dynamics continue to put women and girls at higher risk of acquiring HIV. Six out of seven new HIV infections among adolescents aged between 15 and 19 years in sub-Saharan Africa are among girls and 4200 adolescent girls and young women between 15 and 24 years became infected with HIV every week in 2020
GENEVA, 6 July 2021—Five United Nations organizations have joined forces to launch a new initiative to ensure that all girls and boys in sub-Saharan Africa have equal access to free secondary education by 2025 and to contribute towards preventing HIV. Education Plus, launched at the Generation Equality Forum in Paris, France, is an ambitious five-year high-level drive to accelerate action and investments to expand access to secondary education for all young people and to advance adolescent girls’ and young women’s health, education and rights in sub-Saharan Africa.
Before COVID-19 struck, around 34 million secondary school-aged girls in sub-Saharan Africa were being denied a full education and an estimated 24% of adolescent girls and young women (15–24 years) in the region were not in education, training or employed, compared to 14.6% of young men. One in four young people in sub-Saharan Africa aged 15–24 years are illiterate and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) estimates that in 2020 school closures due to COVID-19 impacted around 250 million students in the region, millions of whom may never return to the classroom.
“We know that keeping girls in secondary school can reduce their risk of HIV infection by a third or more in places where HIV is common. It reduces their risk of child marriage, teenage pregnancy and gender-based and sexual violence and it can provide girls with the important skills and competencies for their economic empowerment,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Bold and consistent political leadership is needed to ensure all children can complete a full round of secondary education in sub-Saharan Africa.”
The co-founders of Education Plus, UNAIDS, UN Women, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, the United Nations Population Fund and UNICEF, are urging countries to use education systems as an entry point to provide a holistic “plus” package of essential elements that adolescent girls and young women need as they become adults. These include comprehensive sexuality education, sexual and reproductive health and rights, including HIV prevention, freedom from gender-based violence and economic empowerment through school-to-work transitions.
Anita Myriam Emma Kouassi, a young activist from Benin, called on leaders to go beyond promises and act to end inequalities and gender discrimination against girls and young women in Africa. “Inequalities and illiteracy leave girls without the ability to take charge of their lives early on and without control over choices around their own bodies and health. We are thus left vulnerable without knowing how to defend ourselves or make our voices heard,” she said. “This is the reason why we cannot do without girls’ education; it is the bedrock and pillar of a strong nation with and for girls.”
To date, five countries—Benin, Cameroon, Gabon, Lesotho and Sierra Leone—have signed on to champion the initiative with a wide range of commitments that will tackle the urgency of effectively addressing the alarming numbers of adolescent girls and young women acquiring HIV and dying from AIDS-related illnesses, among other threats to their survival, well-being, human rights and freedoms, including sexual and gender-based violence and teenage pregnancy.
“Over the next three years, we will work to intensify awareness of sex education through training and the development of dedicated pedagogical material. We will support pregnant girls and young mothers in the case of early pregnancy. We will provide quality sanitary facilities and promote easy access to sanitary towels in schools,” pledged Rose Christiane Ossouka Raponda, the Prime Minister of Gabon. “The new Labour Code, which is currently before Parliament, will enrich our legal framework, particularly with regard to harassment in the workplace. Adolescent girls, young women and women as a whole will be even better protected to promote their social and professional development and their empowerment.”
Education has become an urgent concern amidst the COVID-19 pandemic and its socioeconomic impacts, which have increased girls’ and young women’s exposure to gender-based violence, child marriage and unintended pregnancies, increased the risks of maternal mortality and heightened vulnerabilities to acquiring HIV. Girls in sub-Saharan Africa are especially at risk of never returning to school.
David Moinina Sengeh, the Sierra Leone Minister of Basic and Senior Secondary Education, emphasized that countries must make decisions based on evidence and “Stop at nothing to make sure girls, including pregnant girls, are not left out of education,” adding that secondary education should include sexual and reproductive health in educational curricula. “People say it costs money, but it is going to be more expensive to us when we have high illiteracy in the future,” he argued. “It is already expensive to us when we have maternal mortality, it is already expensive to us when we have major parts of our adult population, women, excluded from the economy.”
The President of Sierra Leone, Julius Maada Bio, pledged that the country’s radical new inclusion policy would expand access to previously marginalized populations, including pregnant girls, parent learners, girls from poor backgrounds and those in hard-to-reach areas. “The governmental of Sierra Leone is committed to empowering adolescent girls, promoting and protecting their rights, accelerating progress on gender equality and social inclusion, reducing teenage pregnancy and new HIV infections.”
The initiative places emphasis on ensuring the meaningful participation and leadership of adolescent girls and young women in all their diversity, with attention to ensuring inclusiveness of those in especially excluded and vulnerable situations. Engaging men and boys with a focus on changing harmful gender norms and masculinities, and as allies and agents of change, is a cross-cutting aspect for Education Plus.
In presenting the Prime Minister of Lesotho’s Education Plus commitment, Dira Khama, the Permanent Secretary for Education, pledged that the country would expand secondary education, with a focus on rural areas, strengthen the implementation of comprehensive sexuality education, introduce vocational and technical streams to strengthen school-to-work transitions and work with parents and communities to reduce sexual and gender-based violence against adolescent girls and young women. The Prime Minister also committed, “To review and implement secondary school fees rationalization policy to reduce the amounts of school fees paid by individual households,” within the next six months to a year.
Education Plus will advocate for gender-responsive reforms in policies, laws and practices to guarantee the education, health and other social and economic rights of adolescents and young people. This includes changes in parental consent requirements and eliminating user fees for adolescents to access basic HIV and other sexual and reproductive health services, supporting pregnant adolescents and young mothers to complete their education and tackling gender-based violence, menstrual hygiene management and mental health, among others.
“It is important to look at HIV prevention systematically and not underestimate the special role of mental health when it comes to safe sex practices,” said Shudufhadzo Musida, Miss South Africa 2020. “In order to bring about mental health awareness, HIV prevention, economic empowerment and gender equality, we need to empower the minds of adolescent girls and young women now more than ever.”
Education Plus was launched as a joint commitment to the Generation Equality Forum. At the high-level virtual launch, Ms Byanyima was joined by Sierra Leone’s Minister of Basic and Senior Secondary Education, David Moinina Sengeh, the Tunisian diplomat and former African Union Youth Envoy, Aya Chebbi, a representative of the Education Plus Young Women’s leadership hub, Anita Myriam Emma Kouassi, and Miss South Africa 2020, Shudufhadzo Musida.
Delighted to launch the #EducationPlus initiative at today’s #GenerationEquality Forum - joint programme with @UNICEF, @UNFPA, @UN_Women, @UNESCO.
— Winnie Byanyima (@Winnie_Byanyima) July 1, 2021
We must ensure all girls in Africa and beyond can complete secondary education.
It’s time to #ActForEqual! https://t.co/5JE6axsPMC pic.twitter.com/myRdhKQF6E
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Related
 Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”
Global celebrities unite behind UNAIDS’ call for world leaders to “take the rights path to end AIDS”

01 December 2024
 Interactive health and HIV game app reaches more than 300 000 young people in Côte d’Ivoire
Interactive health and HIV game app reaches more than 300 000 young people in Côte d’Ivoire

09 September 2024
 Bridging gaps: sex education saves lives in Central African Republic
Bridging gaps: sex education saves lives in Central African Republic

03 September 2024
 Girls’ education for HIV prevention at 1st Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa
Girls’ education for HIV prevention at 1st Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa

08 July 2024

Feature Story
The journey towards comprehensive sexuality education
28 June 2021
28 June 2021 28 June 2021School-based comprehensive sexuality education plays a vital role in promoting the health and well-being of children and adolescents, both now and in their future. It improves sexual and reproductive health outcomes, including for sexually transmitted infections and HIV, promotes safe and gender equitable learning environments and improves access to and achievement in education.
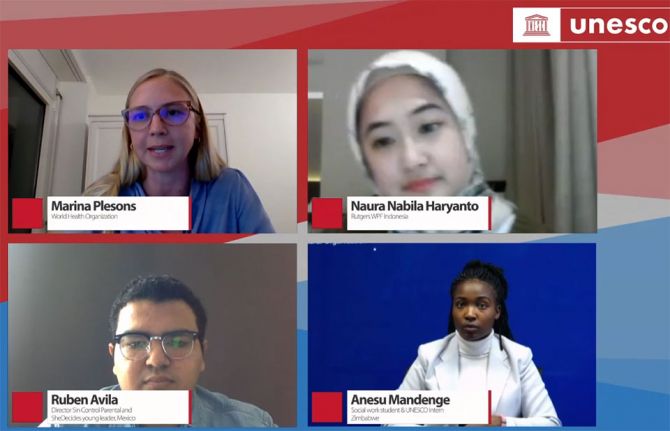
In a preview of the upcoming global report on the status of comprehensive sexuality education, more than 700 people joined an online event opened by Stefania Giannini, the Assistant Director-General, Education, for the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). While some progress has been made, she noted that there’s still a long way to go and underscored comprehensive sexuality education as one of the key priorities for action to achieve gender equality.
People attending the event heard the perspectives and recommendations of young activists for sexual and reproductive health and rights and case studies from Sweden, Tunisia and Namibia, together with engagement from policy-makers on how they are working towards ensuring quality comprehensive sexuality education for all young people.
“Like all journeys, the road towards comprehensive sexuality education is long, and sometimes winding, but it is leading us on the path to brighter, healthier futures for our young people,” Ms Giannini said.
The panel of young people collectively called for the recognition of education as a fundamental right, the need for strong implementation with proper financing and sufficient monitoring and evaluation and truly comprehensive curricula that respond to the needs of all young people.
Shannon Hader, the UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director, Programme, addressed the meeting, referring to the new Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026 and the 2021 United Nations Political Declaration on AIDS and the importance of comprehensive sexuality education to both. “Comprehensive sexuality education is a necessary core intervention—to prevent HIV among young people and also to empower young people to recognize and address issues of violence, sexual abuse and elements of their overall sexual health and well-being. Importantly, gaps in comprehensive sexuality education knowledge are not equal. Inequalities exist based on where young people live, levels of family income or education, digital access and degrees of gender inequality in the community. The global AIDS strategy recognizes we must end inequalities to end AIDS.”
The comprehensive sexuality education global status report is a collaboration between UNESCO, UNAIDS, the United Nations Population Fund, the United Nations Children’s Fund, UN Women and the World Health Organization (WHO), with support from governments and civil society. The report provides a snapshot of the status of school-based comprehensive sexuality education around the world, which can help to inform advocacy and resourcing efforts, as governments and partners work towards the goal of ensuring that all learners receive good quality comprehensive sexuality education throughout their schooling.
“For governments and international stakeholders, we want you to stand up, speak out, change the rules and allocate resources for comprehensive sexuality education,” said Reuben Avila, the Director of Sin Control Parental and a She Decides young leader from Mexico.
The event was held in the lead-up to the Generation Equality Forum (GEF), which will be held from 30 June to 2 July and which will launch a series of concrete, ambitious and transformative actions to achieve immediate and irreversible progress towards gender equality.
”Bodily autonomy and sexual and reproductive health and rights” is one of six Action Coalitions that will be established during the GEF. Among the three actions agreed to for the Action Coalition, the first is to ”Expand comprehensive sexuality education”, with the goal of increasing the delivery of comprehensive sexuality education in and out of school to reach 50 million more children, adolescents and youth by 2026. The goal is fully supported by the Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026, which has a target to reach 90% of all young people with comprehensive sexuality education.
“For meaningful engagement of young people, we have to make sure they have ears, eyes and teeth. The ears mean that young people are aware of their entitlements, voice means that they can advocate for these rights and entitlements to be met by duty-bearers and the teeth means that young people can hold the duty-bearers accountable for doing so,” said Marina Plesons, a technical officer on adolescent sexual and reproductive health and rights at WHO.